Introduction
Quality of life has increasingly been discussed as an important outcome in gerontological research, as it plays an important role in enhancing successful aging (Choi et al., Reference Choi, Lee, Lee and Jung2017). As a complex concept, it has been described in many constructs (Rejeski and Mihalko, Reference Rejeski and Mihalko2001; Hambleton et al., Reference Hambleton, Keeling and McKenzie2009; Gouveia et al., Reference Gouveia, Gouveia, Ihle, Kliegel, Maia, Badia and Freitas2017). In the present research, we focused on health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Within this perspective, attention is given to individuals’ physical and mental health (MH) perceptions and their dimensions, namely physical functioning, physical role functioning, bodily pain (BP), general health (GH) perceptions, vitality (VT), social role functioning, emotional role functioning, and MH (Ware and Sherbourne, Reference Ware and Sherbourne1992).
It is well established that many factors affect HRQoL in old age. On the one hand, a negative relation to HRQoL has been found for obesity (Dale et al., Reference Dale, Bowling, Adamson, Kuper, Amuzu, Ebrahim, Casas and Nüesch2013; Giuli et al., Reference Giuli, Papa, Bevilacqua, Felici, Gagliardi, Marcellini, Boscaro, De Robertis, Mocchegiani, Faloia and Tirabassi2014; Glintborg et al., Reference Glintborg, Nielsen, Wraae, Hougaard, Gudex, Brixen and Andersen2014; Dhana et al., Reference Dhana, Berghout, Peeters, Ikram, Tiemeier, Hofman, Nusselder, Kavousi and Franco2016), depressive symptoms (Sivertsen et al., Reference Sivertsen, Bjørkløf, Engedal, Selbæk and Helvik2015), social isolation (Hawton et al., Reference Hawton, Green, Dickens, Richards, Taylor, Edwards, Greaves and Campbell2011), falls (Stenhagen et al., Reference Stenhagen, Ekström, Nordell and Elmståhl2014; Thiem et al., Reference Thiem, Klaaßen-Mielke, Trampisch, Moschny, Pientka and Hinrichs2014). On the other hand, a positive association with HRQoL has been found for physical activity (PA) (Wanderley et al., Reference Wanderley, Silva, Marques, Oliveira, Mota and Carvalho2011; Dale et al., Reference Dale, Bowling, Adamson, Kuper, Amuzu, Ebrahim, Casas and Nüesch2013; Olsson et al., Reference Olsson, Börjesson, Ekblom-Bak, Hemmingsson, Hellénius and Kallings2015; Haider et al., Reference Haider, Luger, Kapan, Titze, Lackinge, Schindle and Dorner2016) and functional fitness (Takata et al., Reference Takata, Ansai, Soh, Awano, Yoshitake, Kimura, Sonoki, Kagiyama, Yoshida, Nakamichi, Hamasaki, Torisu, Toyoshima and Takehara2010; Olivares et al., Reference Olivares, Gusi, Prieto and Hernandez-Mocholi2011; Wanderley et al., Reference Wanderley, Silva, Marques, Oliveira, Mota and Carvalho2011; Haider et al., Reference Haider, Luger, Kapan, Titze, Lackinge, Schindle and Dorner2016). Although HRQoL has been addressed in all these studies, a better understanding of its relationships is still needed. Bearing in mind the crucial role of HRQoL in old age and the need for tailored approaches to its enhancement, the possibility that the relationship pattern of HRQoL to its correlates may depend on individual factors should be considered. However, so far, evidence on this issue is scarce. For example, while sex differences in older adults’ HRQoL (with men reporting higher HRQoL) and related inequalities have been extensively discussed in prior research (Skar et al., Reference Skar, Juuso and Sodeberg2014; Katz and Calasanti, Reference Katz and Calasanti2015; Olmedo-Alguacil et al., Reference Olmedo-Alguacil, Ramírez-Rodrigo, Villaverde-Gutiérrez, Sánchez-Caravaca, Ferrándiz and Ruiz-Villaverde2016), such sex differences, remain to be further explained. Yet, in this regard, evidence on sex differences in the relation between HRQoL and its correlates in old age is insufficient so far (Orfila et al., Reference Orfila, Ferrer, Lamarca, Tebe, Domingo-Salvany and Alonso2006; Noh et al., Reference Noh, Kim, Park, Kim and Kwon2015; Hajek et al., Reference Hajek, Brettschneider, Lange, Posselt, Wiese, Steinmann, Weyerer, Werle, Pentzek, Fuchs, Stein, Luck, Bickel, Mösch, Wolfsgruber, Heser, Maier, Scherer, Riedel-Heller and König2016; Hart, Reference Hart2016).
Therefore, addressing this open issue, the present study sets out to examine sex differences in HRQoL of older adults, and to investigate whether the relation patterns between HRQoL and its correlates [body mass index (BMI), body strength, aerobic endurance, PA, falls, depressive symptoms, and living alone] differed between sexes between men and women.
Methods
Study design and participants
The present population-based cross-sectional study included a stratified proportional sample of volunteer older adults: 802 participants, 401 males and 401 females, from the Autonomous Region of Madeira, Portugal. Sex and age cohort served as stratification variables. Mean age of the overall sample was 69.8 years (SD=5.6), similarly distributed over the two subgroups (see Table 1). The sample size was determined following an a priori power analysis, which indicated that, to detect a small relation of r=0.15, with a two-tailed α probability of 0.05 and a power of 0.99, the sample size would need to comprise 806 individuals.
Table 1 Descriptive statistics and sex differences in health-related quality of life, health-related parameters, and lifestyle variables
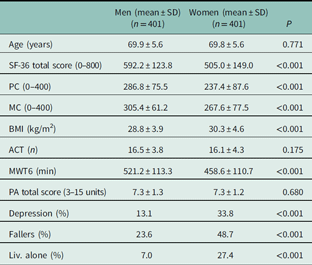
SF-36=36-item Short Form Health Survey; PC=physical component; MC=mental component; BMI=body mass index; ACT=arm curl test; MWT6=6-min walk test; PA=physical activity; Liv. alone=living alone.
P values are results from independent samples t-tests comparing the mean scores in men versus women and of χ 2 tests comparing sample proportions.
Inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) being community dwelling; (2) age between 60 and 79 years; and (3) to be able to walk independently. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) any medical contraindications to sub-maximum exercise (American College of Sports Medicine, 2006); and (2) inability to understand and follow the assessment protocol of the study, explained in Portuguese language.
Recruitment strategies included communications about the project in day-care and social centers, cultural and sports clubs and associations, and residential and public places (eg, open markets, municipal gardens, and churches). The study was also advertised in the local newspaper, radio, and television. Volunteers were then invited to the university laboratory, for the assessments.
Data sources
HRQoL was assessed using the 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36; Ware and Sherbourne, Reference Ware and Sherbourne1992; Portuguese version validated by Ribeiro, Reference Ribeiro2005). The SF-36 includes eight dimensions: physical functioning (PF), role physical (RP), BP, GH, VT, social functioning (SF), role emotional (RE), and MH. Scores of each dimension range from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better HRQoL. Two major components can be obtained by sum scores: (1) physical component (PF+RP+BP+GH) and (2) mental component (VT+SF+RE+MH), with scores ranging from 0 to 400. In this study, the Cronbach’s α coefficient was 0.728 and 0.729 for the physical and the mental component, respectively. The total SF-36 score can be obtained by a sum score: physical component+mental component, with scores ranging from 0 to 800.
PA was assessed using the Baecke questionnaire (Baecke et al., Reference Baecke, Burema and Frijters1982). The questionnaire includes 16 questions, classified into three specific domains: PA at work/household activities, sports, and leisure time. It provides a measure of habitual PA which is the sum of these three specific domains. Numerical coding for most response categories varied from 1 to 5 (Likert scale) ranging from never to always or very often. A detailed description of the scoring procedures for calculation of habitual PA and its sub-component categories (PA at work, sports, and leisure time) is provided by the author. In this study, interviews were taken alternately by four different researchers over the course of data collection. Previously, intra-class correlation coefficients were calculated to determine the test–retest reliability of the questionnaire in a pilot study involving 32 males and 59 females (68.3; SD=7.6 years). Over an interval of one week, correlations ranged between 0.83, 0.85, and 0.85 for the work, sports, and leisure-time indices, respectively. Our reliability scores for work and sports PA were similar to those obtained by Baecke et al. (Reference Baecke, Burema and Frijters1982) (0.88, 0.81) and higher for leisure time index (0.74). The validity of this questionnaire has been also established by Ono et al. (Reference Ono, Hirata, Yamada, Nishiyama, Kurosaka and Tamura2007) for this population using digital pedometry and uniaxial accelerometry (correlations ranged from 0.30 to 0.49).
Functional fitness components were assessed: body strength (using the arm curl test) and aerobic endurance (using the 6-min walk test; Rikli and Jones, Reference Rikli and Jones2013). Validity estimates have been assessed by the authors of the battery. BMI was calculated from weight and height (kg/m2). All tests were developed in the same laboratory and conditions, following the established protocol. All assessors undertook 5 h of theoretical explanation, followed by practical training (10 h). In a pilot study, 50 older adults were assessed. Test–retest correlation (R) were between 0.75 and 0.90.
Individual health (history of depression and falls during the last year) and demographic information (age, living alone) were obtained by questionnaire [see Gouveia et al. (Reference Gouveia, Gouveia, Ihle, Kliegel, Maia, Badia and Freitas2017) for a more detailed description of the testing procedures].
Statistical analyses
For descriptive purposes, we compared sex differences in HRQoL, health-related parameters, and lifestyle variables (using independent samples t-tests to compare mean scores and χ 2 tests to compare sample proportions) and inspected bivariate relations of HRQoL to the health-related parameters and lifestyle variables (BMI, body strength, aerobic endurance, PA, falls, depressive symptoms, and living alone) for the overall sample (using Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficients, r).
Simultaneously taking all these relations into account, we used multiple regression analysis to examine the independent contribution of the correlates of HRQoL. We additionally entered sex as moderator to investigate differences between men and women regarding these relationships. Finally, analyses were repeated separately for the physical and the mental component of HRQoL to investigate whether findings were HRQoL domain specific.
Results
Descriptive statistics
Means and standard deviations
As apparent in Table 1, men showed higher averages in HRQoL total score and the physical and the mental component of HRQoL, compared with women, as well as lower BMI, higher aerobic endurance, and a lower proportion of individuals with depressive symptoms, falls, and living alone. No sex differences were found for body strength and PA.
Bivariate relations
As presented in Table 2, there were significant negative correlations between HRQoL and BMI, depressive symptoms, falls, and living alone. There were significant positive correlations between HRQoL and body strength, aerobic endurance, and PA.
Table 2 Pearson correlations between health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and health-related parameters
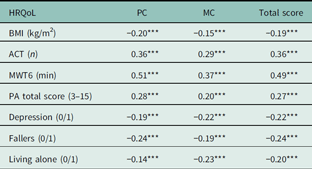
PC=SF-36 physical component; MC=SF-36 mental component; Total score=SF-36 total score; BMI=body mass index; ACT=arm curl test; MWT6=6-min walk test; PA=physical activity; Fallers (0/1), 0=no falls, 1=falls; Depression (0/1), 0=no depressive symptoms, 1=depressive symptoms; Living alone (0/1), 0=living with others, 1=living alone.
***P<0.001.
Examining sex-specific correlation patterns of HRQoL
Simultaneously considering all relations in the multiple regression model, BMI (β=−0.15, P=0.001), body strength (β=0.21, P<0.001), aerobic endurance (β=0.29, P<0.001), PA (β=0.11, P=0.007), depressive symptoms (β=−0.19, P<0.001), falls (β=−0.19, P<0.001), and living alone (β=−0.16, P<0.001) were all significantly related to HRQoL total score.
We further investigated whether these relation patterns differed between men and women. Thereby, considering sex as moderator in the multiple regression model, we found a significant interaction of sex with PA on HRQoL total score (β=0.08, P=0.037). Interestingly, this seemed to account for all previously observed relations of HRQoL to BMI, body strength, aerobic endurance, depressive symptoms, falls, and living alone, also including the initially observed bivariate sex difference in HRQoL, which all did not remain significant (βs<0.07, Ps>0.103). The only significant relation of HRQoL total score remaining was to PA (β=0.12, P=0.004). We did not find any other significant interactions of sex with the predictors (βs<0.06, Ps>0.138).
To investigate the differential sex patterns in more detail, we inspected the relations of the predictors with HRQoL total score in multiple regressions separately for men and women. Interestingly, PA was related to HRQoL only in men (β=0.21, P<0.001), but not in women (β<0.01, P=0.882). Together with the previously reported interaction effect, this suggests that the positive relation of HRQoL total score to PA was significantly higher in men compared with women.
Finally, we further investigated whether these sex-specific relation patterns were universal or whether they differed between the physical and the mental component of HRQoL. Thereby, repeating analyses separately for the two HRQoL components revealed highly similar relation patterns for the physical component of HRQoL, with PA being the only significant correlate of physical HRQoL (β=0.12, P=0.003) and a significant interaction of sex with PA on physical HRQoL (β=0.08, P=0.040) as well as PA being related to physical HRQoL only in men (β=0.22, P<0.001), but not in women (β=0.02, P=0.717). In contrast, for the mental HRQoL component there was no significant interaction of sex with the predictors (βs<0.07, Ps>0.105).
Discussion
In this study, higher scores of general HRQoL have been found in men, compared with women. These results are in line with those reported in several samples of older adults (Skar et al., Reference Skar, Juuso and Sodeberg2014; Olmedo-Alguacil et al., Reference Olmedo-Alguacil, Ramírez-Rodrigo, Villaverde-Gutiérrez, Sánchez-Caravaca, Ferrándiz and Ruiz-Villaverde2016). Differences between men and women have also been identified in our study regarding both the physical and mental components of HRQoL. This finding is consistent with previous results reported by Orfila et al. (Reference Orfila, Ferrer, Lamarca, Tebe, Domingo-Salvany and Alonso2006), in a sample of Spanish older adults assessed by the Nottingham Health Profile.
To explain those sex differences in HRQoL, considering sex as moderator in the multiple regression model, there was a significant interaction of sex with PA on HRQoL total score. The only significant relation of HRQoL remaining was to PA. Additional analyses revealed that PA was only significantly related to HRQoL in men, but not in women. Together with the aforementioned interaction effect, this suggests that, in older adults, PA plays a stronger part in HRQoL in men than in women, and this differential relation may likely explain the higher scores of HRQoL in men.
Assessing HRQoL in a large sample of Spanish older adults, Orfila et al. (Reference Orfila, Ferrer, Lamarca, Tebe, Domingo-Salvany and Alonso2006) described the direct effect of sex on HRQoL as very small and non-significant, when controlled for other predictors in a regression model, and argued that, when considering other predictors, including chronic conditions and functional capacity, the effect of sex is indirect or might not even exist. Interestingly, given our observation that considering sex as moderator in the multiple regression model seemed to account for all the initially observed bivariate sex difference in HRQoL suggests that the pathways of indirect effects postulated by Orfila et al. (Reference Orfila, Ferrer, Lamarca, Tebe, Domingo-Salvany and Alonso2006) may also concern differential relations of HRQoL to PA (which remained the only significant factor in the regression model).
In regard to the question whether sex-specific relation patterns differed between the physical and the mental component of HRQoL, our findings revealed also for the physical component of HRQoL (as discussed for overall HRQoL before) a significant interaction of sex with PA, and a significant relation between PA and physical HRQoL only in men, while such patterns were not observed for the mental HRQoL component. This finding suggests that sex differences in the relation of PA to HRQoL may only be present for the physical component of HRQoL. This seems reasonable given the particular role of physical and fitness factors for physical HRQoL in older adults (in contrast to mental HRQoL; Gouveia et al., Reference Gouveia, Gouveia, Ihle, Kliegel, Maia, Badia and Freitas2017).
The main strength of the present study is the representative and large sample of older men and women from the Autonomous Region of Madeira, which allows the generalizability of the findings in this population, therefore supporting the design of regional policies and tailored interventions related to quality of life and PA promotion.
With respect to the latter notions, as a limitation for establishing cause-effect relationships between HRQoL and the identified correlates we acknowledge the cross-sectional design of this population-based study. In addition, PA was assessed by questionnaires. Further research should be developed using objective assessments. Yet, besides the variability of HRQoL predictors accounted for in this study, with higher relevance given to potentially modifiable factors of HRQoL, other variables should be taken into account in future research, in order to better explain HRQoL in older adults, in both men and women.
In conclusion, the present study suggests that interventions to improve HRQoL in older men should include PA promotion. In addition, the present study reinforces the need for further research. A gap in the available knowledge has been identified, particularly regarding the predictors of HRQoL and its differential relations in older men and women. Thus, in addition to a multidimensional approach, sex differences should be accounted for when designing interventions for improving older adults’ HRQoL, particularly when addressing physical HRQoL. Further comprehensive and longitudinal research is needed to enhance knowledge on this topic, as basis for the regional policies and tailored and sex-specific interventions.
Financial Support
Technical assistance in data collection was supported by the Madeira Regional Government and Regional Secretary of Education and Culture. This study was supported by a doctoral degree grant from the Portuguese national funding agency for science, research and technology (Reference: SFRH/BD/ 29300/2006). A.I. and M.K. acknowledge the support from the Swiss National Center of Competences in Research LIVES – Overcoming vulnerability: life course perspectives, which is financed by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant number: 51NF40-160590).
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Ethical Standards
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of an institutional research committee and with the 1975 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Acknowledgments
We are especially grateful to all older adults who took part in this study and to Ercília Fena, Joana Castro, and Letícia Sousa for the technical assistance in data collection.





