Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Baskin, Dean
Spence, Euan A.
and
Wunsch, Jared
2016.
Sharp High-Frequency Estimates for the Helmholtz Equation and Applications to Boundary Integral Equations.
SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis,
Vol. 48,
Issue. 1,
p.
229.
Kuchta, Miroslav
Nordaas, Magne
Verschaeve, Joris C. G.
Mortensen, Mikael
and
Mardal, Kent-Andre
2016.
Preconditioners for Saddle Point Systems with Trace Constraints Coupling 2D and 1D Domains.
SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing,
Vol. 38,
Issue. 6,
p.
B962.
Kim, Seungil
2017.
Analysis of the non-reflecting boundary condition for the time-harmonic electromagnetic wave propagation in waveguides.
Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications,
Vol. 453,
Issue. 1,
p.
82.
Hewett, D. P.
and
Moiola, A.
2017.
On the maximal Sobolev regularity of distributions supported by subsets of Euclidean space.
Analysis and Applications,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 05,
p.
731.
Hewett, David P.
and
Moiola, Andrea
2017.
A note on properties of the restriction operator on Sobolev spaces.
Journal of Applied Analysis,
Vol. 23,
Issue. 1,
p.
1.
Chandler-Wilde, S. N.
Hewett, D. P.
and
Moiola, A.
2017.
Sobolev Spaces on Non-Lipschitz Subsets of $${\mathbb {R}}^n$$ R n with Application to Boundary Integral Equations on Fractal Screens.
Integral Equations and Operator Theory,
Vol. 87,
Issue. 2,
p.
179.
Fackler, Stephan
2017.
J.-L. Lions' problem concerning maximal regularity of equations governed by non-autonomous forms.
Annales de l'Institut Henri Poincaré C, Analyse non linéaire,
Vol. 34,
Issue. 3,
p.
699.
Esfahani, Amin
and
Pastor, Ademir
2018.
Two dimensional solitary waves in shear flows.
Calculus of Variations and Partial Differential Equations,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 4,
Chandler-Wilde, Simon N.
and
Hewett, David P.
2018.
Well-Posed PDE and Integral Equation Formulations for Scattering by Fractal Screens.
SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis,
Vol. 50,
Issue. 1,
p.
677.
Brasco, Lorenzo
and
Salort, Ariel
2019.
A note on homogeneous Sobolev spaces of fractional order.
Annali di Matematica Pura ed Applicata (1923 -),
Vol. 198,
Issue. 4,
p.
1295.
Borthagaray, Juan Pablo
and
Jr, Patrick Ciarlet
2019.
On the Convergence in $H^1$-Norm for the Fractional Laplacian.
SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 4,
p.
1723.
Zheng, Enxi
and
Wang, Yujie
2019.
Galerkin method for the scattering problem of strip gratings.
Advances in Difference Equations,
Vol. 2019,
Issue. 1,
Perfekt, Karl-Mikael
2019.
The Transmission Problem on a Three-Dimensional Wedge.
Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis,
Vol. 231,
Issue. 3,
p.
1745.
Bonito, Andrea
Lei, Wenyu
and
Pasciak, Joseph E.
2019.
Numerical approximation of the integral fractional Laplacian.
Numerische Mathematik,
Vol. 142,
Issue. 2,
p.
235.
Qadeer, Saad
and
Wilkening, Jon A.
2019.
Computing the Dirichlet--Neumann Operator on a Cylinder.
SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 57,
Issue. 3,
p.
1183.
Arrieta, José M.
Nogueira, Ariadne
and
Pereira, Marcone C.
2019.
Semilinear elliptic equations in thin regions with terms concentrating on oscillatory boundaries.
Computers & Mathematics with Applications,
Vol. 77,
Issue. 2,
p.
536.
Ciarlet, Patrick
2020.
On the Approximation of Electromagnetic Fields by Edge Finite Elements. Part 3: Sensitivity to Coefficients.
SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 3,
p.
3004.
Bonito, Andrea
Lei, Wenyu
and
Salgado, Abner J.
2020.
Finite element approximation of an obstacle problem for a class of integro–differential operators.
ESAIM: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Analysis,
Vol. 54,
Issue. 1,
p.
229.
Nadir-Alexandre, Messai
and
Sébastien, Pernet
2020.
hp non-conforming a priori error analysis of an Interior Penalty Discontinuous Galerkin BEM for the Helmholtz equation.
Computers & Mathematics with Applications,
Vol. 80,
Issue. 12,
p.
2644.
Chandler-Wilde, S. N.
Spence, E. A.
Gibbs, A.
and
Smyshlyaev, V. P.
2020.
High-frequency Bounds for the Helmholtz Equation Under Parabolic Trapping and Applications in Numerical Analysis.
SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis,
Vol. 52,
Issue. 1,
p.
845.
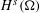 $H^{s}({\rm\Omega})$ and
$H^{s}({\rm\Omega})$ and 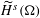 $\widetilde{H}^{s}({\rm\Omega})$, for
$\widetilde{H}^{s}({\rm\Omega})$, for 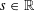 $s\in \mathbb{R}$ and an open
$s\in \mathbb{R}$ and an open 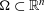 ${\rm\Omega}\subset \mathbb{R}^{n}$. We exhibit examples in one and two dimensions of sets
${\rm\Omega}\subset \mathbb{R}^{n}$. We exhibit examples in one and two dimensions of sets 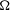 ${\rm\Omega}$ for which these scales of Sobolev spaces are not interpolation scales. In the cases where they are interpolation scales (in particular, if
${\rm\Omega}$ for which these scales of Sobolev spaces are not interpolation scales. In the cases where they are interpolation scales (in particular, if 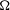 ${\rm\Omega}$ is Lipschitz) we exhibit examples that show that, in general, the interpolation norm does not coincide with the intrinsic Sobolev norm and, in fact, the ratio of these two norms can be arbitrarily large.
${\rm\Omega}$ is Lipschitz) we exhibit examples that show that, in general, the interpolation norm does not coincide with the intrinsic Sobolev norm and, in fact, the ratio of these two norms can be arbitrarily large.
