Published online by Cambridge University Press: 12 November 2021
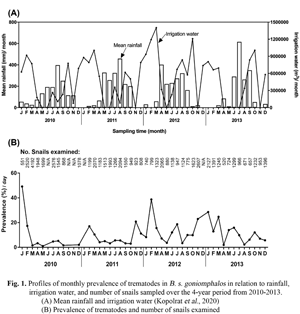
Several trematodes including Opisthorchis viverrini utilize Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos as a snail intermediate host in their life cycles. In order to capture a comprehensive range of host–parasite interactions and their transmission dynamic patterns, B. s. goniomphalos were sampled monthly over 4 consecutive years in an irrigated paddy-field habitat in northeast Thailand. Using a standard cercarial shedding method, a high diversity of trematodes (17 types) was recovered. Virgulate xiphidiocercariae were the most prevalent (7.84%) followed by O. viverrini (0.71%). In addition to seasonal and environmental factors, the quantity of irrigation water for rice cultivation correlated with transmission dynamics of trematodes in B. s. goniomphalos. The peak prevalence of all trematode infections combined in the snails shifted from the cool-dry season in 2010–2012 to the hot-dry season in 2013 associated with an increasing quantity of water irrigation. A low frequency of mixed trematode infections was found, indicating that the emergence of virgulate cercariae, but not of O. viverrini, was negatively impacted by the presence of other trematodes in the same snail. Taken together, the observed results suggest that interactions between host and parasite, and hence transmission dynamics, depend on specific characteristics of the parasite and environmental factors including irrigated water for rice cultivation.