Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 February 2011
In Korea Depleted Uranium(DU) is used in manufacturing a metallic nuclear fuel for the Korean Multi-Purpose Research Reactor(KMRR). In the manufacturing processes it produces DU chips and scraps as a waste material which composed of U-Ti, U-Zr, U-Mo and U-Si intermetallic compound. In this study Air Controlled Oxidizer(ACO) has been developed which facilitates DU to be converted into U308, the most stable form of uranium. Since DU chips oxidize rapidly and their heat of oxidation is very high(4.199kJ/g, U3O8), the inside temperature of the oxidizer is likely going up rapidly. Therefore the oxidizer must be able to be cooled properly or temperature increasement of the oxidizer must be under control. Kang et al.[1] reported for the oxidation of U-0.75wt%/o Ti chips in air that U308 was detected at the temperature above 350°C. And they[2] also reported that the maximum heat generation per unit time during oxidation was as follows:
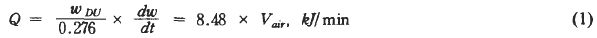

where Q was the maximum heat generation per unit time
WDU was the weight of DU loaded in ACO
dw/dt was the reaction rate
Vair was the flow rate of input air
R was the universal gas constant
and T was the absolute temperature.
From eq.(1) the maximum heat generation per unit time during oxidation is only function of the weight of DU loaded in ACO and the oxidation rate which is dependent on the oxidation temperature or the flow rate of input air.
The ACO consists of an air flow meter, an air heater, an oxidation chamber with inner heater(capacity 7.5kW), an ash collection tank, a fly ash collector, a pressure gauge, a safety valve, and a soaking tank. The air flow meter is used to control the flow rate of input air below theoretical air requirement limit for the complete oxidation of DU. The inner heater is used to heat the inside of the oxidizer to an optimum oxidation temperature. The ash collection tank is used to collect uranium oxide powder after completion of oxidation. The fly ash collector is used both to collect flying ashes and to condense vaporized uranium oxide. Also, in ACO, DU chips are not ignited directly in order to prevent rapid temperature increasement. The oxidation environment only is achieved by heating the inside of oxidizer.
To find effect of the oxidation temperature on the temperature of the oxidation chamber during treatment of DU, we conduct the experiment by changing heating rates of inner heater, 3, 4, 5 and 6kW, respectively. We conduct experiments for 120 minute with 2/min input air. However, it turned out that the complete oxidation is reached within 60 minute. After complete oxidation the weight gains of the DU chips is from 4.5 to 5.0 wt0/o and the DU chips are pulverized and they are converted to U 08 and 979 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 506 1998 Materials Research Society During the oxidation, maximum temperature increases to 470, 497.5, 572.5 and 6771C for heating rates 3, 4, 5 and 6kW, respectively. As the temperatures of the oxidation chamber outside surface are not exceed 1501C, however, DU chips are treated safely. In each experiment, weight before and after oxidation, the oxide forms of the product and the maximum temperature in the oxidation chamber during oxidation are shown in table 1. The maximum temperature profiles of the chamber inside and surface for time and heating rates are shown in Fig. I and 2, respectively.