Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 February 2018
Yellowish dravitic tourmaline (dominated by the oxy-dravite component) associated with secondary fluor-dravite/fluor-schorl and dravite/schorl tourmalines was found in a quartz vein cropping out in the eastern part of the Karkonosze Mountains range, SW Poland. The crystal structure of this tourmaline was refined to an R1 value of 1.85% based on single-crystal data, and the chemical composition was determined by electron-microprobe analysis. The tourmaline, a representative of the alkali-tourmaline group, has the structural formula: (Na0.75Ca0.12□0.13)Σ1(Mg1.93Al0.95Ti0.06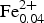 ${\rm Fe}_{{\rm 0}{\rm. 04}}^{{\rm 2 +}} $ V0.01)Σ3(Al5.38Mg0.62)Σ6B3Si6O27(OH)3(O0.46OH0.33F0.21)Σ1, and is characterized by an extremely high Mg/(Mg + Fe) ratio of 0.97–0.99, the WO2– content that reaches 0.59 apfu resulting in a local predominance of the oxy-dravitic component and Mg–Al disorder on the octahedral Y and Z sites of the order of 0.64 apfu. This disordering results in an increasing <Z–O> distance with ~1.925 Å, and unit-cell parameters a = 15.916(1) Å and c = 7.180(1) Å. The tourmaline formed during Variscan prograde metamorphism under the influence of a released (H2O,B,F)-bearing fluid. The fluid mobilized the most soluble components of partly altered silicic volcaniclastic material of the Late Cambrian to Early Ordovician bimodal volcanism to become the protolith for adjacent quartzo-feldspathic schists and amphibolites, and propagated them into the surrounding granitic gneisses of the Kowary unit in the eastern metamorphic cover of the Karkonosze granite.
${\rm Fe}_{{\rm 0}{\rm. 04}}^{{\rm 2 +}} $ V0.01)Σ3(Al5.38Mg0.62)Σ6B3Si6O27(OH)3(O0.46OH0.33F0.21)Σ1, and is characterized by an extremely high Mg/(Mg + Fe) ratio of 0.97–0.99, the WO2– content that reaches 0.59 apfu resulting in a local predominance of the oxy-dravitic component and Mg–Al disorder on the octahedral Y and Z sites of the order of 0.64 apfu. This disordering results in an increasing <Z–O> distance with ~1.925 Å, and unit-cell parameters a = 15.916(1) Å and c = 7.180(1) Å. The tourmaline formed during Variscan prograde metamorphism under the influence of a released (H2O,B,F)-bearing fluid. The fluid mobilized the most soluble components of partly altered silicic volcaniclastic material of the Late Cambrian to Early Ordovician bimodal volcanism to become the protolith for adjacent quartzo-feldspathic schists and amphibolites, and propagated them into the surrounding granitic gneisses of the Kowary unit in the eastern metamorphic cover of the Karkonosze granite.
Associate Editor: Mark Welch