Article contents
Corrosion Rates of Zircaloy-4 by Hydrogen Measurement under High pH, Low Oxygen and Low Temperature Conditions
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 19 April 2012
Abstract
Corrosion tests of Zircaloy-4 were performed in a dilute NaOH solution (pH =12.5) at 303 K for 90 days using the gas flow system (oxygen; < 1 ppb) and a batch method (oxygen; < 0.1 ppm). The corrosion rate was determined by measuring gaseous hydrogen and the hydrogen absorbed into Zircaloy-4 assuming the following reaction: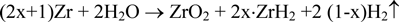
where x represents the Zircaloy-4 hydrogen absorption ratio. The initial hydrogen content in the Zircaloy-4 specimen was controlled to be below 10 ppm. The corrosion rate decreased with time (90-day values: 2.46×10-3 and 2.37×10-3 μm/y for the gas flow method and 6.72×10-2 μm/y for the batch test). The Zircaloy-4 hydrogen absorption ratio during corrosion was over 90%. The large amount of hydrogen absorbed in Zircaloy-4 will play an important role in the long-term safety for the disposal of irradiated Zircaloy materials.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- MRS Online Proceedings Library (OPL) , Volume 1475: Symposium NW – Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management XXXV , 2012 , imrc11-1475-nw35-p28
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2012
References
REFERENCES
- 6
- Cited by

