Introduction
Cereal rye is commonly grown as a winter cover crop because of its cold hardiness, drought tolerance, and ability to grow well on marginal soils (Bushuk Reference Bushuk1976). It has additional uses as a pasture forage, hay, and grain, which is fed to livestock or consumed by humans as food and alcoholic beverages (Bushuk Reference Bushuk1976; Hales et al. Reference Hales, Whitley, Horn, Childs and Goad2007; Shee et al. Reference Shee, Lemenager and Schoonmaker2016). Cereal rye serves multiple purposes across the United States as a late-wintering forage for cattle or as a summer cover crop used to mitigate erosion, moisture loss, and weed interference in the subsequent cash-generating crop (Bunchek et al. Reference Bunchek, Wallace, Curran, Mortensen, VanGessel and Scott2020; Li et al. Reference Li, Allen, Hou, Chen and Brown2013; Wiggins et al. Reference Wiggins, Hayes and Steckel2016). A study conducted in Arkansas indicated that cereal rye fed to cattle had greater nutritional benefits compared to oat (Avena sativa L.) and triticale (×Triticosecale Wittm. ex A. Camus [Secale × Triticum]), resulting in greater average daily gain and weight gain per area (Beck et al. Reference Beck, Stewart, Phillips, Watkins and Gunter2007). Although wheat hectarage exceeded cereal rye nationally in 2018 (19.4 and 0.8 million hectares planted, respectively), Georgia growers planted a comparable number of hectares of both crops (76,923 to 80,972 ha) (USDA 2020). Furthermore, Georgia was second in the nation for cereal rye planted and harvested at 76,923 ha and 6,073 ha, respectively, with a value of US$2.8 million (USDA 2020).
Weed management in cereal rye is challenging because of limited herbicide and tillage options. Although preplant tillage can be an effective approach to removing weeds at planting for growers not using conservation tillage production systems, weed control is needed for the entire season (Taylor and Everman Reference Taylor and Everman2015). In-crop tillage options are limited and often not practical, as cereal rye seed is often broadcast spread or drilled in rows spaced 19 cm apart (Buntin and Cunfer Reference Buntin and Cunfer2017; Tautges et al. Reference Tautges, Goldberger and Burke2016). Thus the success of in-season weed control in both conservation and conventional tillage production systems is highly dependent on herbicides. Registered herbicides are limited to 2,4-D, MCPA, bromoxynil, bromoxynil + pyrasulfotole, and prosulfuron (Marshall Reference Marshall2017). Although prosulfuron is registered, a 10-mo rotational restriction to cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.), peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.), and soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] limits its use, as these crops are often planted immediately after cereal rye harvest (Anonymous 2019c).
Italian ryegrass [Lolium perenne L. ssp. multiflorum (Lam.) Husnot], henbit (Lamium amplexicaule L.), chickweeds (Stellaria spp.), and annual bluegrass (Poa annua L.) are common and troublesome weeds that often escape treatment by registered herbicides (Anonymous 2015, 2018a, 2018b, 2019b; Buntin and Cunfer Reference Buntin and Cunfer2017; Webster Reference Webster2012). Italian ryegrass is the most problematic weed infesting Georgia small grains, including cereal rye. Fast et al. (Reference Fast, Medlin and Murray2009) estimated wheat yield loss at 16% in the presence of 30 Italian ryegrass plants m−2. This resulted in a reduction in grade, an increase in dockage, and reduced price for wheat. Other studies concluded that Italian ryegrass uptake of nitrate and potassium was twice that of wheat and that wheat yield decreased 4.2% for every 10 Italian ryegrass plants m−2. Henbit densities of 82 and 155 plants m−2 reduced wheat yields 13% and 38%, respectively, as a result of reduced tiller and spike densities (Conley and Bradley Reference Conley and Bradley2005). Common chickweed can be extremely competitive for both space and nutrients; common chickweed interference can reduce barley yield up to 80% (Mann and Barnes Reference Mann and Barnes1950).
Wheat has excellent tolerance to mesosulfuron-methyl, pinoxaden, and pyroxsulam (Ellis et al. Reference Ellis, Steckel, Main, de Melo, West and Mueller2010; Grey et al. Reference Grey, Braxton and Richburg2012a,b; Howatt Reference Howatt2006). Additionally, these herbicides provide excellent control of susceptible populations of Italian ryegrass (Ellis et al. Reference Ellis, Steckel, Main, de Melo, West and Mueller2010; Grey et al. Reference Grey, Cutts, Sosnoskie and Culpepper2012b; Howatt Reference Howatt2006). Not only do mesosulfuron-methyl and pyroxsulam control Italian ryegrass and annual bluegrass but they also effectively control other weeds, including henbit and chickweed, with minimal restrictions to commonly planted rotational crops (Anonymous 2012, 2020; Grey et al. Reference Grey, Braxton and Richburg2012a, Reference Grey, Cutts, Sosnoskie and Culpepper2012b). Thifensulfuron-methyl + tribenuron-methyl and halauxifen-methyl + florasulam are also safe for use in wheat; they provide effective control of henbit and chickweed (Anonymous 2018c, 2019a; Jackson et al. Reference Jackson, Paterson, Fairfax and Ouse2018; Lee et al. Reference Lee, Wu and Gast2015; Soltani et al. Reference Soltani, Shrophshire and Sikkema2006). These two herbicides also avoid rotational concerns documented with prosulfuron (Anonymous 2018c, 2019a).
In areas where Italian ryegrass is resistant to Group 1 and 2 POST-applied herbicides, pyroxasulfone and flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone have become viable management tools in wheat and could prove beneficial for cereal rye production. Pyroxasulfone applied shortly after planting has become a major component of ryegrass management with minimal impacts on wheat in both the United States (Hulting et al. Reference Hulting, Dauer, Hinds-Cook, Curtis, Koepke-Hill and Mallory-Smith2014) and Australia (Boutsalis et al. Reference Boutsalis, Gill and Preston2014). The addition of flumioxazin to pyroxasulfone incorporates an additional mechanism of action that broadens the weed control spectrum compared to pyroxasulfone alone, with minimal injury to wheat (Crow et al. Reference Crow, Steckel, Hayes and Mueller2015; Randhawa et al. Reference Randhawa, Westwood, Cahoon and Flessner2018).
Previous studies evaluating cereal rye tolerance to tribenuron demonstrated minimal injury, whereas tolerance to mesosulfuron was variable (MacRae et al. Reference MacRae, Culpepper and Grey2007). There is little information on the tolerance of cereal rye to other wheat herbicides. Therefore the objectives of this study were to determine rye tolerance to commonly used wheat herbicides and to generate data needed for potential registrations through the IR-4 program for minor crop registrations.
Materials and Methods
A study consisting of five experiments was conducted during 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020 at three locations to evaluate the tolerance of cereal rye to eight commonly used wheat herbicides. One on-farm field study was conducted near Chula, GA (31.53’73°N, 83.64’75°W), in 2018 to 2019. In 2019 to 2020, studies at two locations, with two different planting dates at each, were conducted at the Ponder Research Farm near Ty Ty, GA (31.30′18°N, 83.39′03°W), and the Sunbelt Ag Expo near Moultrie, GA (31.14′15°N, 83.71′64°W). Location characteristics, including soil texture, organic matter, soil pH, planting dates, and herbicide application dates, are presented in Table 1. Cereal rye (cultivar ‘Wrens Abruzzi’) was planted with a grain drill (Great Plains Manufacturing, Salina, KS, USA) on conventionally tilled soil in rows spaced 19 cm apart; seeds were drilled 1.25 cm deep at a rate of 100 kg ha−1. Tillage consisted of disking in previous crop debris and field cultivating prior to planting. Production practices were consistent with recommended practices by the University of Georgia Cooperative Extension Service (Buntin and Cunfer Reference Buntin and Cunfer2017). Experiments were maintained weed-free using tillage prior to planting and labeled applications of MCPA or 2,4-D applied to the entire trial area for broadleaf weed control at least 2 wk after postemergence (POST) treatment applications. Locations void of Italian ryegrass were selected to avoid the confounding effect of weed interference.
Table 1. Location, year, soil characteristics, planting dates, and herbicide application dates for five experiments conducted in 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020 in Georgia.
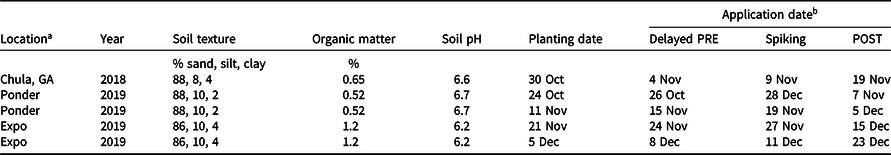
a The Chula, GA, location was conducted on-farm. Ponder locations were conducted at the Ponder Research Farm near Ty Ty, GA, and Expo locations were conducted at the Sunbelt Ag Expo near Moultrie, GA.
b Delayed PRE, spiking, and POST applications were made at the Zadoks 10, 11, and 13 growth stages, respectively.
Treatments were arranged in a randomized complete block design with a factorial treatment arrangement of eight herbicide treatments and two rates of each herbicide treatment. Two nontreated controls were included for comparison, resulting in a total of 18 treatments replicated eight times in 2018 to 2019 and four times at each location in 2019 to 2020. Following label recommendations for use in wheat, three different application timings were implemented depending on herbicide applied: (1) delayed preemergence (PRE) applications when at least 80% of the cereal rye was at Zadoks (Z) 10 stage of growth with a shoot at least 1 cm in length for pyroxasulfone, (2) spike applications with cereal rye 2 to 5 cm in height in the Z 11 stage of growth for pyroxasulfone + flumioxazin, and (3) POST applications when rye was 10 to 13 cm in height with three true leaves in Z 13 growth stage for all other herbicides. Herbicides evaluated, rates applied, and application timings for each herbicide are presented in Table 2. All herbicide applications were made using a CO2-pressurized backpack sprayer equipped with 110012 AIXR nozzles (TeeJet® Technologies, Wheaton, IL, USA). The spray boom was 138 cm long with a nozzle spacing of 46 cm and was calibrated to deliver 140 L ha−1.
Table 2. Herbicide active ingredient, trade name, manufacturer, application rate, and timing to cereal rye for five experiments conducted in 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020 in Georgia. a, b, c, d, e, f
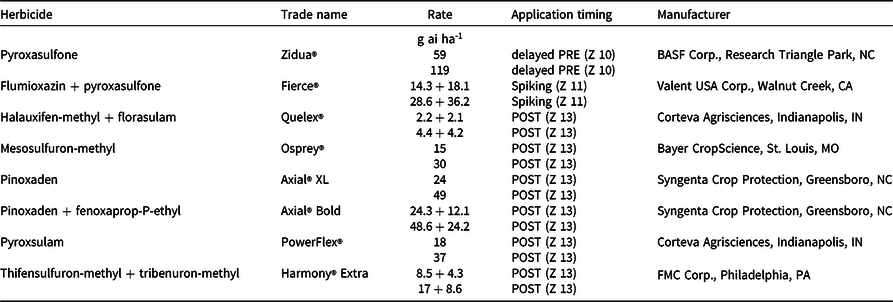
a Delayed PRE, spiking, and POST applications were made at the Zadoks 10, 11, and 13 growth stages, respectively.
b Abbreviation: Z, Zadoks.
c Applications of Quelex included 1% v/v of COC for the lower rate, with 2% v/v utilized with the higher rate.
d Applications of Osprey included 2.34 L ha−1 of both NIS and UAN (28-0-0) with the lower rate, with 4.68 L ha−1 NIS and UAN utilized with the high rate.
e Applications of PowerFlex included 2.34 L ha−1 of COC with the lower rate, with 4.68 L ha−1 utilized with the higher rate.
f Applications of Harmony Extra included 2.34 L ha−1 of NIS with the lower rate, with 4.68 L ha−1 utilized with the higher rate.
To quantify the tolerance of cereal rye to the herbicides evaluated, cereal rye injury was estimated visually (0% to 100%), and cereal rye heights, density, and yield were recorded. All response variables were split into two groups: early-season residual herbicide applications (pyroxasulfone and flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone) and POST herbicide applications. Cereal rye injury, heights, and density were evaluated beginning approximately 17 d after Z 10 applications, 11 d after Z 11 applications, and 10 d after Z 13 applications. Cereal rye injury and heights were recorded for all treatments weekly for 5 additional weeks, with injury evaluated again at harvest. Cereal rye height was quantified by measuring 10 random plants from rows 2 and 6 on the planted bed, resulting in 20 plants measured per plot. Average heights per plot were calculated prior to statistical analysis. Cereal rye density was measured at the first injury evaluation for each application timing and was quantified by counting emerged plants from a 1.5-m section of rows 2 and 6 on the planted bed. At the end of the 2019 to 2020 season, a plot combine (ALMACO, Nevada, IA, USA) was used to collect grain yield from entire plots. Yield was not collected in 2018 to 2019 due to high winds and rain leading to lodging and rotting prior to harvest. Cereal rye yields were adjusted to 14% moisture for statistical analysis.
For statistical analysis, data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) using proc glimmix in SAS (version 9.4, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) to determine the impact of herbicide and application rate on cereal rye injury, heights, density, and grain yield. To compare all herbicides and initially determine suitability for use in cereal rye, maximum injury levels were compared among herbicides regardless of application timing and location. Further data analysis with respect to cereal rye injury, heights, and density was separated into Z 10/11 and Z 13 applications. For Z 10/11 applications, all response variables were separated by location due to a significant site-year × treatment interaction resulting from the time of activating rainfall (Table 3). For Z 13 applications, a significant site-year × treatment interaction was not present; therefore all injury, height, and density data are combined across locations. Cereal rye grain yield was not influenced by the interaction of year × treatment and are combined across harvested locations. Cereal rye injury, heights, density, and grain yield were set as the response variables for all herbicide applications. For all variables, replication was included in the model as a random factor. For Z 13 applications and grain yield, location was also included in the model as a random factor. All P-values for tests of differences between least squares means were compared and adjusted using the Tukey–Kramer method (α = 0.05). The Tukey–Kramer method was chosen because it reduces Type I error compared to Fisher’s protected least significant difference when more than three means are compared to each other, and it can also be used for balanced designs (Blythe Reference Blythe2012; Westfall et al. Reference Westfall, Tobias and Wolfinger2011).
Table 3. Rainfall data accumulated for the first 20 d after applying early-season residual herbicides, by location. a, b, c

a Cumulative rainfall for indicated days after application.
b Abbreviations: DAA, days after application.
c The 2018 study was conducted on-farm near Chula, GA. Studies at the Ponder Research Farm near Ty Ty, GA, and the Sunbelt Ag Expo near Moultrie, GA, were conducted during 2019, with two different planting dates at each location.
Results and Discussion
All Herbicides
To determine the suitability of the herbicides evaluated in this study for use in cereal rye, an analysis was conducted across application timing and location to determine the impact of herbicide and rate when cereal rye injury was maximized. This would equate to 17 DAT for applications at Z 10 (pyroxasulfone), 11 DAT for applications at Z 11 (flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone), and 10 DAT for applications at Z 13 (all POST herbicides). There was a significant herbicide ×rate interaction for cereal rye injury. Generally, rate did not increase injury when POST herbicides were applied at Z 13, but it was more influential in cereal rye response when residual herbicides were applied at Z 10/11. Therefore further analysis is necessary to describe the response of cereal rye to the residual (Z 10/11) and POST (Z 13) herbicides.
Residual Herbicides Applied at Z 10/11
At each site-year, there was a herbicide × rate interaction for cereal rye injury, so the simple effects are presented in Table 4. Both pyroxasulfone rates applied at Z 10 caused 27% to 52% cereal rye injury at two of five locations 17 DAT. Numerically higher cereal rye injury occurred at the two Ponder sites, which both received more than 1 cm of rainfall within 2 d of application (Table 3). For the three other locations where less injury (0% to 16%) was initially observed, rainfall during this same period was less than 0.5 cm. Crop injury is often elevated from soil-applied herbicides due to increased soil moisture along with decreased soil temperatures (Boldt and Barrett Reference Boldt and Barrett1989). At 41 DAT, injury at all site-years receiving more than 4 cm of rainfall within 20 DAT ranged from 13% to 44%, with 25% to 44% injury at the two site-years with the greatest initial rainfall.
Table 4. Cereal rye injury in response to pyroxasulfone applied at Zadoks (Z) 10 or flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone applied at Z 11 from five experiments conducted in 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020 in Georgia. a, b
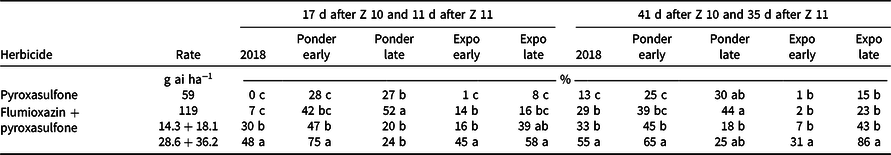
a Means followed by the same letter within a column do not differ significantly (P ≥ 0.05).
b The 2018 study was conducted on-farm near Chula, GA. Studies at the Ponder Research Farm near Ty Ty, GA, and the Sunbelt Ag Expo near Moultrie, GA, were conducted during 2019, with two different planting dates at each location.
Pyroxasulfone reduced cereal rye height 19% to 37% at the two site-years with the greatest early-season injury (Table 5). Pyroxasulfone reduced cereal rye density 27% to 37% at these site-years, while the low rate reduced cereal rye density 26% at one site-year (Table 6). At the other three site-years, pyroxasulfone did not reduce cereal rye density; pyroxasulfone (2X rate) reduced height 11% at one site-year (Tables 5 and 6). Cereal rye height at 41 DAT followed similar trends to early-season measurements; however, by 70 DAT, differences in height were no longer detectable (data not shown).
Table 5. Cereal rye height as influenced by pyroxasulfone applied at Zadoks (Z) 10 or flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone applied at Z 11 from five experiments conducted in 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020 in Georgia. a, b, c, d

a Heights were measured 17 d after delayed PRE applications and 11 d after spike applications. Heights were quantified by measuring 10 plants from rows 2 and 6 on the planted bed, resulting in 20 total plants measured per plot.
b Abbreviation: NTC, nontreated control.
c Means followed by the same letter within a column do not differ significantly (P ≥ 0.05).
d The 2018 study was conducted on-farm near Chula, GA. Studies at the Ponder Research Farm near Ty Ty, GA, and the Sunbelt Ag Expo near Moultrie, GA, were conducted during 2019, with two different planting dates at each location.
Table 6. Cereal rye density as influenced by pyroxasulfone applied at Zadoks (Z) 10 or flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone applied at Z 11 from five experiments conducted in 2018 to 2019 and 2019 to 2020 in Georgia. a, b, c, d

a Stand was quantified 11 d after flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone applications by counting emerged plants from a 1.5-m section of rows 2 and 6 on the planted bed. Stand was then converted to a percentage of the nontreated prior to statistical analysis.
b Abbreviation: NTC, nontreated control.
c Means followed by the same letter within a column do not differ significantly (P ≥ 0.05).
d The 2018 study was conducted on-farm near Chula, GA. Studies at the Ponder Research Farm near Ty Ty, GA, and the Sunbelt Ag Expo near Moultrie, GA, were conducted during 2019, with two different planting dates at each location.
Previous research has demonstrated that pyroxasulfone applied preplant (Price et al. Reference Price, Li and Price2020) and preemergence (Boutsalis et al. Reference Boutsalis, Gill and Preston2014; Palhano et al. Reference Palhano, Norsworthy and Barber2018) reduced wheat density, but labels support a delayed PRE application to minimize injury (Anonymous 2017). In the present study, cereal rye injury exceeded the level of safety required for labeling. Cereal rye frequently emerges more slowly compared to wheat; thus it may have been more sensitive to a delayed PRE application of pyroxasulfone (Clark Reference Clark2007). Although injury was significant at four of five site-years during the first 5 wk after application, cereal rye recovered to less than 10% injury across site-years by 130 DAT with no effect on yield (data not reported).
Flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone applied at Z 11 caused greater cereal rye injury than pyroxasulfone applied at Z 10 at two of five site-years (Table 4). Similar to pyroxasulfone, greater injury levels occurred at the locations where rainfall occurred more closely to application (Table 3). Flumioxazin applied prior to wheat planting caused up to 30% wheat injury and reduced biomass at tillering (Clay et al. Reference Clay, Welch, Dale, Refsell, Odle and Pawlak2010; Crow et al. Reference Crow, Steckel, Hayes and Mueller2015). Cereal injury from mixtures of flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone are likely to be greater than pyroxasulfone alone even with delayed application timings. Flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone (1X rate) caused ≥18% cereal rye injury at four of five site-years 35 DAT (Table 4).
Flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone (1X rate) reduced cereal rye height (14% to 35%) at three site-years; the 2X rate reduced cereal rye height 9% to 53% at all site-years at 11 DAT compared to the nontreated control (Table 5). Additionally, cereal rye density was reduced at two and four site years with the 1X and 2X rate, respectively (Table 6). Cereal rye height 5 wk after application followed trends seen earlier in the season; however, by 65 DAT, height differences were no longer detectable (data not shown). Similar to pyroxasulfone, cereal rye injury was transient, with less than 15% cereal rye injury noted across locations by 120 DAT (data not reported). Interestingly, yield was not influenced by flumioxazin + pyroxasulfone, even with significant decrease in density. The ability of cereal rye to recover from early-season herbicide injury has been reported (Crow et al. Reference Crow, Steckel, Hayes and Mueller2015). Some researchers noted that wheat stand losses up to 60% had no influence on yield at two out of three site-years (Conley and Bradley Reference Conley and Bradley2005).
POST Herbicides Applied at Z 13
There was a herbicide × rate interaction for cereal rye injury and height, so the main effects are presented in Table 7. There was no effect of herbicide on cereal rye density (data not reported). Halauxifen-methyl + florasulam, pyroxsulam, and thifensulfuron-methyl + tribenuron-methyl, when averaged over rate, caused ≤13% throughout the season (Table 7). At 10 DAT, the aforementioned herbicides, averaged over rate, reduced cereal rye height 10% compared to the nontreated control. However, no height differences occurred by 31 DAT. Pinoxaden and pinoxaden + fenoxaprop-P-ethyl caused 29% and 18% cereal rye injury, respectively, and reduced cereal rye height 19% to 22% at 10 DAT (Table 7). Mesosulfuron-methyl, the most injurious of the POST herbicides evaluated, caused 48% and 40% cereal rye injury and reduced cereal rye height 26% and 10% at 10 and 31 DAT, respectively. Other studies have reported that mesosulfuron-methyl caused 11% more cereal rye injury (36%) compared to wheat at 14 DAT (Grey et al. Reference Grey, Cutts, Sosnoskie and Culpepper2012b; MacRae et al. Reference MacRae, Culpepper and Grey2007). Similar to Z 10 and 11 applications, rye recovered from POST herbicide applications with 10% or less injury observed by 120 DAT (data not reported). There was no impact of the POST herbicides evaluated on cereal rye grain yield (346 to 463 kg ha−1) (data not reported). Previous studies reported similar results, with significant early-season injury followed by rapid cereal rye or wheat recovery with no impact on yield (Crow et al. Reference Crow, Steckel, Hayes and Mueller2015; Grey et al. Reference Grey, Cutts, Sosnoskie and Culpepper2012b; MacRae et al. Reference MacRae, Culpepper and Grey2007; Robinson et al. Reference Robinson, Letarte, Cowbrough, Sikkema and Tardif2015).
Table 7. Influence of postemergence herbicides on cereal rye injury and heights when applied at Zadoks 13. a, b, c, d
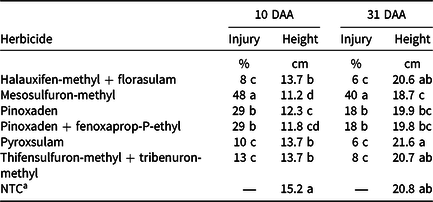
a Data are combined across herbicide rate and five site-years.
b Abbreviations: DAA, days after application; NTC, nontreated control.
c Means followed by the same letter within a column do not differ significantly (P ≥ 0.05).
d Heights were quantified by measuring 10 plants from rows 2 and 6 on the planted bed, resulting in 20 total plants measured per plot.
Cereal rye injury from pyroxasulfone applied at Z 10, pyroxasulfone + flumioxazin applied at Z 11, mesosulfuron-methyl, pinoxaden, and pinoxaden + fenoxaprop-P-ethyl applied at Z 13 exceeded the level of safety to obtain a registration for rates and application methods evaluated in this study. This would result in hesitancy from registrants due to liability issues (Fennimore and Doohan Reference Fennimore and Doohan2008). In contrast, halauxifen-methyl + florasulam, pyroxsulam, and thifensulfuron-methyl + tribenuron-methyl applied at Z 13 caused less than 15% cereal rye injury at the 2X rate with no effect on cereal rye density or yield. These herbicides at the 2X rate reduced cereal rye heights 11% at 10 DAT with rapid recovery; additionally, cereal rye height was not influenced with 1X rates of these herbicides. These herbicides have an acceptable margin of crop safety in cereal rye and could potentially control henbit, chickweed, wild radish (Raphanus raphanistrum L.), cutleaf eveningprimrose (Oenothera laciniata Hill), and nonresistant populations of Italian ryegrass (Anonymous 2018c; Culpepper and Vance Reference Culpepper and Vance2016; Ellis et al. Reference Ellis, Steckel, Main, de Melo, West and Mueller2010; Geier et al. Reference Geier, Stahlman, Peterson and Claassen2011; Lee et al. Reference Lee, Wu and Gast2015; Rauch and Campbell Reference Rauch and Campbell2019). Further research is needed to refine the application timings of the herbicides studied here, as well as the use of tank mixtures to broaden the weed control spectrum.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Tim Richards and Jenna Vance for their technical assistance. Additionally, this research would not have been possible without the hard work and dedication of the student workers at the time these studies were conducted. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.










