Article contents
Surface Chemistry and Durability of Borosilicate Glass
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 25 February 2011
Abstract
Preliminary results show that glass durability is dependent on reactions occurring at the glass-solution interface. CSG glass (18.2 wt. % Na2O,5.97 wt. % CaO, 11.68 wt. % Al2O3, 8.43 wt. % B2O3, and 55.73 wt. % SiO2) dissolution and net surface H+ and OH- adsorption are minimal at near neutral pH. In the acid and alkaline pH regions, CSG glass dissolution rates are proportional to 2 to 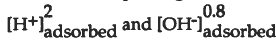 , respectively. In contrast, silica gel dissolution and net H+ and OH" adsorption are minimal and independent of pH in acid to neutral solutions. In the alkaline pH region, silica gel dissolution is proportional 0.9 to
, respectively. In contrast, silica gel dissolution and net H+ and OH" adsorption are minimal and independent of pH in acid to neutral solutions. In the alkaline pH region, silica gel dissolution is proportional 0.9 to 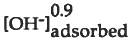 . Although Na adsorption is significant for CSG glass and silica gel in the alkaline pH regions, it is not clear if it enhances dissolution, or is an artifact of depolymerization of the framework bonds.
. Although Na adsorption is significant for CSG glass and silica gel in the alkaline pH regions, it is not clear if it enhances dissolution, or is an artifact of depolymerization of the framework bonds.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Materials Research Society 1994
References
REFERENCES
- 8
- Cited by


