Just as a bounded infinite line is made up of finite ones, so a finite line is made up of infinitely small ones. –Leibniz, De Quadratura Arithmetica
Infinite and infinitely small quantities can be written out of the mathematics altogether via a syncategorematic analysis in favour of expressions referring only to finite quantities and their relations. –Levey, 2021
Calculus necessary leads to them, and people who are not sufficiently expert in such matters get entangled and think they have reached an absurdity. –Leibniz, Elementa nova matheseos universalis
1 Toland’s indictment of mathematicians
In 1716, an anonymous critic claimed to identify a confusion shared by Leibniz and other philosophers of a mathematical bent:
Mais de s’imaginer, qu’ils pourront rendre compte de la nature des choses par de tels Calculs, c’est là precisement que consiste leur erreur.Footnote 1 [Reference Toland76, p. 131] (emphasis added)
The critic has by now been definitively identified as John TolandFootnote 2 (1670–1722); see [Reference Lamarra36, Reference Woolhouse78]. Toland accused Leibniz of allowing his calculus to infect his metaphysics. The critique was apparently written already in 1703Footnote 3 but only published in a 1716 volume of Histoire Critique de la Republique des Lettres.
In the same year (his last), Leibniz penned a response in a detailed letterFootnote 4 to editor Samuel Masson. The letter deals with issues of the philosophy of nature and also comments briefly upon the infinitesimal calculus. Bassler [Reference Bassler11], Arthur [Reference Arthur and De Risi6], and Rabouin and Arthur (RA) [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71] have appealed to one such comment in support of the claim that Leibnizian infinitesimals are syncategorematic (in the sense detailed in Section 3). Contextualizing the letter will help evaluate such claims.
We analyze the Leibnizian exposition on the philosophy of nature and its historical and theological context in Section 2, where we also deal with the meaning of his comments on the calculus. In Section 3 we analyze RA’s reading and show that the 1716 comments on the calculus not only provide no support for an Ishiguro-syncategorematic reading, but support a rather different interpretation of his infinitesimals: they are well-founded ‘fictions of the mind’ (mentis fictiones,Footnote 5 Leibniz to des Bosses [Reference Leibniz53]). In Section 4 we analyze the distinctions infinite number vs. infinite whole, and bounded infinity vs. unbounded infinity in Leibniz, as well as his comparison of the hornangle and inassignables. In Section 5 we analyze the meaning of infinity, fiction, and well-founded fiction in Leibniz. Here we show that, while infinite wholes contradicting the part–whole principle are absolute impossibilities, imaginary roots and infinitesimals are only accidental impossibilities, even if their definitions are taken to be only nominal. In Section 6 we present the conclusions of our contextualisation of the letter to Masson. This text extends our analysis of the Leibnizian heritage pursued in [Reference Bair, Błaszczyk, Ely, Henry, Kanovei, Katz, Katz, Kutateladze, McGaffey, Reeder, Schaps, Sherry and Shnider8] and elsewhere.
2 Monads, rerum natura, and mathematics
Leibniz opens his letter to Masson with a discussion of the concept of
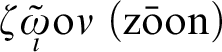 $\zeta\underset{\iota}{\tilde{\omega}}\text{o}\nu~(\text{z}\bar{\textrm {{o}}}\text{on})$
,Footnote
6
i.e., living being. He describes monad as the underlying substance
Footnote
7
of the z
$\zeta\underset{\iota}{\tilde{\omega}}\text{o}\nu~(\text{z}\bar{\textrm {{o}}}\text{on})$
,Footnote
6
i.e., living being. He describes monad as the underlying substance
Footnote
7
of the z
![]() $\bar {\textrm {{o}}}$
on. According to Leibniz, the relation between nature and monadic reality is such that nature is a phenomenon, whereas the monads are the substances underlying natural phenomena. Leibniz first used the term ‘monad’ in 1696; in earlier texts he used various expressions such as ‘individual substance’ [Reference Leibniz58, p. 32], ‘atom of substance’, and ‘metaphysical point’ [Reference Leibniz58, p. 142].Footnote
8
$\bar {\textrm {{o}}}$
on. According to Leibniz, the relation between nature and monadic reality is such that nature is a phenomenon, whereas the monads are the substances underlying natural phenomena. Leibniz first used the term ‘monad’ in 1696; in earlier texts he used various expressions such as ‘individual substance’ [Reference Leibniz58, p. 32], ‘atom of substance’, and ‘metaphysical point’ [Reference Leibniz58, p. 142].Footnote
8
2.1 Leibnizian Passage I
Toward the end of the letter, Leibniz turns to Toland’s claim that mathematicians are not successful as philosophers. After a bit of ad hominem, Leibniz gets down to the business of refuting the claim. His strategy is to draw a line between
-
(1) philosophy, concerned with the ‘nature des choses’, i.e., rerum natura; and
-
(2) mathematics, concerned with applying entities, both ideal and fictional, in geometry and physics.
Toland accused Leibniz of viewing the extension (i.e., the continuum) as made up of mathematical points (the punctiform view).Footnote 9 Leibniz first responds to this accusation, and then comments on the relation between the calculus and the nature des choses:
[Passage I:] I am also far from making extension up of mathematical points. … And, notwithstanding my infinitesimal calculus, I do not admit any real [veritable] infinite number, even though I confess that the multitude of things surpasses any finite number [la multitude des choses passe tout nombre fini], or rather any number. (Leibniz [Reference Leibniz54] as translated by Ariew in [Reference Leibniz58, p. 229])
Passage I draws a line between, on the one hand, the mathematician’s task of exploiting the well-founded fictions of the infinitesimal calculus, and on the other, the philosopher’s task of elucidating the natural phenomena (and perhaps the ultimately real monadic entities which underlie the phenomena) in the framework of an unequivocal rejection of infinite wholes.
In Sections 2.2 and 2.3 we will deal with the distinction Mathematics vs. rerum natura. The distinction infinite wholes vs. well-founded fictions will be analyzed in Section 4.
2.2 Leibnizian Passage II
Unlike the choses whose nature Leibniz seeks to explore in the 1716 letter, mathematical entities exploited in the infinitesimal calculus are only useful fictions (mentis fictiones; see Section 5.1):
[Passage II:] The infinitesimal calculus is useful with respect to the application of mathematics to physics; however, that is not how I claim to account for the nature of things [la nature des choses]. For I consider infinitesimal quantities to be useful fictions. (Leibniz [Reference Leibniz54] as translated by Ariew in [Reference Leibniz58, p. 230])
Leibniz’s comment “however, that is not how I claim to account for the nature of things” is a direct response to Toland’s allegation that Leibniz seeks to account for the nature des choses by means of his calculus (see Section 1). Garber quotes Passage II and notes:
[T]he point seems to be that nature is one thing, and its mathematical representation is another. [Reference Garber23, p. 303]
Garber points out a significant difference between the positions of Leibniz and the Cartesians:
[Leibniz’s] opponents are the Cartesians who have tried to make nature mathematical in a literal sense, to make the physical world over into a physical instantiation of mathematical concepts [whereas Leibniz] can embrace the mathematical representation of dead force in terms of infinitesimals, without having to say that there are real infinitesimals in nature. [Reference Garber23, p. 306]
Thus in Garber’s view, in Passage II Leibniz (disagreeing with the Cartesians) insists on the separation of rerum natura and its mathematical representation.
2.3 Leibnizian evolution on mathematics and rerum natura
The distinction between the mathematical realm and the rerum natura is a crucial feature of Leibniz’s mature philosophy. Whereas he started with a belief that physics could be reduced to mechanics,Footnote 10 and hence to mathematics, over the years mathematics ceased to be perceived by Leibniz as the foundation of physics and turned into a mere representation thereof.
For the young Leibniz, extension (corpus mathematicum) is a component of the matter of choses. As Leibniz explains to Thomasius, a physical body is the compound of matter—which Leibniz identifies with extension and impenetrability—and form, which he identifies with shape:
Space is a primary extended being or a mathematical body (corpus mathematicum), which contains nothing but three dimensions and is the universal locus of all things. Matter is a secondary extended being, or that which has, in addition to extension or mathematical body, also a physical body (corpus physicum), that is, resistance, antitypy, solidity, the property of filling space, impenetrability.Footnote 11 (Leibniz to Thomasius, April 20–30, 1669 [Reference Leibniz37, p. 34]. Transl. Loemker [Reference Leibniz57, p. 100] with minor changes)Footnote 12
During this phase of Leibniz’s development, physical bodies are seen as continuous, exactly as extension is. Namely, they are potentially infinitely divisible:
Matter has quantity too, though it is indefinite, or interminate as the Averroists call it. For being continuous, it is not cut into parts and therefore does not actually have boundaries. (Leibniz to Thomasius, April 20–30, 1669 [Reference Leibniz37, p. 26–27]. Transl. Loemker [Reference Leibniz57, p. 95])Footnote 13
By contrast, in his mature system, Leibniz distinguishes between mathematical extension, which is potentially infinitely divisible, and the matter of physical bodies, which is actually infinitely divided:
But in real things, that is, bodies, the parts are not indefinite—as they are in space, which is a mental thing—but actually specified in a fixed way according to the divisions and subdivisions which nature actually introduces through the varieties of motion. And granted that these divisions proceed to infinity, they are nevertheless the result of fixed primary constituents or real unities, though infinite in number. Accurately speaking, however, matter is not composed of these constitutive unities but results from them. (Leibniz to de Volder, June 30, 1704 [Reference Leibniz52, p. 268]. Transl. Loemker [Reference Leibniz57, p. 536])Footnote 14
Similarly in a March 11, 1706 letter to des Bosses, Leibniz writes:
To pass now from the ideas of geometry to the realities of physics, I hold that matter is actually fragmented into parts smaller than any given, or that there is no part of matter that is not actually subdivided into others exercising different motions. This is demanded by the nature of matter and motion and by the structure of the universe, for physical, mathematical, and metaphysical reasons. (Leibniz to des Bosses, March 11, 1706 [Reference Leibniz53, p. 305]. Transl. Look–Rutherford [Reference Leibniz61, p. 33–35])Footnote 15
The last passage is analyzed by Antognazza, who emphasizes the distinction in Leibnizian thought between the mathematical realm and the rerum natura:
Leibniz is quite consistent in pointing out that the actual infinite he is endorsing concerns the ‘real’ as opposed to the ‘ideal’ order. In the letter of March 11, 1706 to des Bosses … he explicitly stresses that in moving his attention to the actual infinite, he is shifting from the ideal to the real order. [Reference Antognazza1, p. 9]
To avoid confusion between continuous extension, which is an ideal entity, and the actual structure of physical matter, Leibniz employs for the latter the adjective contiguous:
I recall that Aristotle too distinguishes between Contiguum and Continuum: things are continuous if their extremes are one, and are contiguous if their extremes are together. (Pacidius Philaleti, 1676; Leibniz [Reference Leibniz55]. A6.3. 537)Footnote 16
Levey similarly emphasizes the difference between the actual subdivisions of the real world and the potential ones of the ideal mathematical world:
[To Leibniz,] a body is separable into various parts because it actually has contiguous parts that cohere together but which could be brought not to cohere and be separated from one another. … Potentiality, in the sense of potential divisions or potential parts, is a concept that belongs to the ‘ideal’ realm of mathematics and geometry but has no application to the world of matter. [Reference Levey63, note 6, p. 53] (emphasis in the original)
Views similar to that of Antognazza were expressed by Bosinelli [Reference Bosinelli16, p. 168] and Breger [Reference Breger and Li17, p. 124], as acknowledged by Arthur in [Reference Arthur, Nachtomy and Winegar5, p. 156]. But especially, they were expressed by Leibniz himself, who specifically warned his readers against the misunderstandings arising from the conflation of the two realms:
It is the confusion of the ideal with the actual which has muddled everything and caused the labyrinth of the composition of the continuum. (Remarques sur les Objections de M. Foucher, 1695. Gerhardt [Reference Gerhardt25, vol. IV, p. 491]. Transl. Ariew–Garber [Reference Leibniz58, p. 146])Footnote 17
A detailed study of the issue appears in [Reference Ugaglia, Ademollo, Amerini and De Risi77].
Just as the Leibnizian Passage I in Section 2.1, Passage II in Section 2.2 draws a line between the fictional entities (mentis fictiones) of the infinitesimal calculus—well-founded fictions, or useful fictions, as Leibniz also calls them—and the entities of rerum natura. The conflation of the two realms is behind some of the purported evidence in favor of the so-called syncategorematic reading, analyzed in Section 3.
3 Syncategorematics vs. keeping bodies and calculus separate
RA follow [Reference Ishiguro30, chap. 5] in interpreting the Leibnizian term ‘useful fiction’ syncategorematically via a logical analysis of the quantifier clause ‘smaller than every given’. This stance enables RA to claim that Leibnizian infinitesimals are ‘in keeping with the Archimedean axiom’ [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, Abstract] (in the previous installment by Arthur [Reference Arthur4] the refrain was ‘fully in accord with the Archimedean Axiom’).
3.1 Small magnitudes vs. Ishiguro’s alternating quantifiers
In 1990, Ishiguro formulated the following hypothesis concerning Leibnizian infinitesimals:
It seems then that throughout his working life as a mathematician Leibniz did not think of founding the calculus in terms of a special kind of small magnitude. [Reference Ishiguro30, p. 86] (emphasis added)
To explain in what sense Leibniz allegedly did not found the calculus on a special kind of small magnitude, she elaborates as follows:
It seems that when we make reference to infinitesimals in a proposition, we are not designating a fixed magnitude incomparably smaller than our ordinary magnitudes. Leibniz is saying that whatever small magnitude an opponent may present, one can assert the existence of a smaller magnitude. In other words, we can paraphrase the proposition with a universal proposition with an embedded existential claim. (ibid., p. 87; emphasis on ‘ordinary’, ‘universal’, and ‘existential’ added)
Accordingly, when Leibniz asserted that his inassignable
![]() $dx$
, or alternatively
$dx$
, or alternatively
![]() $\epsilon $
, was smaller than every assignable quantity Q, he really meant that for each given
$\epsilon $
, was smaller than every assignable quantity Q, he really meant that for each given
![]() $Q>0$
there exists an ‘ordinary’
$Q>0$
there exists an ‘ordinary’
![]() $\epsilon>0$
such that
$\epsilon>0$
such that
![]() $\epsilon <Q$
.
$\epsilon <Q$
.
Ishiguro interprets Leibniz’s uses of the term ‘infinite quantity’ by a similar paraphrase involving embedded quantifiers. Such an approach has been described as a syncategorematic treatment of statements involving ‘infinite’ and its cognates. Ishiguro goes on to compare the theories of Leibniz and Russell and concludes:
The similarity which we find in the two theories lies in the common intention Leibniz and Russell have of understanding a sentence which ostensibly designates a specific entity, as really, in its logical form, being a quantified sentence; i.e., a universal or an existential sentence. (ibid., p. 99; emphasis on ‘logical’ added)
Taking her cue from Russell, Ishiguro reads Leibnizian ‘useful fictions’ as logical fictions.Footnote 18 In the same vein, Levey writes:
[T]he fiction is intended by Leibniz to be ‘logical’ in character: infinite and infinitely small quantities can be written out of the mathematics altogether via a syncategorematic analysis in favour of expressions referring only to finite quantities and their relations. [Reference Levey, Shapiro and Hellman64, p. 148]
By a similar quantifier sleight-of-hand, RA declare Leibniz’s uses of the term ‘infinitesimal’ to be “fully-in-accord/in-keeping with the Archimedean axiom” (see further in Section 3.3).
3.2 Rabouin on syncategorematic entities
In 2013, Rabouin toys with “the idea that the entities being studied are relational or in Leibniz’s parlance ‘syncategorematic’” [Reference Rabouin67, p. 120] and adds: “This is the reason why Leibniz calls them fictitia (they are terms not referring to individual beings, but to some relational properties)” (ad loc., note 40).
On the other hand, in 2015, Rabouin seeks to distance himself from attributing hidden quantifiers to Leibniz, in the following terms:
The core of the demonstration … is the arbitrariness of the choice of
![]() $\varepsilon $
. But this arbitrariness does not amount, in modern terms, to a universal quantification (at least in classical first order logic), which would be meaningless to Leibniz. [Reference Rabouin and Jullien68, p. 362]
$\varepsilon $
. But this arbitrariness does not amount, in modern terms, to a universal quantification (at least in classical first order logic), which would be meaningless to Leibniz. [Reference Rabouin and Jullien68, p. 362]
Yet in note 25 on the same page Rabouin appears to endorse Ishiguro’s reading: “It is, in Leibniz’ terminology, a ‘syncategorematic’ entityFootnote 19 see Ishiguro (1990) …” (ibid.). Rabouin goes on to claim the following:
It should then be clear why infinitesimals were called by Leibniz ‘fictions’. In and of itself, there is no such thing as a ‘quantity smaller than any other quantity’. This would amount to the existence of a minimal quantity and one can show that a minimal quantity implies contradiction. (ibid.; emphasis added)
What are we to make of Rabouin’s claimed detection of contradiction? While it is true that there is no such thing as a nonzero quantity smaller than any other quantity, Leibniz requires his inassignable infinitesimals to be smaller, not than every quantity, but rather than every assignable quantity; for an illustration in terms of hornangles see Section 4.5. This accords with a glossary entry in (Rabouin’s 2020 coauthor) Arthur’s volume of translations. Here an infinitesimal is defined as
a part smaller than any assignable (see INASSIGNABILIS), a definition to which Leibniz frequently has recourse.Footnote 20 [Reference Arthur2, p. 452]
Thus a particular infinitesimal
![]() $\epsilon>0$
will satisfy
$\epsilon>0$
will satisfy
 $$ \begin{align} \epsilon<\frac12,\; \epsilon<\frac13,\; \epsilon<\frac14,\; \text{etc.}, \end{align} $$
$$ \begin{align} \epsilon<\frac12,\; \epsilon<\frac13,\; \epsilon<\frac14,\; \text{etc.}, \end{align} $$
so long as the denominator is assignable. Due to what appears to be a mathematical misunderstanding, Rabouin is led to a conclusion that a bona fide infinitesimal would be contradictory and hence ‘fictional’.
Once one realizes that the contradiction is not there to begin with, there is no compelling reason to interpret Leibnizian fictionalism as the counterpart of an allegedly contradictory nature of infinitesimals, as Rabouin does in 2015. A geometric illustration of (3.1) in terms of hornangles appears in Section 4.5.
3.3 Letter to Masson and RA’s quantifiers
In Section 3.2, we examined Rabouin’s 2015 attempt to declare Leibnizian infinitesimals contradictory. Five years later in 2020, one finds a related attempt to declare Leibnizian infinitesimals contradictory by Rabouin and Arthur (RA) in [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71] (see also Section 4.2). Infinitesimals do contradict the Archimedean axiom, but if this is what RA mean by their contradictory claim, then their argument (in support of the contention that Leibnizian allegedly syncategorematic infinitesimals are ‘in keeping with the Archimedean axiom’) would be circular: the positing of the Archimedean axiom predetermines the conclusion that non-Archimedean infinitesimals are contradictory.Footnote 21
In search of evidence in support of an Ishiguroan interpretation, RA turn to the 1716 letter to Masson where Leibniz employs the quantifier clause
‘la multitude des choses passe tout nombre fini’.
Via the quantifier clause, RA seek to establish a connection between useful fictions and logical fictions, ‘in keeping with the Archimedean axiom’.
However, in his 1716 letter Leibniz is not referring to mathematical entities, whether fictional or ideal, when he employs the quantifier clause above. Rather, he is referring to natural phenomena and the monads which underlie them (see Section 2). Neither natural phenomena nor the monads are useful fictions, unlike infinitesimals. The quantifier clause in the 1716 letter therefore does not refer to mathematical entities such as infinitesimals and infinite quantities. Rather, it merely reasserts Leibniz’s opposition to infinite wholes as contradictory. RA claim the following similarity:
Leibniz insisted that since every body is actually divided by motions within it into further bodies that are themselves similarly divided without bound, bodies ‘are actually infinite, that is to say, more bodies can be found than there are unities in any given number whatever’ (A VI 4, 1393; LLC 235). That is, their multiplicity ‘surpasses every finite number’.
![]() $^{26}$
$^{26}$
Similarly, when Pierre Varignon asked Leibniz for clarification of his views on the infinitely small in 1702, Leibniz replied (February 2, 1702) that it had not been his intention ‘to assert that there are in nature infinitely small lines in all rigor, or compared with ours, nor that there are lines infinitely greater than ours’. [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, p. 412] (emphasis on ‘Similarly’ added)
Here RA’s note 26 contains the following text:
“26 Cf. what Leibniz wrote to Samuel Masson in the last year of his life: ‘Notwithstanding my Infinitesimal Calculus, I do not at all admit a genuine infinite number, although I confess that the multiplicity of things surpasses every finite number, or rather, every number.’ (GP VI 629)”
We can agree with RA’s comments on Leibniz’s understanding of actual subdivision of bodies. However, RA also claim a similarity in reference to the following Leibnizian texts:
-
(1) his Actu infinitae sunt creaturae (1678–81);
-
(2) letter to Varignon (1702);
-
(3) letter to Masson (1716).
The alleged similarity is apparently based on Leibniz’s calling into question certain notions of infinity in these texts. We analyze their claim in Section 3.4.
3.4 Comparison of letters to Varignon and Masson
In connection with the comparison of the letters, we note the following three points.
1. Notwithstanding the fact that Leibniz briefly mentions the infinitesimal calculus in the 1716 passage, the substance of the sentence is not concerned with infinitesimal calculus, but rather is a reflection on the philosophy of nature that Leibniz deliberately contrasted with the calculus. What is put into question in the 1716 letter is the concept of an infinite taken as a whole (deemed contradictory by Leibniz), in the context of a metaphysical analysis of body and substance.
Meanwhile, the 1702 comment addressed to Varignon deals, not with metaphysics, but with mathematical fictions (the relevant passage from the letter to Varignon appears in Section 5.2 at note 53). Notice that, unlike the 1716 passage, the 1702 passage does not even mention ‘number’, but speaks rather of geometric objects, such as infinitely large lines (i.e., line segments), which are instances of Leibnizian bounded infinity contrasted with unbounded infinite wholes (see Sections 4.3 and 4.4). The 1702 passage reasserts the Leibnizian position that infinitesimal lines need not idealize anything in nature to be useful, and in this sense can be taken to be fictional; see Section 4. Therefore RA’s claimed similarity has no basis.
2. A similar conflation affects RA’s use of the Leibnizian phrase
“So bodies are actually infinite, i.e., more bodies can be found than there are unities in any given number” (Leibniz as translated by Arthur in [Reference Arthur2, p. 235])
part of which is quoted in the passage from RA appearing in Section 3.3. The phrase concerns bodies (in rerum natura) and not infinitesimals. The distinction was emphasized by both Antognazza and Levey (see Section 2.2).
3. Referring to possible connections between mathematics and philosophy in Leibniz and the interpretation that puts differential calculus at the core of Leibniz’ philosophy, Rabouin solo writes:
Leibniz was … very explicit about some connections which he resisted making—although modern commentators tend to put a lot of emphasis on them. [Reference Rabouin, Goethe, Beeley and Rabouin69, note 47, p. 69] (emphasis on ‘resisted making’ ours)
Rabouin goes on to quote Passage II from the 1716 letter (see Section 2.2) as evidence (for a reluctance on the part of Leibniz to make certain connections between mathematics and philosophy). Rabouin’s interpretation of Passage II, insisting on a segregation of mathematics and philosophy, is compatible with our view, but not with the approach pursued by Rabouin and Arthur in [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, p. 412] that seeks to enlist the 1716 letter as evidence in favor of a syncategorematic reading of the Leibnizian calculus. In Sections 4 and 5, we develop an interpretation of Leibnizian infinitesimals that is more faithful to the Leibnizian texts.
4 Well-founded fictions: the mathematics
Leibniz described the infinitesimals of his calculus as well-founded because they perform successfully within the system of rules he developed for the calculus. Similarly, imaginaries are well-founded because mathematical experience shows that they are useful in the solution of the cubic equation and other problems.
Leibniz’s choice of the term multitude in Passage I (Section 2.1) is significant. Here Leibniz reinforces his rejection of a punctiform conception of extension by reminding the reader that he rejects a real infinite number, meaning that he rejects an infinite multitude taken as a whole (implied by the punctiform view of the continuum) as contradictory.
4.1 Part–whole principle
Leibniz held that infinite wholes would contradict the part–whole principle. Already in 1672 Leibniz wrote:
[T]here are as many squares as numbers, that is to say, there are as many square numbers as there are numbers in the universe. Which is impossible. Hence it follows either that in the infinite the whole is not greater than the part, which is the opinion of Galileo and Gregory of St. Vincent, and which I cannot accept; or that infinity itself is nothing, i.e., that it is not one and not a whole. Or perhaps we should say, distinguishing among infinities, that the most infinite, i.e., all the numbers is something that implies a contradiction, … (Leibniz as translated by Arthur in [Reference Arthur2, p. 9]; emphasis added)
Thus already in 1672, Leibniz held that the infinity of all numbers—that we may today refer to as an infinite cardinalityFootnote 22 —contradicts the part–whole principle.Footnote 23 To explain Leibniz’ rejection of infinite wholes in modern terms, one could perhaps surmise that Leibniz would have rejected as incoherent the modern notion of infinite cardinality or cardinal number (a point painstakingly argued in [Reference Arthur and De Risi6]).
While Leibniz himself of course does not distinguish between infinite number and infinite cardinality, he does mention a related distinction between infinite magnitude and infinite multitude in a letter to des Bosses [Reference Leibniz53, p. 31]. The correspondence between Leibniz and Bernoulli indicates that Leibniz was clearly aware of the difference between infinite multitude and infinite number.Footnote 24 The distinction is important because Leibniz’s rejection of an infinite multitude, or collection, does not entail a rejection of infinite magnitude, or quantity, or number, provided they are not considered as a whole. What leads to contradiction is not infinity in itself but an infinity taken as a whole. Regrettably, the notions of infinite whole and infinite quantity have been conflated in recent literature. In particular, such a conflation is at the root of the Ishiguro-syncategorematic interpretation of infinitesimals, analyzed in Section 3.
4.2 Infinite wholes and infinite numbers
Both Arthur [Reference Arthur7] and Rabouin and Arthur [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71] seek to connect the Leibnizian rejection of infinite wholes and his description of infinitesimals as fictional, and to document Leibnizian rejection of infinite number. Thereby they seek to assimilate infinitesimals to infinite wholes.Footnote 25 RA claim the following:
Leibniz never changed his mind and always claimed that such entities do not exist because they imply a contradiction. One can nonetheless use infinities and infinitely small quantities in a calculation provided one can furnish a way of doing correct demonstrations with them; that is, as long as one can identify conditions under which their use will not lead to error. [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, p. 413] (emphasis on ‘such entities’ and ‘conditions’ added)
While no such conditions are ever identified by RA, in their Conclusion they speak of using infinitesimals ‘under certain specified conditions’ [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, p. 441], again unspecified.Footnote 26 The key issue, however, is what is meant exactly by “such entities” mentioned by RA. While Leibniz rejected as contradictory an infinite multitude taken as a whole (see Section 2), RA provide no evidence that Leibniz viewed infinitesimal and infinite quantities as contradictory (and not merely as well-founded fictions).Footnote 27
A similar conflation appears in Rabouin solo, who claims that
[Leibniz] regularly stumbled upon the fact that an ‘infinite number’ or multitude was a notion entailing a contradiction. Infinitely small numbers, of the kind introduced by Wallis in his Arithmetics of the infinites
![]() $($
Arithmetica infinitorum
$($
Arithmetica infinitorum
![]() $)$
as inverse of infinite number, naturally inherited this qualification. [Reference Rabouin70]
$)$
as inverse of infinite number, naturally inherited this qualification. [Reference Rabouin70]
The contradictory nature of infinite wholes is ‘inherited’ not by infinitesimals but by minima, i.e., points viewed as the simplest constituents of the continuum.Footnote 28
Arthur similarly conflates infinite collections and infinite number when he claims the following:
[Leibniz] held that there are actually infinitely many substances, actually infinitely many parts of matter, and actually infinitely many terms in an infinite series:Footnote 29 that is, there are so many that, however many are assigned, there are more, but there is no infinite collection of them, and therefore no infinite number. [Reference Arthur7, p. 152] (emphasis added)
Arthur’s final ‘therefore’ is a non-sequitur if the expression ‘infinite number’ is meant to include infinite quantity (in addition to infinite wholes).
The related issue of nominal definitions is discussed in Section 5.3.
4.3 Bounded and unbounded infinity
A Leibnizian distinction of long standing—at least since his De Quadratura Arithmetica (DQA), Propositio XI and the Scholium following it—is between bounded infinity and unbounded infinity; see, e.g., [Reference Knobloch33, p. 42], [Reference Knobloch, Gavroglu, Christianidis and Nicolaidis34, pp. 266–267]. In this text of fundamental importance for the foundations of the calculus, Leibniz contrasts bounded infinity and unbounded infinity in the following terms:
But as far as the activity of the mindFootnote 30 with which we measure infinite areas is concerned, it contains nothing unusual because it is based on a certain fiction and proceeds effortlessly on the assumption of a certain, though bounded, but infinite line; therefore it has no greater difficulty than if we were to measure an area that is finite in length. … Just as points, even of infinite numbers, are unsuccessfully added to and subtracted from a bounded line, so a bounded line can neither form nor exhaust an unbounded one; however, many times it has been repeated. This is different with a bounded but infinite line thought to be created by some multitude of finite lines, although this multitude exceeds any number. And just as a bounded infinite line is made up of finite ones, so a finite line is made up of infinitely small ones, yet divisible. (Leibniz, DQA [Reference Leibniz59], Scholium following Propositio XI; translation ours; emphasis added)
It is worth noting that bounded/unbounded infinity is not the same distinction as potential/actual infinity. While actual infinity (understood distributively) is possible in the material realm (see Section 2.3), unbounded infinity (understood collectively, i.e., as a whole) is a contradictory concept to Leibniz. Bounded infinity is a term Leibniz reserves mainly to discuss the well-founded fictions used in his infinitesimal calculus, namely the infinitely large and (its reciprocal) infinitely small. In one of his early articles, Knobloch observes:
[Leibniz] distinguished between two infinites, the bounded infinite straight line, the recta infinita terminata, and the unbounded infinite straight line, the recta infinita interminata. He investigated this distinction in several studies from the year 1676. Only the first kind of straight lines can be used in mathematics, as he underlined in his proof of Theorem 11 [i.e., Propositio XI]. He assumed a fictive boundary point on a straight half line which is infinitely distant from the beginning: a bounded infinite straight line is a fictitious quantity. [Reference Knobloch35, p. 97]
An unbounded infinity, which Leibniz viewed as a contradictory concept, can be exemplified by the multitude of natural numbers (which seen as a whole would contradict the part–whole principle; see Section 4.1). A bounded infinity can be exemplified by an inassignable (see below) natural number, say
![]() $\mu $
, or the multitude of all natural numbers up to
$\mu $
, or the multitude of all natural numbers up to
![]() $\mu $
(and thus bounded by
$\mu $
(and thus bounded by
![]() $\mu $
).
$\mu $
).
Leibniz defines an infinitesimal as a “fraction infiniment petite, ou dont le denominateur soit un nombre infini” [Reference Leibniz49, p. 93], such as
![]() $\frac 1\mu $
. Such infinitesimals are routinely used in computing, e.g., the differential ratio
$\frac 1\mu $
. Such infinitesimals are routinely used in computing, e.g., the differential ratio
![]() $\frac {dy}{dx}$
, as in the passage from Cum Prodiisset [Reference Leibniz48] (circ. 1701), where Leibniz also mentions the assignable/inassignable dichotomy:
$\frac {dy}{dx}$
, as in the passage from Cum Prodiisset [Reference Leibniz48] (circ. 1701), where Leibniz also mentions the assignable/inassignable dichotomy:
[A]lthough we may be content with the assignable quantities
![]() $(d)y$
,
$(d)y$
,
![]() $(d)v$
,
$(d)v$
,
![]() $(d)z$
,
$(d)z$
,
![]() $(d)x$
, etc., … yet it is plain from what I have said that, at least in our minds,Footnote
31
the unassignables [inassignabiles in the original Latin]
$(d)x$
, etc., … yet it is plain from what I have said that, at least in our minds,Footnote
31
the unassignables [inassignabiles in the original Latin]
![]() $dx$
and
$dx$
and
![]() $dy$
may be substituted for them by a method of supposition even in the case when they are evanescent … (Leibniz as translated in [Reference Child20, p. 153]).
$dy$
may be substituted for them by a method of supposition even in the case when they are evanescent … (Leibniz as translated in [Reference Child20, p. 153]).
A similar passage appears in Historia et Origo calculi differentialis a G. G. Leibnitzio conscripta.Footnote 32 The assignable/inassignable dichotomy was analyzed in the seminal study by Bos [Reference Bos15].Footnote 33 See [Reference Bair, Błaszczyk, Ely, Katz and Kuhlemann9, sec. 4] for a formalization of the dichotomy in modern mathematics.
4.4 Instances of infinita terminata
In a February 1676 text, Leibniz provided a colorful example of a bounded infinity as follows:
This is a wonder, too: that someone who has lived for infinitely many years can have begun to live, and that someone who lives for a number of years that is greater than any finite number can at some time die. From which it will follow that there is an infinite number.Footnote 34 (Leibniz as translated by Arthur in [Reference Arthur2, p. 51])
In a text Numeri infiniti dated April 10, 1676, Leibniz envisioned the possibility that such numbers—examples of bounded infinities—may be prime:
Two infinite numbers which are not as two finite numbers can be commensurable, namely, if their greatest common measure [i.e., divisor] is a finite number—for instance, if both are prime. (Leibniz as translated by Arthur in [Reference Arthur2, p. 87])
The dating of Numeri infiniti is significant since Arthur commits himself to a tight timeframe for an alleged switch in Leibniz’s thinking about infinitesimals.Footnote 35
RA mention the term terminata (bounded) three times in their article [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71] and specifically in the context of Propositio XI and its Scholium in DQA, but do not pay sufficient attention to the dichotomy of bounded versus unbounded infinity and fail to appreciate its significance.
Thus, in an analysis of Propositio XI involving the evaluation of a (finite) area of a region extending to infinity, Leibniz introduces
a point
![]() $(\mu )$
at infinitely small distance from the axis. In this case, indeed, the straight line
$(\mu )$
at infinitely small distance from the axis. In this case, indeed, the straight line
![]() $(\mu )\lambda $
will still be infinite. (Leibniz as translated by RA in [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, p. 421]).
$(\mu )\lambda $
will still be infinite. (Leibniz as translated by RA in [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, p. 421]).
RA go on to explain this infinity “in the sense that it can be made greater than any given quantity (major qualibet assignabili), yet will be bounded (terminata)” (ibid.; emphasis added). However, there is no source in Leibniz for the clause “it can be made greater than any given quantity.” Rather, Leibniz wrote “it is greater than any given quantity”; RA added the clause “can be made greater, etc.” to help Leibniz conform to the Ishiguro-syncategorematic interpretation (see Section 3). RA’s addition distorts Leibniz’ intended meaning.
Leibniz concludes the discussion of bounded infinities in the Scholium following Propositio XI with the following comment:
Déterminer si la nature [natura rerum] souffre des quantités de ce genre est l’affaire du Métaphysicien; il suffit au Géomètre de démontrer ce qui résulte de leur supposition.Footnote 36 (Leibniz as translated by Parmentier in [Reference Leibniz59, p. 101]).
Here Leibniz observes that, though bounded infinities may not be found in rerum natura, their usefulness to the geometer is independent of the metaphysician’s task of elucidating their relation to natural phenomena.Footnote 37 To be useful, they needn’t be found in nature:
… Therefore everything else will also exist in the mind: and in it everything that I denied to be possible will now be possible.Footnote 38 (Leibniz, Numeri infiniti, as translated by Arthur in [Reference Arthur2, p. 91])
The reference is to a discussion on the previous page of a circle as a fictional polygon with an infinite number of sides:
The circle—as a polygon greater than any assignable, as if that were possible—is a fictive entity, and so are other things of that kind. (Leibniz as translated by Arthur in [Reference Arthur2, p. 89])
4.5 Hornangles and inassignables
Leibnizian hornangles exhibit non-Archimedean behavior (when compared to ordinary angles) not easily paraphrasable in Archimedean terms, and shed light on Leibniz’s attitude toward infinitesimals in general. We provide a geometric illustration of the phenomenon of magnitudes smaller than all assignables (see equation (3.1) in Section 3.2), in terms of the hornangle (also known as angle of contact or angle of contingence), much discussed in thirteenth to seventeenth century literature. Thus, Campanus of Novara (1220–1296) wrote that “any rectilinear angle is greater than an infinite number of angles of contingence” [Reference Murdoch, Kretzmann, Kenny, Pinborg and Stump66, pp. 580–581].
The hornangle is the “angle,” or crevice, between an arc of a circle (or a more general curve) at a point P, and its tangent ray r at P. According to Leibniz, such a hornangle is smaller than every ordinary rectilinear angle formed by the ray r and a secant ray at P.Footnote 39 Meanwhile, the hornangle is certainly not smaller than all other hornangles (including itself).
In a 1686 article, Leibniz considered a more general notion of hornangle, or angle of contact, between a pair of curves with a common tangent at P.Footnote 40 Leibniz defined the osculating circle of a curve at P as the circle forming the least angle of contact with the curve:
Circulus autem ille lineam propositam ejusdem plani in puncto proposito osculari a me dicitur, qui minimum cum ea facit angulum contactus. [Reference Leibniz42]
Choosing the least one among the angles of contact, as Leibniz does here, presupposes that such “angles” are nonzero. A few lines later, Leibniz renames such entities “angle of osculation” to distinguish them from angles of contact in the classical sense (crevice between curve and tangent ray).
Leibniz explicitly compares angles of contact to inassignables in the 1671 text Theoria motus abstracti (TMA). In this early text, Leibniz still composes the continuum of indivisible infinitesimals which he refers to as “points.” Speaking of the space filled by an infinitesimal motion of a body, Leibniz writes:
… this space is still inassignable … although the ratio of a point of a body … to the [part]Footnote 41 of space it fills when moving, is as an angle of contact to a rectilinear angle … (Leibniz as translated by Loemker [Reference Leibniz57, p. 140], TMA, Predemonstrable Foundation 13, A VI.ii N41)
In his mature period, Leibniz’s view of the continuum changes (see Section 2.3), but the non-Archimedean behavior of hornangles in comparison with ordinary rectilinear/assignable angles remains. There are at least three indications that Leibniz viewed hornangles as being nonzero.
1. Choosing the smallest one of the angles of contact as Leibniz does in 1686 presupposes that they are nonzero.
2. In a 1696 letter, Leibniz makes it clear that angles of contact are nonzero:
Our infinitesimal calculus allows us to see that one can only ignore differentias incomparabiliter minores rebus differentiatis (the differences which are incomparably smaller than the differentiated things). So, it does not follow that there is no considerable difference between the degrees of force in the object from each blow by gravitating matter. Otherwise, this would be as if one wanted to prove that angles of contact do not differ amongst themselves because they do not compare with rectilinear angles. (Leibniz to Papin, March 1696, A III, 6, 698).
Here Leibniz uses the term incomparable in the technical sense (akin to inassignable) used in his formulation of the violation of the Archimedean property in a 1695 letter to L’Hôpital.Footnote 42 Of course, they can still be compared to rectilinear angles.Footnote 43
3. A careful analysis of the two passages in [Reference Leibniz42] where Leibniz asserts that they are “nothing” reveal that his intention is to say that they are negligible vis-à-vis incomparably larger quantities: first, angles of contact are negligible vis-à-vis rectilinear angles, and second, angles of osculation are negligible vis-à-vis angles of contact.
We note the unavailability of the option of representing a hornangle by rectilinear angles—either arranged in a sequence or assorted with logical quantifiers. The non-Archimedean behavior of Leibnizian hornangles is not easily paraphrasable in Archimedean terms, suggesting similar behavior of Leibnizian inassignable infinitesimals. A similar situation exists with respect to comparison of infinitesimals and imaginary roots.Footnote 44
Infinitesimals, hornangles, and imaginaries are well-founded fictions that facilitate the art of discovery. Leibnizian well-founded fictions are at most accidentally impossible (they are not contradictory; see Section 5.3). Meanwhile, there are entities that Leibniz sometimes refers to as fictions, such as infinite wholes, which are absolutely impossible (contradictory).Footnote 45 This crucial distinction is not sufficiently taken into account by advocates of the Ishiguro-syncategorematic interpretation.
5 Well-founded fictions: the philosophy
5.1 Instantiation in rerum natura ?
On a number of occasions, Leibniz spoke of infinitesimals as not necessarily found in nature. Thus, in the Specimen Dynamicum of 1695, he concluded his analysis of infinite degrees of impetus as follows:
Hence the nisus is obviously twofold, an elementary or infinitely small one which I also call a solicitation and one formed by the continuation or repetition of these elementary impulsions, that is, the impetus itself. But I do not mean that these mathematical entities are really found in nature as such but merely that they are means of making accurate calculations of an abstract mental kind. (Leibniz [Reference Leibniz47] as translated by Loemker in [Reference Leibniz57, p. 438]; emphasis on solicitation in the original; emphasis on really found in nature and abstract mental kind added)
Over a decade later, des Bosses questioned Leibniz concerning the above passage from Specimen Dynamicum. Leibniz responded as follows concerning the fictionality of infinitesimals:
For I consider both [infinitely small and infinitely large magnitudes] as fictions of the mind, due to abbreviated ways of speaking, which are suitable for calculation, in the way that imaginary roots in algebra are.Footnote 46 (Leibniz as translated by Look and Rutherford in [Reference Leibniz53, p. 33]; emphasis added)
Arthur quotes this passage in [Reference Arthur, Nachtomy and Winegar5, p. 176] and concludes: “This is the syncategorematic infinitesimal described above” (ibid.).Footnote 47 Is it indeed? First, in this passage Leibniz refers to both infinitesimals and imaginary roots as compendia (abbreviations), undermining an Ishiguro-syncategorematic reading (see Section 3) since it is unavailable for imaginary roots.Footnote 48 Furthermore, des Bosses, in formulating his question on March 2, 1706, specifically raised the possibility of the syncategorematic infinite:
I would have conjectured that the infinite that you add can be confined to the syncategorematic; … (des Bosses as translated by Look and Rutherford in [Reference Leibniz61, p. 27])
In his answer 9 days later, on March 11, 1706, Leibniz says not a word about the syncategorematic infinite, and rather speaks of fictions of the mind as quoted above.
Levey reproduces a longer passage from the March 11, 1706 letter containing the one we quoted, and claims that it supports the syncategorematic reading [Reference Levey, Shapiro and Hellman64, p. 146]. However, such a claim overlooks the fact that Leibniz specifically ignored des Bosses’ question about the syncategorematic infinite, as noted above. Levey concludes his Section 2.1 on infinitesimals as follows:
They can be replaced by proofs given in Leibniz’s updated style of Archimedes if full rigor is wanted, and the mathematics in which they figure is not committed to the existence of ‘actual’ infinitesimals in nature for its justification. (op. cit., p. 148; emphasis added)
As Levey appears to acknowledge in his concluding sentence, it is in nature that there may be no infinitesimals; Leibniz viewed them as mentis fictiones. Levey’s stated conclusion is mainly in accord with our reading of Leibnizian infinitesimals. Meanwhile, the Ishiguro-syncategorematic hypothesis pursued elsewhere in Levey’s Section 2.1 remains unsupported.
5.2 Well-founded fictions in relation to rerum natura
The fictional nature of infinitesimals is a constant theme in Leibnizian thought. Thus, in a April 14, 1702 letter to Varignon, Leibniz wrote:
[L]es infinis et infiniment petits pourroient estre pris pour des fictions, semblables aux racines imaginaires, sans que cela dût faire tort à nostre calcul, ces fictions estant utiles et fondées en realité.Footnote 49 [Reference Leibniz50, p. 98]
In this passage, Leibniz asserts that interpreting the infinite and infinitely small as useful fictions would cause no harm to ‘our calculus’.Footnote 50 In a June 20, 1702 letter to Varignon, Leibniz wrote:
Entre nous je crois que Mons. de Fontenelle … en a voulu railler, lorsqu’il a dit qu’il vouloit faire des elemens metaphysiques de nostre calcul. Pour dire le vray, je ne suis pas trop persuadé moy même, qu’il faut considerer nos infinis et infiniment petits autrement que comme des choses ideales ou comme des fictions bien fondées.Footnote 51 [Reference Leibniz51, p. 110] (emphasis added)
In this case Leibniz adds a qualification: infinitesimals are well-founded fictions (‘fictions bien fondées’). It is difficult to see how fictions that are, according to Leibniz, well-founded could also be, as per RA, contradictory.Footnote 52 On the contrary, for Leibniz consistency is a requirement for a well-founded fiction and thus for mathematical existence. In this respect Leibniz is closer than many mathematicians of subsequent generations to Hilbert’s formalism (where existence depends on consistency alone). By ascribing to Leibniz the use of contradictory concepts, RA rule out an interpretation whereby Leibniz, like Hilbert, views conception of mathematical existence as consistency; see [Reference Katz and Sherry32] for details.
Leibniz expressed similar sentiments concerning ideal notions in a February 2, 1702 letter to Varignon:Footnote 53
D’où il s’ensuit, que si quelcun n’admet point des lignes infinies et infiniment petites à la rigueur metaphysique et comme des choses reelles, il peut s’en servir seurement comme des notions ideales qui abregent le raisonnement,Footnote
54
semblables à ce qu’on appelle racines imaginaires dans l’analyse commune (comme par exemple
![]() $\sqrt {-2}$
), …Footnote
55
[Reference Leibniz49, p. 92] (emphasis added)
$\sqrt {-2}$
), …Footnote
55
[Reference Leibniz49, p. 92] (emphasis added)
The idea of imagining infinitesimals also appears in a March 30, 1699 letter to Wallis, where Leibniz rejects Wallis’ position that infinitesimals are nothings:
[F]or the calculus it is useful to imagine Footnote 56 infinitely small quantities, or, as Nicolaus Mercator called them, infinitesimals, such that when at least the assignable ratio between them is sought, they precisely may not be taken to be nothings. (Leibniz as translated by Beeley in [Reference Beeley12, note 38]; emphasis added)
In the same letter, Leibniz makes a revealing comment concerning the status of inassignables:
Whether inassignable quantities are real or fictions, I will not argue for now; it is enough that they serve as a help for thinking, and that they always carry a proof with them, with only the style changed; and so I have noted, that if anyone should substitute incomparably or sufficiently small (quantities) for infinitely small ones, I do not object. (Leibniz to Wallis, March 30, 1699, GM [Reference Gerhardt25] IV, 63; translation ours)
Here Leibniz refuses to commit himself to either a realist or a fictionalist position. Beeley offers the following intriguing speculation:
This of course opens up the whole question of whether Leibniz really held that infinitesimals could exist in nature. On some occasions he does indeed seem to be denying their existence. But I think that we need to be careful here, because denial of the existence of infinitesimals is generally coupled with the argument that the success of the calculus does not depend on metaphysical discussions concerning reality. When he makes such claims, this seems to be no more than a get-out clause vis-à-vis opponents who seek to provide metaphysical arguments against his calculus. Seen within the context of Leibniz’ dynamics, particularly in respect of dead force (vis mortua) it is evident that he must be committed in some way to the existence of infinitesimals.Footnote 57 [Reference Beeley and Leibniz13, p. 42]
Our main arguments in the present text are independent of resolving Beeley’s ‘get-out clause’ hypothesis. On many occasions, Leibniz did reject infinitesimal creatures. Thus, in a June 20, 1702 letter to Varignon, Leibniz wrote:
Je croy qu’il n’y a point de creature au dessous de la quelle il n’y ait une infinité de creatures, cependant je ne crois point qu’il y en ait, ny même qu’il y en puisse avoir d’infiniment petites et c’est ce que je crois pouvoir demonstrer. Il est que les substances simples (c’est à dire qui ne sont pas des estres par aggregation) sont veritablement indivisibles, mais elles sont immaterielles, et ne sont que principes d’action. [Reference Leibniz51, p. 110]
In the same vein, in a March 11, 1706 letter to des Bosses, Leibniz wrote:
Yet you see that it should not be concluded from this that an infinitely small portion of matter (such as does not exist) must be assigned to any entelechy, even if we usually rush to such conclusions by a leap. (Leibniz as translated by Look and Rutherford in [Reference Leibniz53, p. 35])
5.3 Theory of knowledge: two types of impossibility
The terms “contradictory” and “impossible” have different meanings for Leibniz. In Leibnizian theory of knowledge, the fact that something is (1) not possible does not mean that it is (2) absolutely impossible or contradictory.
Leibniz introduces a related distinction on several occasions. Thus, in the Confessio Philosophi [Reference Leibniz38, p. 128], he refers to (1) as “impossible by accident” and contrasts it with (2) “absolute impossibility,” i.e., contradiction. He gives the examples of a species with an odd number of feet, and an immortal mindless creature, which are, according to him, harmoniae rerum adversa, i.e., “contrary to the harmony of things” (trans. Sleigh in [Reference Leibniz60, p. 57]), but not contradictory.
In his 1683 text Elementa nova matheseos universalis, Leibniz explains that some mathematical operations cannot be performed in actuality, but nonetheless one can exhibit “a construction in our characters” (in nostris characteribus [Reference Leibniz41, p. 520])—meaning that one can carry out a formal calculation, such as those with imaginary roots, regardless of whether the mathematical notions involved idealize anything in nature. Leibniz goes on to discuss in detail the cases of imaginary roots and infinitesimals. For convenience of reference, we labeled four passages [A], [B], [C], and [D]. Leibniz mentions infinitesimals in passage [C]:
[A] And some extractions of roots are such that roots are surd and they do not exist in natura rerum, and we call them imaginary, and the problem is impossible, as when our analysis shows that the requested point must be exhibited by the intersection of a specific circle and a specific straight line, in which case it may happen that this circle by no means reaches this line, and then the intersection is imaginary …
[B] There is a big difference between imaginary quantities, or those impossible by accident, and absolutely impossible ones, which involve a contradiction: e.g., when it is found that solving a problem requires that 3 be equal to 4, which is absurd.
[C] But imaginary quantities, or [quantities] impossible by accident, namely quantities that cannot be exhibited for lack of a sufficient condition, which is required for having an intersection, can be compared with infinite and infinitely small quantities, which are generated in the same way.…
[D] And it is true that calculus necessary leads to them, and people who are not sufficiently expert in such matters get entangled and think they have reached an absurdity [absurdum]. Experts know instead that this apparent impossibility [apparentem illam impossibilitatem] only means that a parallel line is traced instead of a straight line making the required angle, and this parallelism is the required angle, or quasi-angle.Footnote 58 [Reference Leibniz41, pp. 520–521]Footnote 59
Passages [B] and [C] indicate that (natural instantiations of) infinitesimals are only impossible by accident, or only apparently impossible. Therefore there are no grounds for attributing absolute impossibility or contradiction to them, or for lumping them with infinite wholes, as per RA (see Section 3.3). Infinite wholes are absolutely impossible because they are contrary to the part–whole principle (see Section 4.1), which is a necessary truth. Thus, in a 1678 letter to Elisabeth [Reference Leibniz40], Leibniz described the concept of “the number of all possible units”Footnote 60 as impossible [Reference Leibniz58, p. 238]. In his Historia et Origo [Reference Gerhardt24], he presents a derivation of the part–whole principle from the principle of identities and the definitions of whole and part:
[T]hat mighty axiom, ‘The whole is greater than its part’, could be proved by a syllogism of which the major term was a definition and the minor term an identity. (Leibniz as translated by Child in [Reference Child20, pp. 29–30])
RA seek to undercut infinitesimals on the grounds that their definition, in terms of violation of Euclid’s Definition V.4,Footnote 61 is only nominal, and claim the following:
Although this concept contains a contradiction, other subsidiary concepts contained in it may permit the derivation of true entailments. [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71, p. 406]
Does the concept of infinitesimal contain a contradiction as claimed by RA? In his 1686 comments that shed light on the Leibnizian theory of knowledge, Leibniz wrote merely that a nominal definition could harbor contradictions, not that it must do so:
Et tandis qu’on n’a qu’une definition nominale, on ne se sçauroit asseurer des consequences qu’on en tire; car si elle cachoit quelque contradiction ou impossibilité, on en pourroit tirer des conclusions opposées. [Reference Leibniz43, pp. 1568–1569]
With regard to both imaginaries and infinitesimals, Leibniz makes it clear in the 1683 passage cited above (paragraph [C]) that their natural instantiations are (at most) only conditionally or accidentally impossible, rather than contradictory. Esquisabel and Raffo Quintana examine the issue and reach the following conclusion:
[U]nlike the infinite number or the number of all numbers, for Leibniz infinitary concepts do not imply any contradiction, although they may imply paradoxical consequences. [Reference Esquisabel and Raffo Quintana22, p. 641]Footnote 62
If “the principle of non-contradiction [is] the principle of the minimal condition of intelligibility” [Reference Grosholz and Yakira28, p. 44] then one can easily perceive why infinitesimals, unlike infinite wholes, are ubiquitous in Leibniz’s mathematical oeuvre.
5.4 Infinitesimals, infinite wholes, and nominal definitions
To summarize, in a 1672/3 text Confessio Philosophi, Leibniz speaks of the distinction between accidental impossibility and absolute impossibility (equivalent to contradiction), and mentions two examples of accidental impossibility, specifying that they are contrary to the principle of the harmoniae rerum.
Furthermore, in a 1683 text Elementa nova matheseos universalis Leibniz mentions that imaginary roots do not exist in rerum natura, and contrasts imaginary quantities impossible by accident, on the one hand, and absolutely impossible entities involving a contradiction such as
![]() $3=4$
, on the other. Leibniz goes on to compare imaginary quantities (impossible by accident) to infinitely small quantities, and points out that people who are not sufficiently expert tend to confuse apparent impossibility with absurdity.
$3=4$
, on the other. Leibniz goes on to compare imaginary quantities (impossible by accident) to infinitely small quantities, and points out that people who are not sufficiently expert tend to confuse apparent impossibility with absurdity.
Finally, in a 1686 text Discours de Metaphysique Leibniz speaks of nominal definitions and warns that they might harbor contradictions (but not that they must necessarily do so). Even if the definition of an infinitesimal as violating Euclid’s Definition V.4 were nominal (as RA claim), it would follow at most that infinitesimals, possibly contrary to the principle of the harmoniae rerum, may not idealize anything in nature, a state of affairs that can be described as accidental impossibility. Meanwhile, infinite wholes are contrary to the part–whole principle (which Leibniz consistently takes to be a necessary truth), and therefore do involve an absurdity.
6 Conclusion
Bassler [Reference Bassler11], Arthur [Reference Arthur and De Risi6] and Rabouin–Arthur [Reference Rabouin and Arthur71] attempt to enlist Leibniz’s 1716 letter to Masson in support of an Ishiguro-syncategorematic reading of the Leibnizian calculus, claiming that its procedures are in keeping with the Archimedean axiom.Footnote 63 Rabouin and Arthur assimilate Leibnizian infinitesimals to infinite wholes and surmise that Leibniz viewed infinitesimals as contradictory. Such a reading rules out an interpretation whereby Leibniz viewed mathematical existence as consistency, as did Hilbert.
Contextualizing the Leibnizian comments on the calculus in the 1716 letter suggests a different reading. The letter is consistent with Leibniz’s position in 1695 [Reference Leibniz44, Reference Leibniz45] that infinitesimals violate Euclid’s Definition V.4 when compared to assignable quantities (hardly in keeping with the Archimedean axiom).Footnote 64 Like imaginary roots, infinitesimals are useful fictions that are at most accidental impossibilities that violate the principle of the harmony of things if they do not idealize anything in nature. Infinitesimals are therefore to be contrasted with infinite wholes, which are absolute impossibilities since they contradict the part–whole principle, a necessary truth in Leibnizian thought. Our conclusions are compatible with those of Esquisabel and Raffo Quintana, who similarly reject the contention by Rabouin and Arthur that Leibniz viewed infinitesimals as contradictory.
Leibniz wrote to Huygens as follows:
[Nieuwentijt] me fait une objection sur un point qui m’est commun avec Messieurs Fermat, Barrow, Newton et tous les autres, qui ont raisonné sur les grandeurs infiniment petites. [Reference Leibniz46]
Here Leibniz asserts the existence of a point in common between his reasoning with infinitesimals and that of his illustrious predecessors. To maintain the syncategorematic hypothesis, its proponents Arthur, Bassler, Levey, and Rabouin would face an unenviable alternative: either (1) claim that Leibniz was untruthful in his letter to Huygens, or (2) argue that, in Leibniz’s view, the infinitesimals of Fermat, Barrow, and Newton were similarly syncategorematic.
The 1716 letter to Masson provides no basis for doubting that Leibniz based his calculus on a special kind of small magnitudes that he viewed as mentis fictiones.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Roger Ariew and Philip Beeley for helpful suggestions, to David Schaps for expert advice on Greek spelling and Latin usage, and to Stephan Meier-Oeser for providing access to the autograph manuscripts of the letter from Leibniz to Masson relied upon in note 6.



