Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Ramm, A. G.
2015.
Creating materials in which heat propagates along a line.
Bollettino dell'Unione Matematica Italiana,
Vol. 8,
Issue. 3,
p.
165.
Ramm, A. G.
2015.
Scattering of electromagnetic waves by many small perfectly conducting or impedance bodies.
Journal of Mathematical Physics,
Vol. 56,
Issue. 9,
Ramm, A. G.
2016.
The Foundations of Chaos Revisited: From Poincaré to Recent Advancements.
p.
119.

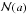 𝒩(
𝒩(