Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref.
Muller, Iris
2002.
Racines orthogonales, formes quadratiques et orbites d'algèbres de Lie simples graduées.
Journal of Algebra,
Vol. 250,
Issue. 1,
p.
288.
Bopp, Nicole
and
Rubenthaler, Hubert
2004.
Noncommutative Harmonic Analysis.
p.
79.

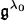 est de dimension un.
est de dimension un.