Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 October 2002
To control the generation of dust in a steelmaking reactor, it is necessary to understand the underlying physical mechanisms. An experimental device has been developed to study the main emission mechanism, i.e. the projections from bursting bubbles. We visualized the burst on liquid steel and quantified the subsequent emission. The chemical evolution inside the fume exhaust system is simulated by thermodynamic calculations : the key parameters for controlling dust mineralogy are the Fe/Zn ratio, the oxygen activity (p$_{{\rm CO_2}}$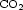 /p$_{{\rm CO}}$
/p$_{{\rm CO}}$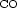 ) and the temperature evolution.
) and the temperature evolution.