Studies have shown that physical health is better, levels of trust higher and violence lower in societies where income is more equally distributed. Reference Wilkinson and Pickett1 When income differences are measured at the level of whole nations or very large regions, such as the American states, the evidence for a negative effect of inequality on health is highly consistent, and multilevel studies have shown that this impact is not confounded by individual income or socio-economic status or the curvilinear relationship between income and inequality. Reference Wilkinson and Pickett1–Reference Wolfson, Kaplan, Lynch, Ross and Backlund4 Studies that have examined income inequality within smaller regions and neighbourhoods provide much less consistent evidence. For example, a study of income inequality in British regions found an increased risk in scores on the General Health Questionnaire for rich people, but not for poor people. Reference Weich, Lewis and Jenkins5 We believe that measuring income inequality within subnational or substate areas is inappropriate; deprived areas have poorer health, not because of inequalities within them, but because they are poor relative to the wider society. It seems to be the degree of social stratification across the whole society that matters for population health, which also means that ecological studies are the most appropriate study design in this field of research.
We have recently shown that other health and social problems, including mental illness, are also more common in more unequal societies. Reference Wilkinson and Pickett6–Reference Wilkinson and Pickett8 These relationships reflect human sensitivity to social relations and to the impact of income inequality on the scale of social hierarchy and status competition in a society.
The burden of mental health problems in the UK today is very high. For example, estimates suggest that one million British children – one in ten between the ages of 5 and 16 – are mentally ill and that in any secondary school with 1000 students, 50 will have severe depression, 100 will be distressed, between 10 and 20 will have obsessive–compulsive disorder and between 5 and 10 girls will have an eating disorder. Reference Donnellan9 Among UK adults, in a national survey conducted in 2000, 23% of adults had a mental illness in the previous 12 months, and 4% of adults had had more than one disorder in the previous year. 10 In the USA, one in four adults have been mentally ill in the past year and almost a quarter of these episodes were severe; over their lifetime more than half of US adults will experience mental illness.
Income inequality and rates of mental illness
But are such levels of mental illness an inevitable consequence of modern life in high-income societies? Not at all. Rates of mental illness vary substantially between rich societies. Comparable data on the prevalence of mental illness – free from cultural differences in reporting, diagnosis, categorisation and treatment have only recently become available. In 1998, the World Health Organization (WHO) established the World Mental Health Survey Consortium to estimate the prevalence of mental illness in different countries, the severity of illness and patterns of treatment. Although their methods do not entirely overcome worries about cultural differences in interpreting and responding to such questions, at least the same diagnostic interviews are used in each country.
We used these data as part of our investigation into the impact of income inequality on health and social problems; we examined the prevalence of mental illness in the WHO surveys from Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, The Netherlands, New Zealand, Spain and the USA, Reference Demyttenaere, Bruffaerts, Posada-Villa, Gasquet, Kovess and Lepine11,Reference Wells, Oakely-Brown, Scott, Mcgee, Baxter and Kokaua12 and from three national surveys using similar methodology from Australia, 13 Canada 14 and the UK. 10
Figure 1 shows the association in rich countries between income inequality and the proportion of adults who have been mentally ill in the 12 months prior to being interviewed. This is a strong relationship (r = 0.73, P<0.01), and clearly a much higher percentage of the population have a mental illness in more unequal countries; only Italy is somewhat of an outlier, with lower levels of mental illness than we might expect on the basis of its level of income inequality. Inequality is associated with threefold differences in prevalence: in Germany, Italy, Japan and Spain, fewer than 1 in 10 people have been mentally ill within the past year; in Australia, Canada, New Zealand and the UK it is more than 1 in 5 people, and in the USA more than 1 in 4.
Among the nine countries with data from WHO surveys, we can also examine subtypes of mental illness, specifically, anxiety disorders, mood disorders, impulse–control disorders and addictions, as well as a measure of severe mental illness. Anxiety disorders, impulse–control disorders and severe illness are all strongly correlated with inequality, mood disorders less so. Anxiety disorders represent the largest subgroup in all these countries, and the percentage of all mental illnesses that are anxiety disorders is itself significantly higher in more unequal countries.
As a separate test of the hypothesis that greater income inequality leads to an increase in the prevalence of mental illness, we repeated our analysis within the 50 states of the USA. State-specific estimates of mental illness are collected by the United States Behavioural Risk Factor Surveillance Study. Reference Zahran, Kobau, Moriarty, Zack, Holt and Donehoo15 We found that state-level income inequality is significantly associated with mental illness in adult women and with the percentage of children in each state with ‘moderate or severe difficulties in the area of emotions, concentration, behaviour, or getting along with others’. 16 However, we found no association for adult men. This may be related to gender differences in willingness to report mental illness in the USA, as these data are self-reported mental illness rather than being derived from diagnostic interviews. Among other US-based studies none have used diagnostic interviewers, however studies have shown that state-level Reference Fiscella and Franks17 and county-level Reference Kahn, Wise, Kennedy and Kawachi18 income inequality are associated with a significant increased risk of reporting depressive symptoms, and state-level inequality with self-reported mental health. Reference Shi, Starfield, Politzer and Regan19 Only one study found no effect for depressive symptoms. Reference Henderson, Liu, Diez Roux, Link and Hasin20
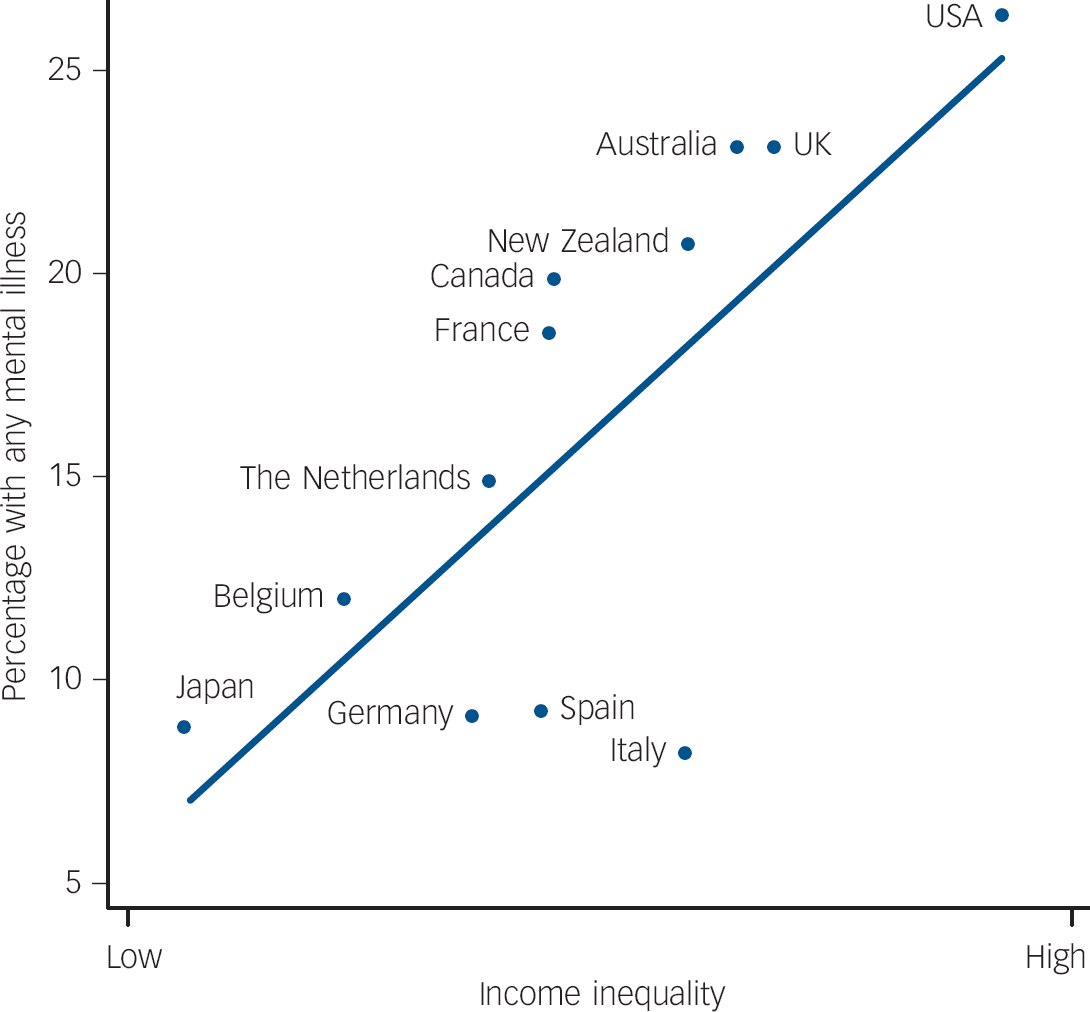
Fig. 1 More people have mental illnesses in more unequal countries.
Why do more people tend to have mental health problems in more unequal places? Psychologist Oliver James uses an analogy with infectious disease to explain the link. What James terms the ‘affluenza’ virus is a ‘set of values which increase our vulnerability to emotional distress’, and he argues that these values are more common in affluent societies. Reference James21 They entail placing a high value on acquiring money and possessions, looking good in the eyes of others and wanting to be famous. He goes on to argue that these values increase the risk of depression, anxiety, substance misuse and personality disorder. Philosopher Alain de Botton claims that our anxiety about our social status is ‘a worry so pernicious as to be capable of ruining extended stretches of our lives’. Reference de Botton22 When we fail to maintain our position in the social hierarchy we are ‘condemned to consider the successful with bitterness and ourselves with shame’. Economist Robert Frank calls the same phenomenon ‘luxury fever’. Reference Frank23 As inequality increases and the super rich at the top spend more and more on luxury goods, the desire for such things cascades down the income scale and the rest of us struggle to compete and keep up. Advertisers play on this, making us dissatisfied with what we have, and encouraging invidious social comparisons – more unequal societies spend more in advertising. Reference Wilkinson and Pickett6 Economist Richard Layard describes us as having an ‘addiction to income’ – the more we have, the more we feel we need and the more time we spend on striving for material wealth and possessions, at the expense of our family life, relationships and quality of life. Reference Layard24
Although not all these authors make the link specifically with income inequality, it is not surprising that the tendencies they describe are stronger in more unequal societies. Our impression is that greater inequality increases status competition and status insecurity. Internationally and among the 50 states of the USA, income inequality is strongly related to low levels of trust, to weaker community life and to increased violence. Mental health is profoundly influenced by the quality and sufficiency of social relationships and all these measures suggest that both are harmed by inequality.
Inequality and drug misuse
We have also found that the use of illegal drugs, such as cocaine, marijuana and heroin, is more common in more unequal societies. The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime publishes a World Drug report, 25 which contains separate data on the use of opiates, cocaine, cannabis, ecstasy and amphetamines. Combining these into a single index (equally weighted, using z-scores), we found a strong tendency for drug use to be more common in more unequal countries (r = 0.63, P<0.01). Within the 50 American states, there is also a tendency for addiction to illegal drugs and deaths from drug overdose to be higher in the more unequal states. 26
Although we must be cautious in extrapolating to humans, animal studies show that low social status profoundly affects neurological systems. Researchers at Wake Forest School of Medicine housed 20 macaque monkeys in individual cages. Reference Morgan, Grant, Gage, Mach, Kaplan and Prioleau27 They next housed the animals in groups of four and observed the social hierarchies that developed in each group, noting which animals were dominant and which subordinate. They scanned the monkey's brains before and after they were put into groups. Next, they taught the monkeys that they could administer cocaine to themselves by pressing a lever – they could take as much or as little as they liked. Monkeys that had become dominant had higher levels of dopamine activity than they had exhibited before becoming dominant, whereas monkeys that became subordinate when housed in groups showed no changes in dopamine, and the dominant monkeys took significantly less cocaine than the subordinate monkeys. The subordinate monkeys medicated themselves against the impact of their low social status. This kind of experimental animal evidence adds plausibility to our inference that inequality is causally related to mental illness.
As well as trust, social capital, violence, mental illness and drug misuse, income inequality is also linked to physical morbidity and mortality, to low social mobility and poor educational achievement, to bullying in schools, and rates of imprisonment, teenage births and the status of women in society. As inequality grows, so do the social distances and distinctions between us, and so does the potential for the pain of low social status, stigma and shame. Reference Friedli28 To a great extent, we see ourselves through each other's eyes and, in more unequal societies more of us find ourselves wanting in those reflections.
But what are the clinical and policy implications of our findings? The most recent review of health inequalities in England calls attention to the need to tackle the individual causes of poor health across the life course, and acknowledges the social gradient in health, whereby even the health of those close to the top of society is worse than those at the very top. 29 But the Marmot Review, although it calls for a minimum income for healthy living, fails to deal with the real implications of research on income inequality and health and social problems – we have to constrain runaway salaries and the bonus culture as well as raising the incomes of the poorest.
Implications
The clinical implications of our results are relatively straightforward. If people suffer mental distress as a consequence of low social status, stigma and shame, then their treatment must emphasise their human worth and be conducted within a respectful relationship. The policy implications are more diverse and numerous, but fall into two camps. To make the UK a more equal and consequently a healthier and happier society, we must redistribute income through taxes and benefits, find ways to reduce income differences in market incomes before taxes, or both. Research suggests that the key to the latter strategy is strong trade unions. But ways of reducing income differences before taxes might also include employee representation on corporate remuneration boards, greater transparency in salary ratios in both the public and private sector, and all forms of institutional democracy – cooperatives, mutual societies, employee-owned companies, etc. If we want to commit the UK to as rapid a reversal of inequality as the massive rise experienced during the 1980s, then we need to encourage all mechanisms that help to reduce income differences. As professionals dedicated to improving the health of the population, our role in calling for greater equality is as important in the 21st century as the efforts of the great public health reformers of the Victorian era who called for improvements in sanitation, housing, nutrition and working conditions.
To end on an optimistic note, it is worth remembering that the UK has not always been among the most unequal of the rich, market democracies. Our current inequality, and our unacceptably high prevalence of mental and physical illness, as well as other health and social problems, is not a fixed characteristic of British culture – we used to be more equal, and we could be so again.




eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.