Article contents
Chemical Vapor Deposition of Boron Phosphide Thin Films
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 May 2012
Abstract
Boron Phosphide (BP) is a promising material for use as a room temperature semiconductor detector of thermal neutrons. The absorption of a thermal neutron by a 10B nucleus in BP can yield 2.3MeV of energy which in solid state BP can yield ∼0.5 million electron-hole pairs that would be detectable with minimal amplification in a device. BP thin films are grown according to the net reaction below in a cold wall chemical vapor deposition (CVD) reactor: 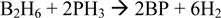 Thin film depositions are performed using diborane and phosphine with a balance of hydrogen gas at near atmospheric pressure with RF induction heating. The resultant BP films are characterized by Raman, XRD, SEM, TEM and TEM-EELS for chemical composition, surface and bulk morphology. BP growths on Si and SiC substrates are compared. SiC provides reduced lattice mismatch for growth of BP and growth of heteroepitaxial BP on SiC will be discussed.
Thin film depositions are performed using diborane and phosphine with a balance of hydrogen gas at near atmospheric pressure with RF induction heating. The resultant BP films are characterized by Raman, XRD, SEM, TEM and TEM-EELS for chemical composition, surface and bulk morphology. BP growths on Si and SiC substrates are compared. SiC provides reduced lattice mismatch for growth of BP and growth of heteroepitaxial BP on SiC will be discussed.
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 3
- Cited by


