Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Pakes, Anthony G.
1989.
On the asymptotic behaviour of the extinction time of the simple branching process.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 2,
p.
470.
Pakes, Anthony G.
1989.
On the asymptotic behaviour of the extinction time of the simple branching process.
Advances in Applied Probability,
Vol. 21,
Issue. 2,
p.
470.
Nagaraja, H. N.
1992.
Order Statistics from Discrete Distributions.
Statistics,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 3,
p.
189.
Anderson, Clive W.
Coles, Stuart G.
and
Hüsler, Jürg
1997.
Maxima of Poisson-like variables and related triangular arrays.
The Annals of Applied Probability,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 4,
Robert, Christian Y.
and
Segers, Johan
2008.
Tails of random sums of a heavy-tailed number of light-tailed terms.
Insurance: Mathematics and Economics,
Vol. 43,
Issue. 1,
p.
85.
Dembińska, Anna
2008.
Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences.
p.
1.
Withers, Christopher
Withers, Christopher
Nadarajah, Saralees
and
Nadarajah, Saralees
2010.
Maximum of continuous versions of Poisson and negative binomial type distributions.
Теория вероятностей и ее применения,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 3,
p.
598.
Withers, C. S.
and
Nadarajah, S.
2011.
Maximum of Continuous Versions of Poisson and Negative Binomial-Type Distributions.
Theory of Probability & Its Applications,
Vol. 55,
Issue. 3,
p.
525.
Falk, Michael
Hüsler, Jürg
and
Reiss, Rolf-Dieter
2011.
Laws of Small Numbers: Extremes and Rare Events.
p.
343.
Shimura, Takaaki
2012.
Discretization of distributions in the maximum domain of attraction.
Extremes,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 3,
p.
299.
Dembińska, Anna
2014.
Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online.
Withers, Christopher S.
and
Nadarajah, Saralees
2016.
The distribution of the maximum of a first-order moving average: The discrete casex.
Communications in Statistics - Theory and Methods,
Vol. 45,
Issue. 16,
p.
4729.
Dkengne, Pascal Sielenou
Eckert, Nicolas
and
Naveau, Philippe
2016.
A limiting distribution for maxima of discrete stationary triangular arrays with an application to risk due to avalanches.
Extremes,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 1,
p.
25.
He, Xin
2017.
Conditioning Galton–Watson Trees on Large Maximal Outdegree.
Journal of Theoretical Probability,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 3,
p.
842.
Rohrbeck, Christian
Eastoe, Emma F.
Frigessi, Arnoldo
and
Tawn, Jonathan A.
2018.
Extreme value modelling of water-related insurance claims.
The Annals of Applied Statistics,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 1,
Verzi, Stephen J.
Rothganger, Fredrick
Parekh, Ojas D.
Quach, Tu-Thach
Miner, Nadine E.
Vineyard, Craig M.
James, Conrad D.
and
Aimone, James B.
2018.
Computing with Spikes: The Advantage of Fine-Grained Timing.
Neural Computation,
Vol. 30,
Issue. 10,
p.
2660.
Evin, Guillaume
Dkengne Sielenou, Pascal
Eckert, Nicolas
Naveau, Philippe
Hagenmuller, Pascal
and
Morin, Samuel
2021.
Extreme avalanche cycles: Return levels and probability distributions depending on snow and meteorological conditions.
Weather and Climate Extremes,
Vol. 33,
Issue. ,
p.
100344.
Wagenknecht, Lynne Elaine
Lawrence, Jean M.
Isom, Scott
Jensen, Elizabeth T.
Dabelea, Dana
Liese, Angela D.
Dolan, Lawrence M.
Shah, Amy S.
Bellatorre, Anna
Sauder, Katherine
Marcovina, Santica
Reynolds, Kristi
Pihoker, Catherine
Imperatore, Giuseppina
Divers, Jasmin
and
Study, SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth
2022.
Trends in Incidence of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Youth, 2002-2018: SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study.
SSRN Electronic Journal ,
Kane, Ibrahim Lawal
Tahir, Khadija Umar
and
Rabe, Anasu
2023.
Extreme Rainfall Modeling through the Lens of Extreme Value Theory: A Case Study of Katsina City, Nigeria.
UMYU Scientifica,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 3,
p.
92.
Wagenknecht, Lynne E
Lawrence, Jean M
Isom, Scott
Jensen, Elizabeth T
Dabelea, Dana
Liese, Angela D
Dolan, Lawrence M
Shah, Amy S
Bellatorre, Anna
Sauder, Katherine
Marcovina, Santica
Reynolds, Kristi
Pihoker, Catherine
Imperatore, Giuseppina
and
Divers, Jasmin
2023.
Trends in incidence of youth-onset type 1 and type 2 diabetes in the USA, 2002–18: results from the population-based SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth study.
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology,
Vol. 11,
Issue. 4,
p.
242.


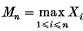 , where the
, where the