Article contents
INTEGRAL MONODROMY GROUPS OF KLOOSTERMAN SHEAVES
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 June 2018
Abstract
We show that integral monodromy groups of Kloosterman 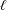 $\ell$-adic sheaves of rank
$\ell$-adic sheaves of rank 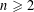 $n\geqslant 2$ on
$n\geqslant 2$ on 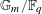 $\mathbb{G}_{m}/\mathbb{F}_{q}$ are as large as possible when the characteristic
$\mathbb{G}_{m}/\mathbb{F}_{q}$ are as large as possible when the characteristic 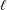 $\ell$ is large enough, depending only on the rank. This variant of Katz’s results over
$\ell$ is large enough, depending only on the rank. This variant of Katz’s results over 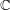 $\mathbb{C}$ was known by works of Gabber, Larsen, Nori and Hall under restrictions such as
$\mathbb{C}$ was known by works of Gabber, Larsen, Nori and Hall under restrictions such as 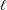 $\ell$ large enough depending on
$\ell$ large enough depending on 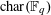 $\operatorname{char}(\mathbb{F}_{q})$ with an ineffective constant, which is unsuitable for applications. We use the theory of finite groups of Lie type to extend Katz’s ideas, in particular the classification of maximal subgroups of Aschbacher and Kleidman–Liebeck. These results will apply to study hyper-Kloosterman sums and their reductions in forthcoming work.
$\operatorname{char}(\mathbb{F}_{q})$ with an ineffective constant, which is unsuitable for applications. We use the theory of finite groups of Lie type to extend Katz’s ideas, in particular the classification of maximal subgroups of Aschbacher and Kleidman–Liebeck. These results will apply to study hyper-Kloosterman sums and their reductions in forthcoming work.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © University College London 2018
Footnotes
Current address:Centre de recherches mathématiques, Université de Montréal, Case postale 6128, Montréal QC H3C 3J7, Canada corentin.perretgentil@gmail.com
References
- 3
- Cited by

