No CrossRef data available.
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 13 January 2025
Let  be a commutative ring containing a primitive
be a commutative ring containing a primitive 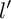 $l'$th root
$l'$th root 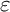 $\varepsilon $ of
$\varepsilon $ of 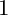 $1$. The infinitesimal q-Schur algebras
$1$. The infinitesimal q-Schur algebras  over
over  form an ascending chain of subalgebras of the q-Schur algebra
form an ascending chain of subalgebras of the q-Schur algebra  , which are useful in studying representations of the Frobenius kernel of the associated quantum linear group. Let
, which are useful in studying representations of the Frobenius kernel of the associated quantum linear group. Let  be the quantized enveloping algebra of
be the quantized enveloping algebra of 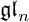 $\mathfrak {gl}_n$ over
$\mathfrak {gl}_n$ over  . There is a natural surjective algebra homomorphism
. There is a natural surjective algebra homomorphism 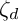 $\zeta _{d}$ from
$\zeta _{d}$ from  to
to  . The map
. The map 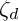 $\zeta _{d}$ restricts to a surjective algebra homomorphism
$\zeta _{d}$ restricts to a surjective algebra homomorphism 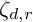 $\zeta _{d,r}$ from
$\zeta _{d,r}$ from  to
to  , where
, where  is a certain Hopf subalgebra of
is a certain Hopf subalgebra of  , which is closely related to Frobenius–Lusztig kernels of
, which is closely related to Frobenius–Lusztig kernels of  . We give the extra defining relations needed to define the infinitesimal q-Schur algebra
. We give the extra defining relations needed to define the infinitesimal q-Schur algebra  as a quotient of
as a quotient of  . The map
. The map 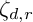 $\zeta _{d,r}$ induces a surjective algebra homomorphism
$\zeta _{d,r}$ induces a surjective algebra homomorphism  , where
, where  is the modified quantum algebra associated with
is the modified quantum algebra associated with  . We also give a generating set for the kernel of
. We also give a generating set for the kernel of 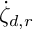 $\dot {\zeta }_{d,r}$. These results can be used to give a classification of irreducible
$\dot {\zeta }_{d,r}$. These results can be used to give a classification of irreducible  -modules over a field of characteristic p.
-modules over a field of characteristic p.