No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
On the (J, pn, qn) method of summation
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 January 2009
Extract
Core share and HTML view are not available for this content. However, as you have access to this content, a full PDF is available via the ‘Save PDF’ action button.
In the following discussion we shall assume that pn≧0, qn≧0 for all n and that qn + 1 > qn → ∞. The (J, pn, qn) method of summation is defined as follows.
The series 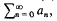 with the partial sum sn, is called summable (J, pn, qn) to s, and we write
with the partial sum sn, is called summable (J, pn, qn) to s, and we write 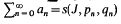 if the series
if the series

and 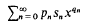 converge to the sum functions p*(x) and p(s)(x) respectively for 0<x<1 and if τ(x) = p(s)(x)/p*(x)→s as x→1–0.
converge to the sum functions p*(x) and p(s)(x) respectively for 0<x<1 and if τ(x) = p(s)(x)/p*(x)→s as x→1–0.
Information
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society , Volume 28 , Issue 1 , February 1985 , pp. 59 - 66
- Copyright
- Copyright © Edinburgh Mathematical Society 1985
References
REFERENCES
1.Borwein, D., ‘On methods of summability based on power series’, Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh 64 (1957), 343–349.Google Scholar
3.Ishiguro, K., ‘A Tauberian theorem for (J, pn) summability’, Proc. Japan Acad. 40 (1964), 807–812.Google Scholar
4.Ishiguro, K., ‘Two Tauberian Theorems for (J, pn) summability’, Proc. Japan Acad. 41 (1965), 40–45.Google Scholar

