Selection from hunting and human persecution can potentially affect heritable behavioural traits (Allendorf & Hard, Reference Allendorf and Hard2009), including some characters associated with the shy–bold continuum of behaviour (Wilson et al., Reference Wilson, Clark, Coleman and Dearstyne1994) that could be related to attacks of large carnivores on people (Penteriani et al., Reference Penteriani, Delgado, Pinchera, Naves, Fernández-Gil and Kojola2016). In North America and Eurasia, many of these attacks are by the brown bear Ursus arctos (Penteriani et al., Reference Penteriani, Delgado, Pinchera, Naves, Fernández-Gil and Kojola2016; Bombieri et al., Reference Bombieri, Naves, Penteriani, Selva, Fernández-Gil and López-Bao2019) and, although rare, they can undermine conservation efforts (Herrero, Reference Herrero2002; Penteriani et al., Reference Penteriani, Delgado, Pinchera, Naves, Fernández-Gil and Kojola2016). Studies of attacks by brown bears on people have focused mainly on the characteristics of the bears and the type and behaviour of the people involved (Bombieri et al., Reference Bombieri, Naves, Penteriani, Selva, Fernández-Gil and López-Bao2019), but geographical patterns of bear attacks have rarely been assessed. In their global study of brown bear attacks on people, Bombieri et al. (Reference Bombieri, Naves, Penteriani, Selva, Fernández-Gil and López-Bao2019) did not find a significant difference in the number of attacks between continents or between countries with different hunting practices. For the Cantabrian Mountains of Spain, some data on attacks by bears were provided by Naves et al. (Reference Naves, Fernández, Revilla and Penteriani2017), but the lack of definition of a bear attack prevents full interpretation of these data.
As a result of human persecution, the brown bear population in the Cantabrian Mountains became separated into western and eastern subpopulations in the early 20th century, and the two subpopulations have been genetically disconnected for most of the time since then (Pérez et al., Reference Pérez, Vázquez, Naves, Fernández, Corao and Albornoz2009). Although effective protection from the end of the 20th century has promoted an increase of the population and the migration of males between the two subpopulations (Gonzalez et al., Reference Gonzalez, Blanco, Ballesteros, Alcaraz, Palomero and Doadrio2016), gene flow was detected for the first time only in 2008 (Pérez et al., Reference Pérez, Naves, Vázquez, Seijas, Corao and Albornoz2010). Here, we study the geographical patterns of attacks by brown bears on people in the Cantabrian Mountains and discuss the factors that may explain the concentration of attacks in the eastern subpopulation, where there are fewer bears.
The ranges of the western (5,500 km2) and eastern subpopulations (3,100 km2) are separated by 90 km of disturbed habitat devoid of breeding females (Fig. 1), and the number of bears in the western subpopulation is almost six times greater (Gonzalez et al., Reference Gonzalez, Blanco, Ballesteros, Alcaraz, Palomero and Doadrio2016). During 2009–2018 a mean of 28.1 and 4.9 females with cubs have been detected annually in the western and the eastern subpopulations, respectively (Fundación Oso Pardo, 2020). The main economic activity in the Cantabrian bear range is cattle farming, although tourism is becoming more prominent; in 2017 human population densities were 11.0 and 7.1 inhabitants/km2 in the areas of the western and eastern subpopulations, respectively (National Statistics Institute, 2017).

Fig. 1 The ranges of the western and eastern subpopulations of the brown bear Ursus arctos in the Cantabrian Mountains, Spain, and the location of recorded attacks of bears on people during 1989–2019.
During 1989–2019 we compiled details of all known attacks by bears on people in the Cantabrian Mountains, i.e. incidents in which a bear made intentional physical contact with a person, resulting in injury to the person (Smith & Herrero, Reference Smith and Herrero2018). We compiled information on attack cases from a wide network of wardens, hunters and naturalists in the Cantabrian Mountains with whom we have been in contact since 1989, when we began ongoing annual monitoring of females with cubs (Gonzalez et al., Reference Gonzalez, Blanco, Ballesteros, Alcaraz, Palomero and Doadrio2016). Cases involving serious injury were widely featured in the media, but those resulting in minor injuries would otherwise have gone undetected. For every attack we spoke with the people directly affected (except in one case, for which we spoke with a friend of the person affected to whom he recounted the attack the day after it occurred), and the following day or within a few days we visited each attack site to measure the bear's footprints and assess the circumstances of the event.
We recorded seven attacks of bears on people, spanning 1999–2018 (Fig. 1, Table 1). In all cases the bears reacted defensively to unexpected encounters, as has been noted in other studies (Smith & Herrero, Reference Smith and Herrero2018; Støen et al., Reference Støen, Ordiz, Sahlén, Arnemo, Sæbø and Mattsing2018; Bombieri et al., Reference Bombieri, Naves, Penteriani, Selva, Fernández-Gil and López-Bao2019). We did not record any lethal attacks. Of the seven people involved in the attacks, four suffered minor or minimal injuries, and three were admitted to hospital (Table 1).
Table 1 Details of the seven attacks by brown bears Ursus arctos on people (all men) recorded in the Cantabrian Mountains, Spain (Fig. 1), during 1989–2019.
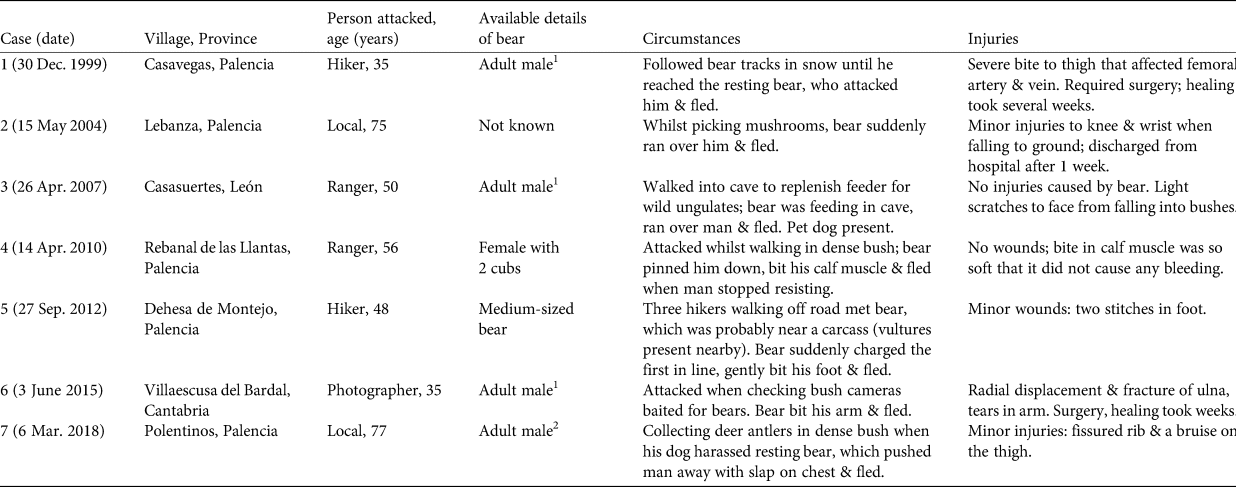
1 Deduced from paw print size.
2 Observed during the field inspection.
Although we have worked extensively throughout the range of the Cantabrian bear, all the attacks recorded were in the eastern part of the range (Fig. 1), even though the number of bears in this subpopulation is much lower than in the western subpopulation. The observed frequency of attacks in the eastern subpopulation was significantly different from expected (χ 2 with Yates correction = 35.29, df = 1, P < 0.0001).
At least four of the seven attacks were by different individual bears, thus ruling out the involvement of a single unusually aggressive individual. In one attack a female with two 15 month-old cubs was involved (case 4, Table 1) and the other attacks were by solitary bears. In case 5, the person who suffered the attack rated the bear as a medium-sized specimen, and in at least four cases (1, 3, 6 and 7) the bears were large adult males (in three cases forepaw width was > 120 mm, authors' unpubl. data; in the other case we observed the bear during our follow-up field inspection). Although male bears can move extensively, the time lapse between the oldest (1999, case 1) and most recent (2015 and 2018, cases 6 and 7) attacks by large males suggests they were caused by different individuals (Table 1).
The people attacked were a representative sample of the normal users of bear range (wardens, hikers, and local people collecting non-timber forest products; Table 1), all of them moving cross-country. The same range of users devoted to similar activities pass through the area of the western subpopulation, where we recorded no attacks during 1989–2019.
Differences in accessibility and habitats could play a role in bear attacks. Lamamy et al. (Reference Lamamy, Bombieri, Zarzo-Arias, González-Bernardo and Penteriani2019) compared the landscape characteristics of the two subpopulations. The eastern range has fewer rocky and rugged areas, which could potentially facilitate human–bear encounters, but this area has a lower human density, with shorter road and trail lengths, generally at higher altitudes and in more forested areas, which could potentially have the opposite effect. However, the differences between the western and eastern landscapes are subtle, and we believe it unlikely these differences alone could give rise to the disparity in the number of attacks between the two areas.
Excluding the presence of one particularly aggressive bear in the eastern subpopulation, differences in people's activities between the two areas, or a higher human population density and a closer proximity of bears to people in the eastern subpopulation, a plausible explanation for the unbalanced geographical attack pattern may be that the bears of the eastern subpopulation are bolder than those to the west. Benazzo et al. (Reference Benazzo, Trucchi, Cahill, Delser, Mona and Fumagalli2017), noting the docile temperament of the Apennine bears (no attacks on people were recorded during the last 100 years), examined any divergence between Apennine and non-Apennine bears at 22 genes associated with tame or aggressive behaviour. They found a significant enrichment of fixed differences in these genes, suggesting that genetic drift or hunting of the more aggressive or bold individuals may have led to a genetically mediated shift in Apennine bear behaviour. As the Cantabrian bear population was separated into the western and eastern subpopulations during the early 20th century, a similar process may have led to genetically mediated differences in bear behaviour in the two subpopulations. The inbreeding that has characterized the small Cantabrian subpopulation until recently may have fixed some characters that were selected by chance, possibly because the boldest or most aggressive individuals were eliminated from the western subpopulation but some of them survived in the east, later disseminating this trait. Selection as a result of hunting and human persecution can potentially affect heritable behavioural traits in brown bears (Leclerc et al., Reference Leclerc, Zedrosser, Swenson and Pelletier2019) and other large mammals (Lone et al., Reference Lone, Loe, Meisingset, Stamnes and Mysterud2015). In the absence of genetic analyses comparing the two Cantabrian bear subpopulations this explanation remains speculative, but supports the hypothesis previously discussed by Penteriani et al. (Reference Penteriani, Delgado, Pinchera, Naves, Fernández-Gil and Kojola2016) that genetic variations along the shy–bold continuum may influence attacks of large carnivores on people and thus the chances of the recovery of threatened populations.
Acknowledgements
We thank Juan Traba, John Muddeman and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Author contributions
Study conception: all authors; project management: GP; data collection: GP, assisted by co-authors; writing: JCB, assisted by co-authors.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical standards
This research abided by the Oryx guidelines on ethical standards.




