Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Tanaka, M.
Mimori, T.
Minematsu, T.
and
Tada, I.
1989.
The acquirement of growth ability for third-stage larvae of Strongyloides ratti during the head-passage in the rat.
International Journal for Parasitology,
Vol. 19,
Issue. 7,
p.
757.
Tindall, N. R.
and
Wilson, P. A. G.
1990.
A basis to extend the proof of migration routes of immature parasites inside hosts: estimated time of arrival of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis and Strongyloides ratti in the gut of the rat.
Parasitology,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 2,
p.
275.
Tindall, N. R.
and
Wilson, P. A. G.
1990.
An extended proof of migration routes of immature parasites inside hosts: pathways of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis and Strongyloides ratti in the rat are mutually exclusive.
Parasitology,
Vol. 100,
Issue. 2,
p.
281.
Tindall, N. R.
and
Wilson, P. A. G.
1990.
A technique for skin application of exact doses ofNippostrongylus brasiliensisto rats.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 64,
Issue. 1,
p.
15.
Cook, G. C.
1990.
Parasitic Disease in Clinical Practice.
p.
91.
Viney, M. E.
Matthews, B. E.
and
Walliker, D.
1992.
On the biological and biochemical nature of cloned populations of Strongyloides ratti.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 66,
Issue. 1,
p.
45.
1993.
Mating in the nematode parasite
Strongyloides ratti
: proof of genetic exchange
.
Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences,
Vol. 254,
Issue. 1341,
p.
213.
Viney, M. E.
1994.
A genetic analysis of reproduction in Strongyloides ratti.
Parasitology,
Vol. 109,
Issue. 4,
p.
511.
Wilson, P. A. G.
1994.
Doubt and certainty about the pathways of invasive juvenile parasites inside hosts.
Parasitology,
Vol. 109,
Issue. S1,
p.
S57.
McHugh, T.D.
Jenkins, T.
Greenwood, R.
and
McLaren, D.J.
1994.
The migration and attrition of Strongyloides ratti in naive and sensitized rats.
Journal of Helminthology,
Vol. 68,
Issue. 2,
p.
143.
Takamure, A.
1995.
Migration route of Strongyloides venezuelensis in rodents.
International Journal for Parasitology,
Vol. 25,
Issue. 8,
p.
907.
1996.
Developmental switching in the parasitic nematode
strongyloides ratti
.
Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences,
Vol. 263,
Issue. 1367,
p.
201.
Gemmill, Alan W.
Viney, Mark E.
and
Read, Andrew F.
1997.
HOST IMMUNE STATUS DETERMINES SEXUALITY IN A PARASITIC NEMATODE.
Evolution,
Vol. 51,
Issue. 2,
p.
393.
Koga, Masataka
Huang, Xuyang
Noda, Kanami
and
Tada, Isao
1998.
Strongyloides ratti: histological study of the descending route of larvae from the head in experimentally infected rats.
Parasitology International,
Vol. 47,
Issue. 3,
p.
219.
Viney, M.E
1999.
Exploiting the Life Cycle of Strongyloides ratti.
Parasitology Today,
Vol. 15,
Issue. 6,
p.
231.
Paterson, S.
and
Viney, M. E.
2003.
Functional consequences of genetic diversity inStrongyloides rattiinfections.
Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences,
Vol. 270,
Issue. 1519,
p.
1023.
MATSUDA, Kiku
KIM, Byeong-Su
WHANG, In-Soo
LIM, Chae-Woong
and
BAEK, Byeong-Kirl
2003.
Migration of Strongyloides venezuelensis in Rats after Oral Inoculation of Free-Living Infective Larvae.
Journal of Veterinary Medical Science,
Vol. 65,
Issue. 9,
p.
971.
Thompson, Fiona J.
Mitreva, Makedonka
Barker, Gary L.A.
Martin, John
Waterson, Robert H.
McCarter, James P.
and
Viney, Mark E.
2005.
An expressed sequence tag analysis of the life-cycle of the parasitic nematode Strongyloides ratti.
Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology,
Vol. 142,
Issue. 1,
p.
32.
Grant, W.N.
Stasiuk, S.
Newton-Howes, J.
Ralston, M.
Bisset, S.A.
Heath, D.D.
and
Shoemaker, C.B.
2006.
Parastrongyloides trichosuri, a nematode parasite of mammals that is uniquely suited to genetic analysis.
International Journal for Parasitology,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 4,
p.
453.
Viney, M.E.
2006.
The biology and genomics of Strongyloides.
Medical Microbiology and Immunology,
Vol. 195,
Issue. 2,
p.
49.
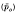 recovered between 20 and 25 h in this site had a mean value of 0·316 ± 0·021 in 48 animals. In 40 other rats infected simultaneously the mean proportion of the dose
recovered between 20 and 25 h in this site had a mean value of 0·316 ± 0·021 in 48 animals. In 40 other rats infected simultaneously the mean proportion of the dose 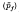 that reached the small intestine was at least 0·837+0·013. Proof resides in verification of the inequality
that reached the small intestine was at least 0·837+0·013. Proof resides in verification of the inequality 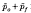 > 1. With appropriate statistical tests the excess of the sum of the means of these two proportions over unity is shown to have a probability of occurring by chance of 1 in 3·5 × 106. Thus it is effectively certain that the naso-frontal portion of the head is part of at least one pathway taken by this parasite on its way from the skin to the intestine of its host. By suitable protection of the infection site it was confirmed that migration to the head was achieved by an internal route and not as a result of grooming. Larvae were recovered from the cranium in the same rats over the period 15–40 h, but the peak proportion of the dose occurred at 20 h, and
> 1. With appropriate statistical tests the excess of the sum of the means of these two proportions over unity is shown to have a probability of occurring by chance of 1 in 3·5 × 106. Thus it is effectively certain that the naso-frontal portion of the head is part of at least one pathway taken by this parasite on its way from the skin to the intestine of its host. By suitable protection of the infection site it was confirmed that migration to the head was achieved by an internal route and not as a result of grooming. Larvae were recovered from the cranium in the same rats over the period 15–40 h, but the peak proportion of the dose occurred at 20 h, and 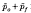 < in this location. Whether the cranium is also part of the pathway is therefore still undecided. The significance of this novel analysis in the general context of in-host migration of infective stages is discussed and it is concluded, following its application to data sets from other authors, that the only cases in which proof can be demonstrated are the anterior skull of the rat for S. ratti (present data) and the lung of the same host for Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Twohy, 1956).
< in this location. Whether the cranium is also part of the pathway is therefore still undecided. The significance of this novel analysis in the general context of in-host migration of infective stages is discussed and it is concluded, following its application to data sets from other authors, that the only cases in which proof can be demonstrated are the anterior skull of the rat for S. ratti (present data) and the lung of the same host for Nippostrongylus brasiliensis (Twohy, 1956).