Article contents
Davidlloydite, ideally Zn3(AsO4)2(H2O)4, a new arsenate mineral from the Tsumeb mine, Otjikoto (Oshikoto) region, Namibia: description and crystal structure
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 July 2018
Abstract
Davidlloydite, ideally Zn3(AsO4)2(H2O)4, is a new supergene mineral from the Tsumeb mine, Otjikoto (Oshikoto) region, Namibia. It occurs as elongated prisms (∼10:1 length-to-width ratio) that are flattened on {010}, and up to 100 × 20 × 10 μm in size. The crystals occur as aggregates (up to 500 μm across) of subparallel to slightly diverging prisms lying partly on and partly embedded in fine-grained calcioandyrobertsite. Crystals are prismatic along [001] and flattened on {010}, and show the forms {010} dominant and {100} subsidiary. Davidlloydite is colourless with a white streak and a vitreous lustre; it does not fluoresce under ultraviolet light. The cleavage is distinct on {010}, and no parting or twinning was observed. The Mohs hardness is 3 – 4. Davidlloydite is brittle with an irregular to hackly fracture. The calculated density is 3.661 g cm–3. Optical properties were measured with a Bloss spindle stage for the wavelength 590 nm using a gel filter. The indices of refraction are α = 1.671, β = 1.687, γ = 1.695, all ±0.002; the calculated birefringence is 0.024; 2Vobs = 65.4(6)°, 2Vcalc = 70°; the dispersion is r < v, weak; pleochroism was not observed. Davidlloydite is triclinic, space group P1, with a = 5.9756(4), b = 7.6002(5), c = 5.4471(4) Å, α = 84.2892(9), β = 90.4920(9), γ = 87.9958(9)°, V = 245.99(5) Å3, Z = 1 and a:b:c = 0.7861:1:0.7167. The seven strongest lines in the X-ray powder diffraction pattern [listed as d (Å), I, (hkl)] are as follows: 4.620, 100, (011, 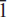 10); 7.526, 71, (010); 2.974, 49, (200, 0
10); 7.526, 71, (010); 2.974, 49, (200, 0 1); 3.253, 40, (021, 120); 2.701, 39, (
1); 3.253, 40, (021, 120); 2.701, 39, ( 10, 002,
10, 002, 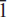
 1); 5.409, 37, (001); 2.810, 37, (210). Chemical analysis by electron microprobe gave As2O5 43.03, ZnO 37.95, CuO 5.65, H2O(calc) 13.27, sum 99.90 wt.%. The H2O content and the valence state of As were determined by crystal structure analysis. On the basis of 12 anions with H2O = 4 a.p.f.u., the empirical formula is (Zn2.53Cu0.39)Σ2.92As2.03O8(H2O)4.
1); 5.409, 37, (001); 2.810, 37, (210). Chemical analysis by electron microprobe gave As2O5 43.03, ZnO 37.95, CuO 5.65, H2O(calc) 13.27, sum 99.90 wt.%. The H2O content and the valence state of As were determined by crystal structure analysis. On the basis of 12 anions with H2O = 4 a.p.f.u., the empirical formula is (Zn2.53Cu0.39)Σ2.92As2.03O8(H2O)4.
The crystal structure of davidlloydite was solved by direct methods and refined to an R1 index of 1.51% based on 1422 unique observed reflections collected on a three-circle rotating-anode (MoKα radiation) diffractometer equipped with multilayer optics and an APEX-II detector. In the structure of davidlloydite, sheets of corner-sharing (As5+O4) and (ZnO4) tetrahedra are linked by ZnO2(H2O)4 octahedra. The structure is related to that of parahopeite.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland 2012
References
- 14
- Cited by


