Article contents
Inductive Logic Programming in Databases: From Datalog to 
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 May 2010
Abstract
In this paper we address an issue that has been brought to the attention of the database community with the advent of the Semantic Web, i.e., the issue of how ontologies (and semantics conveyed by them) can help solving typical database problems, through a better understanding of Knowledge Representation (KR) aspects related to databases. In particular, we investigate this issue from the ILP perspective by considering two database problems, (i) the definition of views and (ii) the definition of constraints, for a database whose schema is represented also by means of an ontology. Both can be reformulated as ILP problems and can benefit from the expressive and deductive power of the KR framework 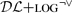 . We illustrate the application scenarios by means of examples.
. We illustrate the application scenarios by means of examples.
Keywords
Information
- Type
- Regular Papers
- Information
- Theory and Practice of Logic Programming , Volume 10 , Special Issue 3: Logic Programming in Databases: from Datalog to Semantic-Web Rules , May 2010 , pp. 331 - 359
- Copyright
- Copyright © Cambridge University Press 2010
References
- 5
- Cited by

