Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Trachenko, Kostya
Dove, Martin T
Pruneda, Miguel
Artacho, Emilio
Salje, Ekhard
Geisler, Thorsten
Todorov, Ilian
and
Smith, Bill
2003.
Radiation-induced structural changes, percolation effects and resistance to amorphization by radiation damage.
MRS Proceedings,
Vol. 792,
Issue. ,
Geisler, T.
Berndt, J.
Meyer, H.-W.
Pollok, K.
and
Putnis, A.
2004.
Low-temperature aqueous alteration of crystalline pyrochlore: correspondence between nature and experiment.
Mineralogical Magazine,
Vol. 68,
Issue. 6,
p.
905.
Romano, Sandra S.
D�rr, Wolfgang
and
Zulauf, Gernold
2004.
Cambrian granitoids in pre-Alpine basement of Crete (Greece): evidence from U-Pb dating of zircon.
International Journal of Earth Sciences,
Vol. 93,
Issue. 5,
p.
844.
Trachenko, Kostya
Dove, Martin T
Geisler, Thorsten
Todorov, Ilian
and
Smith, Bill
2004.
Radiation damage effects and percolation theory.
Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter,
Vol. 16,
Issue. 27,
p.
S2623.
Hoskin, Paul W.O.
2005.
Trace-element composition of hydrothermal zircon and the alteration of Hadean zircon from the Jack Hills, Australia.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,
Vol. 69,
Issue. 3,
p.
637.
Nasdala, Lutz
Hanchar, John M.
Kronz, Andreas
and
Whitehouse, Martin J.
2005.
Long-term stability of alpha particle damage in natural zircon.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 220,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
83.
Rasmussen, Birger
2005.
Zircon growth in very low grade metasedimentary rocks: evidence for zirconium mobility at ~250°C.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,
Vol. 150,
Issue. 2,
p.
146.
Geisler, Thorsten
Vinx, Roland
Martin-Gombojav, Nergui
and
Pidgeon, Robert T.
2005.
Ion microprobe (SHRIMP) dating of detrital zircon grains from quartzites of the Eckergneiss Complex, Harz Mountains (Germany): implications for the provenance and the geological history.
International Journal of Earth Sciences,
Vol. 94,
Issue. 3,
p.
369.
Schaltegger, Urs
Pettke, Thomas
Audétat, Andreas
Reusser, Eric
and
Heinrich, Christoph A.
2005.
Magmatic-to-hydrothermal crystallization in the W–Sn mineralized Mole Granite (NSW, Australia).
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 220,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
215.
Rayner, N.
Stern, R. A.
and
Carr, S. D.
2005.
Grain-scale variations in trace element composition of fluid-altered zircon, Acasta Gneiss Complex, northwestern Canada.
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,
Vol. 148,
Issue. 6,
p.
721.
Tromans, Desmond
2006.
Solubility of crystalline and metamict zircon: A thermodynamic analysis.
Journal of Nuclear Materials,
Vol. 357,
Issue. 1-3,
p.
221.
Kröner, A.
Wilde, S.A.
Zhao, G.C.
O’Brien, P.J.
Sun, M.
Liu, D.Y.
Wan, Y.S.
Liu, S.W.
and
Guo, J.H.
2006.
Zircon geochronology and metamorphic evolution of mafic dykes in the Hengshan Complex of northern China: Evidence for late Palaeoproterozoic extension and subsequent high-pressure metamorphism in the North China Craton.
Precambrian Research,
Vol. 146,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
45.
Pidgeon, R.T.
and
Nemchin, A.A.
2006.
High abundance of early Archaean grains and the age distribution of detrital zircons in a sillimanite-bearing quartzite from Mt Narryer, Western Australia.
Precambrian Research,
Vol. 150,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
201.
Horie, Kenji
Hidaka, Hiroshi
and
Gauthier-Lafaye, François
2006.
Elemental distribution in zircon: Alteration and radiation-damage effects.
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C,
Vol. 31,
Issue. 10-14,
p.
587.
McFarlane, Christopher R.M.
Connelly, James N.
and
Carlson, William D.
2006.
Contrasting response of monazite and zircon to a high-T thermal overprint.
Lithos,
Vol. 88,
Issue. 1-4,
p.
135.
Utsunomiya, Satoshi
Valley, John W.
Cavosie, Aaron J.
Wilde, Simon A.
and
Ewing, Rodney C.
2007.
Radiation damage and alteration of zircon from a 3.3 Ga porphyritic granite from the Jack Hills, Western Australia.
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 236,
Issue. 1-2,
p.
92.
ZHENG, Y.‐F.
GAO, T.‐S.
WU, Y.‐B.
GONG, B.
and
LIU, X. M.
2007.
Fluid flow during exhumation of deeply subducted continental crust: zircon U‐Pb age and O‐isotope studies of a quartz vein within ultrahigh‐pressure eclogite.
Journal of Metamorphic Geology,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 2,
p.
267.
Sapienza, Giovanna T.
Griffin, William L.
O'Reilly, Suzanne Y.
and
Morten, Lauro
2007.
Crustal zircons and mantle sulfides: Archean to Triassic events in the lithosphere beneath south-eastern Sicily.
Lithos,
Vol. 96,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
503.
Pelleter, Ewan
Cheilletz, Alain
Gasquet, Dominique
Mouttaqi, Abdellah
Annich, Mohammed
El Hakour, Abdelkhalek
Deloule, Etienne
and
Féraud, Gilbert
2007.
Hydrothermal zircons: A tool for ion microprobe U–Pb dating of gold mineralization (Tamlalt–Menhouhou gold deposit — Morocco).
Chemical Geology,
Vol. 245,
Issue. 3-4,
p.
135.
Renna, Maria Rosaria
Tribuzio, Riccardo
and
Tiepolo, Massimo
2007.
Origin and timing of the post-Variscan gabbro–granite complex of Porto (Western Corsica).
Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,
Vol. 154,
Issue. 5,
p.
493.
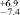 (2σ) Ma, which is in good agreement with an apatite fission track age of 22.2
(2σ) Ma, which is in good agreement with an apatite fission track age of 22.2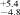 (2σ) Ma. The hydrothermal alteration event occurred contemporaneously with the main rifting phase of the Red Sea and widespread low- temperature mineralizations along the Red Sea coast.
(2σ) Ma. The hydrothermal alteration event occurred contemporaneously with the main rifting phase of the Red Sea and widespread low- temperature mineralizations along the Red Sea coast.