Household food insecurity (HFI) has been associated with obesity risk among adult women in developed countries (mostly in the USA) but it is unclear if this relationship is present among female adolescents( Reference Lohman, Stewart and Gundersen 1 – 4 ). Recent reviews by Eisenman et al. ( Reference Eisenmann, Gundersen and Lohman 5 ), Pérez-Escamilla( Reference Pérez-Escamilla 6 ), Larson and Story( Reference Larson and Story 7 ) and Franklin et al. ( Reference Franklin, Jones and Love 8 ) have found mixed results regarding the association between HFI and overweight/obesity risk among children and adolescents. Several factors including birth weight, sex and age have been found to modify this relationship( Reference Pérez-Escamilla 6 ). It is important to note, however, that the vast majority of the evidence available thus far has been derived from North American samples and that most studies have combined children and adolescents in their analyses( Reference Lohman, Stewart and Gundersen 1 , Reference Casey, Simpson and Gossett 2 , 4 , Reference Eisenmann, Gundersen and Lohman 5 ).
A cross-sectional analysis of the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study found an inverse association between HFI and the likelihood of childhood obesity in kindergarten( Reference Rose and Bodor 9 ). In contrast, a longitudinal analysis of the same study found a positive association between HFI at kindergarten and BMI gains by the 3rd grade( Reference Jyoti, Frongillo and Jones 10 ). Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III documented that food insufficiency was inversely associated with the risk of overweight among girls aged 2–7 years, but positively associated with this risk among 8–16-year-old girls( Reference Alaimo, Olson and Frongillo 11 ). Analyses of the 1999–2002 NHANES found that HFI was positively associated with the risk of overweight among children aged 3–17 years( Reference Casey, Simpson and Gossett 2 ). However, NHANES IV results found no association between HFI and five different body fat indicators among children aged 8–17 years( Reference Gundersen, Garasky and Lohman 3 ). Studies conducted outside North America also report inconsistent results. Whereas studies conducted in Korea( Reference Oh and Hong 12 ) and Mexico( Reference Ortiz-Hernandez, Acosta-Gutierrez and Nunez-Perez 13 ) have found a positive relationship between HFI and child body weight outcomes, a study from Colombia( Reference Isanaka, Mora-Plazas and Lopez-Arana 14 ) did not find this relationship.
Few studies have tested the HFI–obesity relationship among women in less developed countries( Reference Isanaka, Mora-Plazas and Lopez-Arana 14 – Reference Dubois, Francis and Burnier 16 ). Velásquez-Melendez et al. ( Reference Velasquez-Melendez, Schlussel and Brito 15 ) recently documented that moderate but not mild or severe HFI was associated with obesity in a representative sample of adult Brazilian women. Because the same survey included a large sample of adolescent females, we are in a unique position to test for this association among this highly vulnerable population subgroup in Brazil, a country that is currently immersed in the epidemiological and nutrition transitions( Reference Victora, Aquino and do Carmo Leal 17 ). The specific objective of the present study was to examine the association between HFI and excessive weight in a representative sample of Brazilian adolescent females after adjusting for key potential confounders.
Methods
The data were derived from the third wave of the Demographic and Health Survey (DHS), conducted in 2006–2007, in Brazil( 18 ). This was a population-based survey targeting women of reproductive age, including mothers of children younger than 5 years of age. DHS was a nationally representative cross-sectional study with a complex sampling design. It included both household- and individual-level measures. Ten sampling strata were defined based on a combination of the five Brazilian geographical regions and urban v. rural areas. The respondents’ sampling weights were derived from the household sampling weights and took into account the possibility that there may be more than one eligible woman in each household. Response rate was 86·5 %. The weights were adjusted due to non-response within households and were calibrated based on official population estimates released by the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics( 18 , 19 ).
Data from 15 575 women living in 14 617 households were collected. For the present analysis, data were available for the key variables (weight, height and HFI) for 1529 adolescent females aged 15–19 years who were neither breast-feeding nor pregnant. There were no available data for adolescents aged 13–14 years from this DHS since it comprised information about women of reproductive age, from 15 to 49 years old.
Structured questionnaires were applied through in-person interviews and anthropometric measures were taken. Data collected included socio-economic status, lifestyle, reproductive history and household food security.
Weight and height of all eligible women in the selected households were measured according to WHO recommendations( 20 ). These measurements were conducted twice for each participant, and the mean was calculated. Height was measured using a stadiometer with 1 mm precision that was calibrated at the beginning and end of each working day. Weight was measured with an electronic scale with 100 g precision, which was also calibrated at the beginning and end of each day. BMI (kg/m2) was calculated as weight (in kilograms) divided by the square of height (in metres)( 18 ).
Excessive weight was the outcome variable. We used age-adjusted BMI growth charts provided by WHO( 21 ) in order to classify excessive weight, a variable including overweight and obese participants. The prevalence of excessive weight for adolescents aged 15–18 years considered the 85th percentile as the cut-off point. For adolescents aged 19 years we defined excessive weight as BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2. The 2006–2007 DHS data set provides the adolescent's age only in rounded years (instead of years and months) or date of birth, e.g. an adolescent was recorded as being 16 years old regardless of whether she was 16·3 years or 16·7 years. In order to overcome this limitation we calculated for each rounded year, i.e. 16·0 years in this example, a mean BMI value considering the WHO reference age-specific values for each month within the 15–18 years range. The specific BMI cut-off points used to classify excessive weight prevalence at ages 15, 16, 17 and 18 years (based on the age- and sex-adjusted 85th BMI percentiles) were 23·9, 24·4, 24·8 and 25·0 kg/m2, respectively. The same procedure was implemented to evaluate underweight prevalence, based on the 5th BMI percentile of the WHO reference (adolescents aged 15–18 years) and BMI < 18·5 kg/m2 (adolescents aged 19 years).
HFI was measured with the previously used and extensively validated Brazilian Food Insecurity Scale (EBIA). EBIA represents an adaptation of the US Household Food Security Survey Module, developed during the early 1990s and first fielded in the 1995 US Current Population Survey( Reference Radimer 22 – Reference Hamilton, Cook and Thompson 25 ). The detailed description of the adaptation and validation of the EBIA scale can be found elsewhere( Reference Perez-Escamilla and Segall-Correa 26 – Reference Segall-Corrêa, Perez-Escamilla and Marín-León 29 ), but it is important to state that several validity criteria such as content and face validity, item parallelism across socio-economic strata, predictive validity (socio-economic strata predicts food insecurity level) and convergent validity (i.e. food insecurity level predicts dietary quality), as well as good internal consistency, were all met( Reference Frongillo 30 ). The EBIA is composed of fifteen dichotomous (yes/no) questions that evaluate food insecurity experiences, ranging from the worry or concern that the household may run out of food to sacrificing the quality of the diet and to restricting the amount of food consumed, and ultimately to going for a whole day with little or no food due to economic limitations. Each household is assigned a summative food insecurity score based on the number of affirmative responses to the scale items. Households were classified as food secure (HFI score = 0), mildly food insecure (score = 1–5), moderately food insecure (score = 6–10) or severely food insecure (score = 11–15). These cut-off points, initially proposed by Pérez-Escamilla et al.( Reference Perez-Escamilla, Segall-Correa and Kurdian Maranha 27 ), were subsequently confirmed based on the equivalence of the thresholds for households with and without children, both of which are based on scales derived from the interval-level Rasch model( Reference Melgar-Quinonez, Nord and Perez-Escamilla 28 ).
Food security/insecurity level (security, mild insecurity, moderate insecurity, severe insecurity) was the key independent variable. The covariates included in the analyses were: self-reported skin colour/ethnicity (white, black, brown, yellow, indigenous); years of schooling (0–4, 5–8, 9–11); area of residence (urban, rural); geographical region (North, Northeast, Southeast, South, Midwest); log-transformed per capita family income (in Brazilian reais, 1 real ≈ US$ 0·47 in 2006–2007); smoking habit (yes, no); number of people residing in the household; marital status (single/widowed/divorced, married or cohabiting); and age as a continuous variable. These covariates were selected based on theoretical and empirical considerations. In addition they were the same used in the previous study examining the relationship of interest among adult Brazilian women( Reference Velasquez-Melendez, Schlussel and Brito 15 ). Thus, this choice of covariates allows for our findings to be directly compared with those in the previous study.
We first analysed the distribution of covariates across HFI levels. In a second stage, we examined the univariate association between HFI and excessive weight using a Poisson regression model. Finally we conducted a multivariate analysis also using a Poisson regression model and adjusting for covariates. Results are presented as crude and adjusted prevalence ratios (PR) and their respective 95 % confidence intervals. Estimates were weighted and standard errors were corrected to take into account the complex sampling design by means of svy commands in the STATA statistical software package version 9·2 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
The project was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Sexually Transmitted Diseases/AIDS Reference and Training Centre of the Health Secretariat of the state of São Paulo.
Results
The weighted prevalence of any level of household food insecurity was 40·8 % (mild = 26·6 %, moderate = 9·4 % and severe = 4·8 %). Any level of food insecurity was found to be more prevalent among black and indigenous adolescents, those with 0–4 years of schooling, those residing in the Northeast region, those in the lowest quartile of per capita family income, smokers, those residing in households with five or more people and those aged 15 years (Table 1).
Table 1 Food (in)security level according to socio-economic and demographic variables: female adolescents (n 1529) aged 15–19 years, Demographic and Health Survey, Brazil, 2006–2007Footnote *

* Estimates were weighted and standard errors were corrected to take account of the complex sampling design.
† P values refer to the χ 2 test for difference of proportions.
Excessive weight was found in 21·9 % of the female adolescents (overweight = 12·9 % and obesity = 9·0 %), 73·3 % had normal weight and 4·8 % were underweight. The weighted prevalence of excessive weight was significantly higher for young women living in severely food-insecure households (36·8 %) compared with their counterparts living in households with moderate (14·9 %) or mild food insecurity (16·5 %) or food security (24·2 %; P = 0·036; Table 2).
Table 2 Crude and adjusted prevalence ratios estimated by Poisson regression models for the effect of food (in)security level on excessive weight: female adolescents (n 1529) aged 15–19 years, Demographic and Health Survey, Brazil, 2006–2007Footnote *
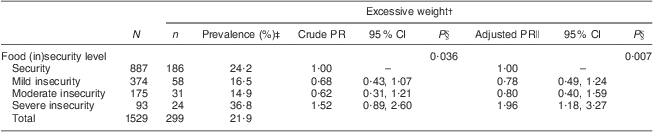
PR, prevalence ratio.
* Estimates were weighted and standard errors were corrected to take account of the complex sampling design.
† Excessive weight was classified as BMI ≥ 85th percentile of the WHO reference for adolescents aged 15–18 years and BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 for those aged 19 years.
‡ χ 2 for the prevalence of excessive weight between food insecurity categories = 0·047.
§ P values refer to the log-likelihood ratio test.
∥ Adjusted for self-reported skin colour (white = reference category, black, brown, yellow, indigenous), years of schooling (≥9 = reference category, 5–8, 0–4), area of residence (urban = reference category, rural), geographical region (North = reference category, Northeast, Southeast, South, Midwest), per capita family income (log-transformed), smoking habit (no = reference category, yes), marital status (single/widow/divorced = reference category, married/cohabiting), number of people living in the household (1–2 = reference category, 3–4, ≥5) and age in years (continuous).
Severe food insecurity was significantly and independently associated with excessive weight after adjusting for self-reported skin colour, years of schooling, geographical region, log-transformed per capita family income, area of residence, smoking habit, number of people residing in the household, marital status and age (PR = 1·96; 95 % CI 1·18, 3·27; P = 0·007; Table 2).
Discussion
The main finding from the present study is that Brazilian female adolescents who lived in severely food-insecure households were two times more likely to have excessive weight than their food-secure counterparts. This association persisted after adjusting for known confounders including self-reported skin colour, years of schooling, geographical region, log-transformed per capita family income, area of residence, smoking habit, number of people residing in the household, marital status and age.
Representative surveys recently conducted in Brazil with different samples of adolescents corroborate the global obesity prevalence of 9·0 % found in the current study( Reference Araujo, Toral and Silva 31 , 32 ). Based on data derived from the 2006–2007 DHS, it appears that food insecurity is a contributing factor for obesity in adult women and for excessive weight in adolescent women from Brazil. Among adult Brazilian women, moderate but not mild or severe food insecurity was associated with increased obesity prevalence( Reference Velasquez-Melendez, Schlussel and Brito 15 ). By contrast, in the present study with adolescents, the most severe level of food insecurity was the one associated with excessive weight prevalence. Thus the level of food insecurity associated with obesity seems to differ when comparing adult v. adolescent women. It is possible that physiological changes associated with puberty make adolescent women (vis-à-vis adult women) more resistant to body fat accumulation even if their lifestyle coping behaviours to deal with mild to moderate levels of food insecurity in the Brazilian context are similar to those of their adult counterparts. An additional reason for the difference in level of severity at which adolescents v. mature women are affected may be that parents shield children and adolescents from some of the effects of household food insecurity.
Our results support the association between food insecurity and excessive weight. These results are in line with those previously reported by Santos et al. ( Reference Santos, Gigante and Domingues 33 ) showing a higher prevalence of obesity for children and adolescents living in households with food insecurity, although these results were restricted to one Brazilian city only. In the USA, the relationship between food insecurity and childhood weight gain and obesity has been reported only in a few studies( Reference Jyoti, Frongillo and Jones 10 , Reference Bronte-Tinkew, Zaslow and Capps 34 , Reference Metallinos-Katsaras, Sherry and Kallio 35 ). Most of the studies did not find significant associations( Reference Eisenmann, Gundersen and Lohman 5 , Reference Franklin, Jones and Love 8 , Reference Bhargava, Jolliffe and Howard 36 ) or found that children living in food-insecure households had a lower probability of being obese( Reference Rose and Bodor 9 ). However, in low- and middle-income countries food insecurity has been consistently associated with underweight but not with obesity. In Bogota, food insecurity was associated with stunting but not with obesity among children( Reference Isanaka, Mora-Plazas and Lopez-Arana 14 ). These results have recently been replicated in Brazil where it has been shown that children in households with higher levels of food insecurity have a lower height-for-age Z-scores( Reference Reis 37 ).
The ‘food insecurity–obesity’ paradox detected in our study has been previously described( Reference Tanumihardjo, Anderson and Kaufer-Horwitz 38 ). It has been hypothesized that coping mechanisms associated with food insecurity can eventually lead to overconsumption of energy and thus overweight and obesity. Poorer families may purchase more energy-dense foods, especially in societies where these foods are cheaper, following classic economic consumer theories( Reference Finkelstein and Strombotne 39 ). For instance, while a comparative study reported that food insecurity was associated with increased odds for overweight among 10-year-olds in Quebec, Canada, it documented that 10–11-year-olds living in food-insecure households in Jamaica, a less developed country, were at lower odds of being overweight( Reference Dubois, Francis and Burnier 16 ). It is possible that the hunger–obesity paradox may be directly related with the way different countries experience the nutrition transition. It seems that only when the nutrition transition reaches a stage at which energy-dense foods become available at affordable prices does food insecurity become a risk factor for overweight or obesity.
Our study supports the food insecurity–obesity paradox. It is possible that in the case of adolescent women in Brazil the food insecurity threshold for triggering obesogenic lifestyle behaviours, such as increased dietary energy density at the expense of nutrient density and physical inactivity, may not be set until the most severe, high level of food insecurity is reached. A nationally representative study conducted in 2009 found that Brazilian adolescents had poor eating habits, and that these were even worse among those with mothers with less schooling and who lived in less wealthy families( Reference Levy, Castro and Cardoso 40 ).
It is also possible that strong body image concerns among young Brazilian women( Reference Monteiro, D'A Benicio and Conde 41 , Reference Kakeshita and Almeida 42 ) might protect them against the obesogenic influence of food insecurity until the problem becomes severe and they can no longer cope with it without implementing lifestyle behaviours that lead to body fat accumulation.
Social assistance programmes targeting poor families may be potentially associated with increased weight and obesity risk among adult American women( Reference Webb, Schiff and Currivan 43 , Reference Gibson 44 ). In Brazil, severely food-insecure adolescents are more likely to be enrolled in food and social assistance programmes since the conditional cash transfer programme and programmes with a focus on youth are targeting the most socially and economically vulnerable population( Reference Soares and Sátyro 45 ). A recent study has evaluated the Brazilian cash transfer programme and found that the enrolled families spend more than 76 % of the benefit purchasing food. The authors have reported that the programme has facilitated, and increased quantitatively and qualitatively, the purchase of food. However 78 % of the families reported that the purchased foods are insufficient for the whole month, which drives those families towards the adoption of a low-cost and highly energy-dense diet. Some additional results have shown a low intake of some healthy foods. Few people ate meat four or more times weekly (18·2 %), legumes/vegetables (30·4 %) and fruits (15·1 %), while consumption of pasta (55·4 %), manioc flour (55·4 %) and sugar/sweets (85·9 %) was much higher( 46 , Reference Rivera Castineira, Currais Nunes and Rungo 47 ). Another population-based study of families with youth under 20 years old has shown that 73·7 % of food-secure families consumed at least one fruit daily and 62·1 % consumed dairy products every day in comparison to 11·4 % and 5·5 %, respectively, in families with moderate and severe food insecurity. The majority of those families consumed grains, oil, sugar and beans on a daily basis, and they spent roughly 68 % of their monthly income on food purchases( Reference Panigassi, Segall-Corrêa and Marin-León 48 ).
An important limitation of the present study is its cross-sectional design and the lack of information on lifestyle coping mechanisms associated with different levels of household food insecurity. The evidence for a relationship between food insecurity and excessive weight (overweight plus obesity) is still inconclusive with most studies being cross-sectional, thus precluding our ability to understand the temporal sequence of the association (i.e. does food insecurity lead to obesity or does obesity lead to food insecurity? Or is this relationship bidirectional?). Thus, there is a need for longitudinal dynamic studies that collect information not only on household food security status across time( Reference Jyoti, Frongillo and Jones 10 , Reference Bronte-Tinkew, Zaslow and Capps 34 ) but also on how children, adolescents and adults within the household cope with these changes with special emphasis on dietary intake and physical activity adaptations. Ultimately the goal is to better understand how these coping behaviours influence body fat accumulation at different stages of the life cycle( 4 ). Another limitation is the small sample size achieved in the excessive weight and severely food-insecure group and the lack of potential extrapolation to adolescent boys.
Conclusion
The present study suggests that severe but not moderate or mild food insecurity, as measured by EBIA, is independently associated with excessive weight among female adolescents living in a middle-income country deeply immersed in epidemiological and nutrition transitions. The Brazilian government should take these findings into account when designing, delivering and evaluating food and social assistance programmes that reach out to young women.
Acknowledgements
The Demographic and Health Survey (DHS), from which the data used in the current paper are derived, was funded by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. The authors of the present paper had access to the data set produced by the DHS, but did not receive any funding to write the paper. The authors declare no conflict of interest. G.K., M.M.S. and R.P.-E. designed the research; M.M.S. and G.V.M. conducted the research; M.M.S. and G.K. analysed the data; G.K., G.V.M., M.M.S., A.M.S.-C., R.P.-E. and A.A.M.S. wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.




