Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 March 2024
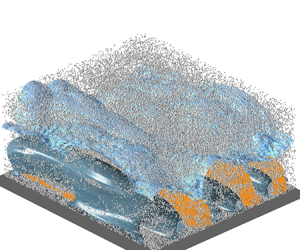
A spatially developing flat-plate boundary layer free from and two-way coupled with inertial solid particles is simulated to investigate the interaction between particles and the turbulent/non-turbulent interface. Particle Stokes numbers based on the outer scale are  $St=2$ (low), 11 (moderate) and 53 (high). The Eulerian–Lagrangian point-particle approach is deployed for the simulation of particle-laden flow. The outer edge of the turbulent/non-turbulent interface layer is detected as an iso-surface of vorticity magnitude. Results show that the particles tend to accumulate below the interface due to the centrifugal effect of large-scale vortices in the outer region of wall turbulence and the combined barrier effect of potential flow. Consequently, the conditionally averaged fluid velocity and vorticity vary more significantly across the interface through momentum exchange and the feedback of force in the enstrophy transport. The large-scale structures in the outer layer of turbulence become smoother and less inclined in particle-laden flow due to the modulation of turbulence by the inertial particles. As a result, the geometric features of the interface layer are changed, namely, the spatial undulation increases, the fractal dimension decreases and the thickness becomes thinner in particle-laden flow as compared with unladen case. These effects become more pronounced as particle inertia increases.
$St=2$ (low), 11 (moderate) and 53 (high). The Eulerian–Lagrangian point-particle approach is deployed for the simulation of particle-laden flow. The outer edge of the turbulent/non-turbulent interface layer is detected as an iso-surface of vorticity magnitude. Results show that the particles tend to accumulate below the interface due to the centrifugal effect of large-scale vortices in the outer region of wall turbulence and the combined barrier effect of potential flow. Consequently, the conditionally averaged fluid velocity and vorticity vary more significantly across the interface through momentum exchange and the feedback of force in the enstrophy transport. The large-scale structures in the outer layer of turbulence become smoother and less inclined in particle-laden flow due to the modulation of turbulence by the inertial particles. As a result, the geometric features of the interface layer are changed, namely, the spatial undulation increases, the fractal dimension decreases and the thickness becomes thinner in particle-laden flow as compared with unladen case. These effects become more pronounced as particle inertia increases.
Q. Wei, P. Wang and X. Zheng contributed equally to this work.
To send this article to your Kindle, first ensure no-reply@cambridge.org is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about sending to your Kindle. Find out more about saving to your Kindle.
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service.
To save this article to your Dropbox account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Dropbox account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox.
To save this article to your Google Drive account, please select one or more formats and confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you used this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your Google Drive account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive.