No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
The crystal structure of trisodium hexachlororhodate (Na3RhCl6)
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 14 February 2018
Abstract
Commercially available trisodium hexachlororhodate (Na3RhCl6) was dehydrated and characterized by laboratory X-ray powder diffraction. The crystal structure is isostructural to the Na3CrCl6 structure type with space group P 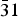 $\bar 31$ c. Unit-cell parameters are a = 6.8116(1) Å, c = 11.9196(2) Å, V = 478.95(2) Å3, and Z = 2.
$\bar 31$ c. Unit-cell parameters are a = 6.8116(1) Å, c = 11.9196(2) Å, V = 478.95(2) Å3, and Z = 2.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- New Diffraction Data
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © International Centre for Diffraction Data 2018
References
Böcker, M., Gerlitzki, N., and Meyer, G. (2001). “Crystal structure of trisodium homium(III) hexachloride, Na3HoCl6
,” Z. Kristallogr.
216, 19.Google Scholar
Cheary, R. W., Coelho, A. A., and Cline, J. P. (2004). “Fundamental parameters line profile fitting in laboratory diffractometers,” J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol.
109, 1–25.Google Scholar
Coelho, A. A. (2003). “Indexing of powder diffraction patterns by iterative use of singular value decomposition,” J. Appl. Crystallogr.
36, 86–95.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
de Wolff, P. M. (1968). “A simplified criterion for the reliability of a powder pattern indexing,” J. Appl. Crystallogr.
1, 108–113.Google Scholar
Friedrich, G., Fink, H., and Seifert, H. J. (1987). “Über Alkali-hexachlorochromate(III): Na3CrCl6
,” Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.
548, 141–150.Google Scholar
Hinz, D., Gloger, T., and Meyer, G. (2000). “Ternäre Halogenide vom Typ A3MX6. Kristallstrukturen von Na3TiCl6 und K3TiCl6
,” Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.
626, 822–824.Google Scholar
Krylov, V. V., Danilov, M. P., Stepareva, N. N., and Kotlyar, Yu. A. (1983). “Phase interactions in the NaCl-RhCl3 system,” Russ. J. Inorg. Chem.
28, 1230–1232.Google Scholar
Le Bail, A., Duroy, H., and Fourquet, J. L. (1988). “Ab-initio structure determination of LiSbWO6 by X-ray powder diffraction,” Mater. Res. Bull.
23, 447–452.Google Scholar
Liao, W., and Dronskowski, R. (2004). “Trisodium yttrium(III) hexachloride,” Acta Crystallogr.
E60, i72–i73.Google Scholar
Meyer, G. (1984). “Na3gdcl6: Einkristalle der Tieftemperaturform bei der metallothermischen Reduktion von GdCl3 mit Na,” Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.
517, 191–197.Google Scholar
Meyer, G., Ax, P., Schleid, T., and Irmler, M. (1987). The chlorides Na3MCl6 (M = Eu-Lu, Y, Sc): synthesis, crystal structures, and thermal behaviour,” Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.
554, 25–33.Google Scholar
Rietveld, H. M. (1969). “A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures,” J. Appl. Crystallogr.
2, 65–71.Google Scholar
Schurz, C. M., Meyer, G., and Schleid, T. (2011). “Na3dycl6
,” Acta Crystallogr.
E67, i33.Google Scholar
Yamada, K., Kumano, K., and Okuda, T. (2005). “Conduction path of the sodium ion in Na3InCl6 studied by X-ray diffraction and 23Na and 115In NMR,” Solid State Ion.
176, 823–829.Google Scholar

