Published online by Cambridge University Press: 18 October 2021
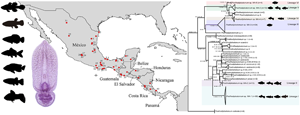
Trematode taxonomy is mainly based on the morphological traits of adults. The identification of metacercariae is challenging because such traits are not developed in larval forms, and they even may show some level of morphological variability. Studies testing the potential correspondence between morphological differences and genetic variation of parasites are still lacking. The metacercariae of Posthodiplostomum minimum are probably the diplostomids more widely distributed in North and Middle American freshwater fish, and their intraspecific morphological variability has been attributed to the effect exerted by the host. Here, we tested the hypothesis whether they represent a single species, or a species complex by assessing the genetic divergence and phylogenetic relationships of metacercariae sampled from several host species in a wide geographical range across Middle America. The internal transcribed spacers (ITS1-5.8S-ITS2), and the mitochondrial COI gene were sequenced for 124 and 55 metacercariae, respectively. Phylogenetic analysis inferred from ITS sequences uncovered six well-supported monophyletic lineages. The six lineages show no correspondence to any Posthodiplostomum species for which sequences are available thus far in GenBank. Lineages exhibit some degree of host specificity; Lineages I, II, IV and V are primarily parasites of cyprinodontiforms of the families Poeciliidae, Goodeidae, Profundulidae and Fundulidae. In poeciliids there are at least four candidate species of Posthodiplostomum, some of them occurring in sympatry; instead, Lineages II and VI are exclusively parasites of cichlids. This study contributes to our understanding of the diversity of larval forms of diplostomids and provides an opportunity to further study their life cycles.
Current address: Escuela Nacional de Estudios Superiores Unidad Mérida. Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM). Km. 4.5 Carretera Mérida-Tetiz, Municipio de Ucú, C.P. 97357, Yucatán, Mexico.