To the Editor,
The article by Yılmaz, et al is very enlightening.
Reference Yılmaz, Cetinkaya, Ozel, Tatliparmak and Ak1
The study used entrapment duration, pH levels, creatinine levels, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels, and aspartate transaminase-to- alanine transaminase (AST-to-ALT) ratio as key predictors of dialysis requirements in identifying high-risk patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) who require dialysis.
Of the predictors in the study, except for the entrapment duration, acquiring these data at disaster sites is challenging and requires assessment at a medical facility. However, prehospital preliminary assessments are important to enable more targeted referrals for patients requiring dialysis.
Reference van Rein, Houwert, Gunning, Lichtveld, Leenen and van Heijl2
To identify simple indicators readily accessible at disaster sites and potentially meaningful for assessing dialysis requirements, we conducted a retrospective study of earthquake casualty data from a tertiary hospital in an earthquake-stricken area. We collected patients’ gender, age, entrapment duration, CRAMS score (circulation, respiration, abdomen, motor, and speech), multiple injuries, and AKI. With Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) version 26.0.0.0 (IBM Corporation; Armonk, New York USA), logical regression was used for analysis, and P <.05 was considered statistically significant.
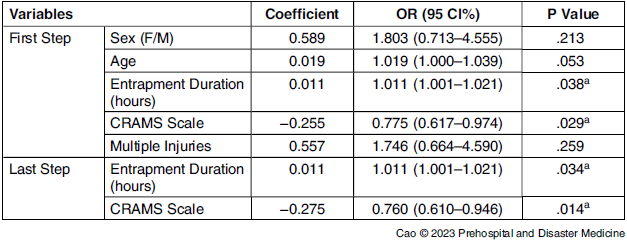
In total, 263 trauma patients who admitted to the hospital after earthquake were extracted from the hospital system, and two cases of patients lacking relevant data were excluded. Finally, 261 cases were included in the study. Of the enrolled patients, the number of males were 145 (55.6%), females were 116 (44.4%), with an average age of 43.5 (SD = 22.7) years. The median entrapment duration (25% quartile,75% quartile) was 24 (12, 93) and the median CRAMS score (25% quartile,75% quartile) was 10 (9, 10). A total of 158 cases (60.5%) were complicated with multiple injuries, and 25 cases (9.6%) required dialysis for AKI. Logical regression analysis showed that compression time and CRAMS score had statistical significance (P < .05; Table 1).
Table 1. Logistic Regression Analysis of Factors Affecting Debris Requirement
As stated in the original, we agree quite well that entrapment duration, pH levels, creatinine levels, LDH levels, and AST-to-ALT ratio are indicators of dialysis needs. Multiple studies have provided support for the use of these data in assessing kidney injury.
Reference Omrani, Najafi, Bahrami, Najafi and Safari3,Reference Heidari Beigvand, Heidari, Hashemi and Saberinia4
At the same time, CRAMS score plays an important role in the timely assessment of trauma severity in earthquake victims.
Reference He, Hu and Jiang5
However, statistical significance is shown for the data presented, and the confidence intervals are wide; we hope to expand the sample size for further research in the future. We believe that entrapment duration and CRAMS score can initially identify high-risk patients with AKI and need dialysis in disaster sites, and can provide a complementary scheme to the SAFE-QUAKE score system.
To the Editor,
The article by Yılmaz, et al is very enlightening. Reference Yılmaz, Cetinkaya, Ozel, Tatliparmak and Ak1 The study used entrapment duration, pH levels, creatinine levels, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels, and aspartate transaminase-to- alanine transaminase (AST-to-ALT) ratio as key predictors of dialysis requirements in identifying high-risk patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) who require dialysis.
Of the predictors in the study, except for the entrapment duration, acquiring these data at disaster sites is challenging and requires assessment at a medical facility. However, prehospital preliminary assessments are important to enable more targeted referrals for patients requiring dialysis. Reference van Rein, Houwert, Gunning, Lichtveld, Leenen and van Heijl2 To identify simple indicators readily accessible at disaster sites and potentially meaningful for assessing dialysis requirements, we conducted a retrospective study of earthquake casualty data from a tertiary hospital in an earthquake-stricken area. We collected patients’ gender, age, entrapment duration, CRAMS score (circulation, respiration, abdomen, motor, and speech), multiple injuries, and AKI. With Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) version 26.0.0.0 (IBM Corporation; Armonk, New York USA), logical regression was used for analysis, and P <.05 was considered statistically significant.
In total, 263 trauma patients who admitted to the hospital after earthquake were extracted from the hospital system, and two cases of patients lacking relevant data were excluded. Finally, 261 cases were included in the study. Of the enrolled patients, the number of males were 145 (55.6%), females were 116 (44.4%), with an average age of 43.5 (SD = 22.7) years. The median entrapment duration (25% quartile,75% quartile) was 24 (12, 93) and the median CRAMS score (25% quartile,75% quartile) was 10 (9, 10). A total of 158 cases (60.5%) were complicated with multiple injuries, and 25 cases (9.6%) required dialysis for AKI. Logical regression analysis showed that compression time and CRAMS score had statistical significance (P < .05; Table 1).
Table 1. Logistic Regression Analysis of Factors Affecting Debris Requirement
Note: First Step: Input variables sex, age, time under the rubble, CRAMS scale, multiple injuries.
Last Step: Input variables time under the rubble, CRAMS scale.
Abbreviation: CRAMS, circulation, respiration, abdomen, motor, and speech.
a P < .05.
As stated in the original, we agree quite well that entrapment duration, pH levels, creatinine levels, LDH levels, and AST-to-ALT ratio are indicators of dialysis needs. Multiple studies have provided support for the use of these data in assessing kidney injury. Reference Omrani, Najafi, Bahrami, Najafi and Safari3,Reference Heidari Beigvand, Heidari, Hashemi and Saberinia4 At the same time, CRAMS score plays an important role in the timely assessment of trauma severity in earthquake victims. Reference He, Hu and Jiang5 However, statistical significance is shown for the data presented, and the confidence intervals are wide; we hope to expand the sample size for further research in the future. We believe that entrapment duration and CRAMS score can initially identify high-risk patients with AKI and need dialysis in disaster sites, and can provide a complementary scheme to the SAFE-QUAKE score system.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare none.