No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On the involution fixity of simple groups
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 04 June 2021
Abstract
Let 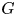 $G$ be a finite permutation group of degree
$G$ be a finite permutation group of degree 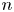 $n$ and let
$n$ and let 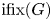 ${\rm ifix}(G)$ be the involution fixity of
${\rm ifix}(G)$ be the involution fixity of 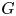 $G$, which is the maximum number of fixed points of an involution. In this paper, we study the involution fixity of almost simple primitive groups whose socle
$G$, which is the maximum number of fixed points of an involution. In this paper, we study the involution fixity of almost simple primitive groups whose socle  $T$ is an alternating or sporadic group; our main result classifies the groups of this form with
$T$ is an alternating or sporadic group; our main result classifies the groups of this form with 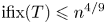 ${\rm ifix}(T) \leqslant n^{4/9}$. This builds on earlier work of Burness and Thomas, who studied the case where
${\rm ifix}(T) \leqslant n^{4/9}$. This builds on earlier work of Burness and Thomas, who studied the case where 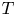 $T$ is an exceptional group of Lie type, and it strengthens the bound
$T$ is an exceptional group of Lie type, and it strengthens the bound 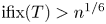 ${\rm ifix}(T) > n^{1/6}$ (with prescribed exceptions), which was proved by Liebeck and Shalev in 2015. A similar result for classical groups will be established in a sequel.
${\rm ifix}(T) > n^{1/6}$ (with prescribed exceptions), which was proved by Liebeck and Shalev in 2015. A similar result for classical groups will be established in a sequel.
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press on Behalf of The Edinburgh Mathematical Society


