Unconditionally converging polynomials on Banach spaces
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 October 2008
Extract
In the study of polynomials acting on Banach spaces, the weak topology is not such a good tool as in the case of linear operators, due to the bad behaviour of the polynomials with respect to the weak convergence. For example,
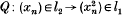
is a continuous polynomial taking a weakly null sequence into a sequence having no weakly Cauchy subsequences. In this paper we show that the situation is not so bad for unconditional series. Recall that 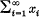 is a weakly unconditionally Cauchy series (in short a w.u.C. series) in a Banach space E if for every f ε E* we have that
is a weakly unconditionally Cauchy series (in short a w.u.C. series) in a Banach space E if for every f ε E* we have that 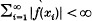 and
and 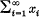 is an unconditionally converging series (in short an u.c. series) if every subseries is norm convergent.
is an unconditionally converging series (in short an u.c. series) if every subseries is norm convergent.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Mathematical Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society , Volume 117 , Issue 2 , March 1995 , pp. 321 - 331
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge Philosophical Society 1995
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by


