Article contents
Crystal Structures of Long-Period Stacking-Ordered Phases in the Mg-TM-RE Ternary Systems
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 January 2013
Abstract
Crystal structures of long-period stacking-ordered (LPSO) phases in the Mg-TM (transition-metal)-RE(rare-earth) systems were investigated by atomic resolution high-angle annular dark-field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). The 18R-type LPSO phase is constructed by stacking 6-layer structural blocks, each of which contains four consecutive close-packed planes enriched with TM and RE atoms. Formation of the TM6RE8 clusters with the L12 type atomic arrangement is commonly observed in both Mg-Al-Gd and Mg-Zn-Y LPSO phases. The difference between the crystal structures of Mg-Al-Gd and Mg-Zn-Y LPSO phases can be interpreted as the difference in the in-plane ordering of the TM6RE8 clusters in the structural block. The Mg-Al-Gd LPSO phase exhibits a long-range in-plane ordering of Gd and Al, which can be described by the periodic arrangement of the Al6Gd8 clusters with the L12 type atomic arrangement on lattice points of a two-dimensional 2 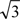 $\sqrt 3 $ a Mg × 2
$\sqrt 3 $ a Mg × 2 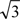 $\sqrt 3 $ a Mg primitive hexagonal lattice, although the LPSO phase in the Zn/Y-poor Mg-Zn-Y alloys exhibits a shortrange in-plane ordering of the Zn6Y8 clusters.
$\sqrt 3 $ a Mg primitive hexagonal lattice, although the LPSO phase in the Zn/Y-poor Mg-Zn-Y alloys exhibits a shortrange in-plane ordering of the Zn6Y8 clusters.
Information
- Type
- Articles
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 2013
References
REFERENCES
- 7
- Cited by

