The intestinal epithelial cell layer constitutes the largest and most important barrier against the external environment. Tight contact between the enterocytes prevents access of intraluminal toxins, antigens and enteric microbiota to underlying tissue compartments. A compromised intestinal barrier function is suggested to be associated with the pathogenesis of a number of intestinal diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, coeliac disease, post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome and food allergy(Reference Farhadi, Banan and Fields1–Reference Spiller4). Accumulating evidence about the progression of inflammatory bowel disease, a chronic relapsing and remitting disease for which the aetiology remains unknown, shows that an increased intestinal permeability intensifies the exposure of the lamina propria to luminal contents, activating an abnormal immune response(Reference Groschwitz and Hogan3, Reference Clayburgh, Shen and Turner5).
Interestingly, nutrition can affect the epithelial barrier, and hence possibly influence disease development. We have shown in several controlled studies that dietary Ca protects against intestinal infections with foodborne pathogens(Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Lettink-Wissink and Van Doesburg6–Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink8). Ca also has cytoprotective effects by precipitating cytotoxic surfactants, such as secondary bile acids(Reference Govers, Termont and Lapre9, Reference Lapre, De Vries and Koeman10). In addition, supplemental Ca attenuates the development of colitis(Reference Schepens, Schonewille and Vink11). In the latter study, total intestinal permeability was quantified by the analysis of urinary Cr-EDTA excretion. We observed that supplemental Ca prevented the colitis-related increase in intestinal permeability in HLA-B27 transgenic rats(Reference Schepens, Schonewille and Vink11). Another example of dietary modulation of intestinal permeability is the supplementation of short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides (scFOS), which may be regarded as a prebiotic. Work from our group has shown that these dietary scFOS impair the resistance to intestinal infection in rats(Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink8, Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Ten Bruggencate and Lettink-Wissink12, Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink13). Subsequently, we showed that this decrease in barrier functioning was associated with a higher total intestinal permeability in rats(Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink14).
The dietary effects on intestinal permeability in the studies mentioned earlier were investigated by the addition of Cr-EDTA to the diet and subsequent measurement of urinary Cr-EDTA excretion. As Cr-EDTA is stable throughout the intestinal tract, the urinary excretion of this marker provides information regarding total intestinal permeability(Reference Aabakken15). By choosing permeability probes that have limited exposure to certain parts of the intestinal epithelium, region-specific permeability measurements can be performed(Reference Meddings and Gibbons16). For example, the saccharide probes lactulose and mannitol can be used to measure small-intestinal permeability, because they are instantly degraded by the colonic microbiota. Since lactulose only passes the gut wall paracellularly and mannitol passes transcellularly, the lactulose:mannitol ratio is used to express small-intestinal permeability(Reference Arrieta, Bistritz and Meddings2).
We hypothesised that both a high-Ca diet and a scFOS diet mainly influence colonic permeability. As colitis is suggested to result from increased translocation of micro-organisms due to a higher colonic permeability and Ca attenuated colitis development(Reference Schepens, Schonewille and Vink11), dietary Ca probably has its main effect on permeability of the colon. Since scFOS are fermented in the colon, where they change the luminal content, which possibly influences the colonic mucosa, we also hypothesised that scFOS mainly affect colonic permeability. The aim of the present study was to localise these effects. Therefore, we added Cr-EDTA, lactulose and mannitol as permeability markers to the rat diets. As no specific colonic permeability marker exists, this can be determined by comparing total (Cr-EDTA) and small (lactulose:mannitol ratio) intestinal permeability. To gain even more insight into the effect of dietary Ca and scFOS on permeability, we performed Ussing chamber experiments with the faecal waters derived from the in vivo study.
Material and methods
Experimental design of the nutritional study: animals and diets
The experimental protocol was approved by the Animal Welfare Committee of Wageningen University and Research Centre (Wageningen, The Netherlands). Specific pathogen-free outbred male Wistar rats (WU, Harlan, Horst, The Netherlands), 8 weeks old and with a mean body weight of 267 g at the start of the experiment, were housed individually in metabolic cages. Rats were maintained in temperature- and humidity-controlled environment in a 12 h light–dark cycle. Rats were fed ad libitum a purified ‘humanised’ Western diet which contained in the control situation (per kg): 200 g acid casein, 326 g maize starch, 162 g glucose, 160 g palm oil, 40 g maize oil, 50 g cellulose and 5·16 g CaHPO4.2H2O (corresponding to 30 mmol Ca/kg diet; Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA). In addition, the diets contained the following permeability markers per kg: 2 g Cr-EDTA, 7·5 g lactulose (Solvay Arzneimittel GmbH, Hannover, Germany) and 2·5 g mannitol (Sigma-Aldrich) (see below). Lactulose and mannitol were added to the diet to avoid stressful supplementation by oral gavage which might have an impact on intestinal permeability and transit time. Moreover, the continuous exposure of the rats to the permeability probes excludes a possible day–night rhythm in intestinal permeability. Vitamins and minerals (other than Ca) were added to both the diets according to AIN-93(Reference Reeves, Nielsen and Fahey17). This control diet was low in Ca and had a high fat content to mimic the composition of a Western human diet. The diet high in Ca contained 120 mmol Ca/kg diet, and in the scFOS group, the control diet was supplemented with 60 g scFOS/kg diet (6 % (w/w); Raftilose ®P95, Orafti, Tienen, Belgium), both at the expense of glucose. The degree of polymerisation of the supplemented scFOS ranges between 2 and 8, and therefore they are classified as scFOS. Inert Cr-EDTA was added to the diets to quantify total intestinal permeability(Reference Arslan, Atasever and Cindoruk18). Cr-EDTA solution was prepared as described elsewhere and subsequently freeze dried(Reference Binnerts, Van het Klooster and Frens19). To check the complete formation of the Cr-EDTA complex, the prepared Cr-EDTA solution was passed through a cation-exchange resin column (Chelex 100 Resin; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). No uncomplexed Cr3+ ions were present. Potential binding and subsequent precipitation of Cr-EDTA to Ca were determined by quantification of the Cr-EDTA concentration in the faecal water. This was similar in the different dietary groups, so binding of Cr-EDTA to Ca was concluded to be absent. Small-intestinal permeability was assessed using lactulose and mannitol(Reference Arrieta, Bistritz and Meddings2, Reference Bjarnason20). Food intake was recorded daily, and animal weight was recorded three times every week. After 14 d of experimental feeding, rats were anaesthetised with isoflurane and killed.
Measurement of intestinal permeability
Total 24 h urine samples were collected every 2 d during the experiment. For Cr-EDTA measurement, urine was acidified with 50 g/l TCA, centrifuged for 2 min at 14 000 g and diluted with 0·5 g/l CsCl. Then, Cr was analysed by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrophotometry. Urinary lactulose and mannitol were analysed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection on a Au electrode. The analyses were performed with a 600E System controller pump (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) with a He degassing unit and a model 400 EC detector (EG&G, Princeton, NJ, USA). With a WPS-3000 autosampler (Dionex, Sunnyvale, CA, USA), 20 μl of the (diluted) sample were injected on a Carbopac MA-1, 250 × 4 mm, column (Dionex) thermostated at 30°C. Lactulose and mannitol were eluted isocratically at a flow rate of 0·40 ml/min with 480 mm-NaOH followed by a washing step of 1000 mm-NaOH and 1000 mm-sodium acetate. Data analysis was done with Chromeleon software version 6.60 (Dionex).
Ussing chambers
All faeces were collected on the last 3 d of the nutritional experiment and freeze dried. Faecal water was prepared as described earlier(Reference Sesink, Termont and Kleibeuker21). The animal welfare committee of Utrecht University (Utrecht, The Netherlands) approved the animal protocol. Specific pathogen-free outbred male Wistar rats (n 6; WU), 7–8 weeks old, were killed by CO2 inhalation. The colon was taken out and washed in Ringer solution (25 mm-NaHCO3, 117·5 mm-NaCl, 1·25 mm-CaCl2, 5·7 mm-KCl, 1·2 mm-NaH2PO4, 1·2 mm-MgSO4 and 5 g glucose, pH 7·4 when gassed with 95 % O2–5 % CO2 at 37°C), and its muscle layers were stripped off. The tissue sections were cut into specimens of appropriate size and randomly mounted in Ussing chambers (manufactured by Technical Services of Utrecht Institute for Pharmaceutical Sciences), each side containing the Ringer solution. After a 30 min equilibration period, baseline transepithelial resistance was measured, and the Ringer solution in the mucosal compartment was replaced by fresh Ringer solution (negative control), or Ringer solution containing no Ca, or faecal water prepared from faeces of the different dietary groups of the nutritional study described earlier. Colonic tissue was thus exposed to faecal water pools of either control rats, Ca-fed rats or scFOS-fed rats. The Ca chelator ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid served as a positive control for enhanced permeability due to Ca binding (8 mm as final concentration in Ringer solution in both compartments). At the same time, fluorescein isothiocyanate-labelled 4 kDa dextran (FITC-dextran) was added at the mucosal side (1 mg/ml as final concentration). Samples were taken every 30 min from the serosal compartment for subsequent fluorescence measurement and replaced by fresh Ringer solution. The experiment was carried out for 180 min, after which endline transepithelial resistance was determined. Flux was expressed as nanomol of FITC-dextran crossing 1 cm2 of colonic epithelium in 1 h (nmol/cm2 per h).
Statistical analysis
All the results are expressed as means with their standard errors. The predefined comparisons of interest for the nutritional study were control rats v. Ca-fed rats and control rats v. scFOS-fed rats. For the in vitro experiments, the predefined comparisons of interest were: faecal water of control rats v. faecal water of Ca-fed rats, faecal water of control rats v. faecal water of scFOS-fed rats and the negative control v. withdrawal of Ca from the Ringer solution. Statistics were done by one-way ANOVA or Kruskal–Wallis test, depending on the normality of the data. If significant, this was followed by Student's t test (for normally distributed data) or Mann–Whitney U test (for non-normally distributed data) to identify the significant dietary effects. Differences were considered statistically significant when P < 0·05 (all two-sided). Statistical analyses were conducted with GraphPad Prism version 5.01 (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
Results
Animal growth and food intake
Rats fed the high-Ca diet did not differ from rats fed the low-Ca control diet with respect to growth (5·8 (se 0·3) and 6·3 (se 0·3) g/d, respectively; P = 0·16). However, animal growth in the scFOS group was significantly lower (4·7 (se 0·3) g/d, P = 0·0002) in accordance with a previous study(Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Ten Bruggencate and Lettink-Wissink12). Food intake of rats fed the low-Ca control diet and of rats fed the high-Ca diet was similar (21·6 (se 0·4) and 21·4 (se 0·5) g/d, respectively; P = 0·72), while food intake of the scFOS-fed rats was significantly less than that of control rats (18·4 (se 0·4) g/d, P < 0·0001).
Dietary calcium and short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides influence total intestinal permeability
Dietary Ca supplementation caused a direct and persistent decrease in urinary Cr-EDTA excretion; the decrease was 24 % in rats fed the high-Ca diet compared with rats fed the low-Ca control diet on day 14 (P < 0·05; Fig. 1). Urinary excretion of Cr-EDTA by scFOS-fed rats was lower than that by control rats at the beginning of the experiment (day 2). This might represent shorter exposure of the intestinal epithelium to luminal contents due to more rapid gut transit on the scFOS diet, which has been observed in past studies(Reference Hansen, Knudsen and Eggum22). From day 2, urinary Cr-EDTA excretion by scFOS-fed rats increased gradually with time compared with the control group, probably reflecting relatively slow gut microbiota adaptations due to scFOS. After 2 weeks, dietary scFOS had increased total intestinal permeability by 30 % (P < 0·05; Fig. 1).

Fig. 1 Effect of dietary Ca and short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides (scFOS) on urinary Cr-EDTA excretion, a marker for total intestinal paracellular permeability. Results are expressed as means with their standard errors (n 13). * Mean values of Ca-fed rats were significantly different compared with control rats (P < 0·05). † Mean values of scFOS-fed rats were significantly different compared with control rats (P < 0·05). –○–, Control; –●–, Ca; –Δ–, scFOS.
Effect of calcium and short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides on small-intestinal permeability
Dietary effects on the lactulose:mannitol ratio were smaller and, surprisingly, in the opposite direction compared to total intestinal permeability as measured by Cr-EDTA. The lactulose:mannitol ratio on day 14 was 15 % higher for rats fed the high-Ca diet (0·23 (se 0·006), P = 0·0014) and 16 % lower for rats fed the scFOS diet (0·17 (se 0·009), P = 0·0038) compared with rats fed the low-Ca control diet (0·20 (se 0·005)).
We also considered the lactulose and mannitol fluxes individually to gain more insight and specify whether paracellular permeability was changed. However, we did not observe significant dietary effects on individual lactulose (P = 0·61) and mannitol excretion in urine (P = 0·36; Fig. 2). This indicates that paracellular permeability in the small intestine remained the same. In combination with the Cr-EDTA results, it can therefore be concluded that both Ca and scFOS affect permeability only in the colon.
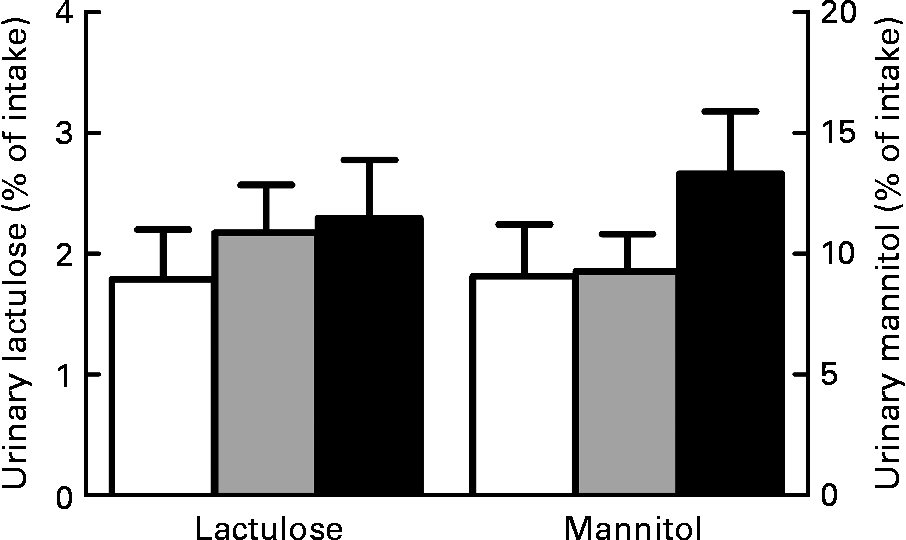
Fig. 2 Effect of dietary Ca and short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides (scFOS) on individual urinary lactulose and mannitol excretion. Results are expressed as means with their standard errors (n 13). □, Control; ![]() , Ca; ■, scFOS.
, Ca; ■, scFOS.
Effect of faecal water from rats fed supplemental calcium or short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides in Ussing chambers
Faecal waters were prepared from faeces of the in vivo rat experiment and tested in Ussing chambers using colonic tissue. Diet influenced the pH of pools of faecal water (control: 6·1; Ca: 6·5 and scFOS: 5·5). No dietary effects were observed on transepithelial resistance (P = 0·23), while the positive control (ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid) caused a decrease in resistance as expected (P = 0·0019; data not shown). Also, the paracellular flux of FITC-dextran crossing the epithelial barrier was similar for all faecal waters at all time points (P = 0·67; Fig. 3). Obviously, the FITC-dextran flux was increased in the positive control due to the addition of the Ca chelator ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (P = 0·0002). So, diet-modified faecal waters did not influence colonic permeability in Ussing chambers. Furthermore, the Ca-free Ringer solution at the luminal side of the Ussing chamber did not influence dextran flux either (P = 0·09; Fig. 3).
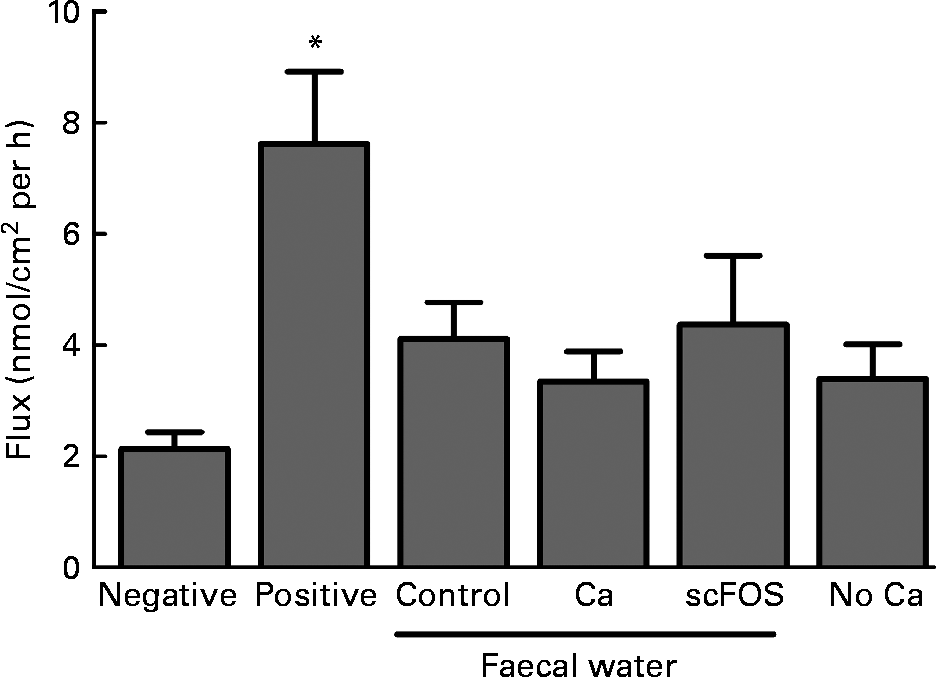
Fig. 3 Effect of faecal water from rats fed a control diet, Ca-supplemented diet or short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides (scFOS)-supplemented diet on fluorescein isothiocyanate-labelled 4 kDa dextran (FIFC-dextran) flux, a marker for permeability, across stripped colonic tissue in Ussing chambers. Also, the Ca-free Ringer solution at the luminal side of the Ussing chamber was studied (‘no Ca’). Results (means with their standard errors) are expressed as nanomol of FITC-dextran crossing 1 cm2 of colonic epithelium in 1 h. The interval of time shown (60–90 min) is representative for the whole experiment. Negative (Ringer), n 12; positive (ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid in Ringer), n 10; faecal water of control rats, n 9; faecal water of Ca-fed rats, n 10; faecal water of scFOS-fed rats, n 9; no Ca (n 13). * Mean values were significantly different compared with negative control (P = 0·0002).
Discussion
The present study demonstrates that the effect of dietary Ca and scFOS on permeability in rats is localised in the colon. Supplemental Ca clearly decreased total intestinal permeability, as determined by Cr-EDTA as a marker. At the same time, it caused a less pronounced increase in the lactulose:mannitol ratio but without affecting the individual lactulose excretion, representing small-bowel permeability. Taken together, it can be concluded, although indirectly, that the overall permeability is decreased by Ca supplementation and that the effect is localised in the colon. The same applies for scFOS, although the results are opposite: dietary scFOS increased total intestinal permeability as measured by Cr-EDTA, whereas a minor decrease in the lactulose:mannitol ratio was observed without an effect on individual urinary lactulose values. Therefore, we can indirectly conclude that the increase in permeability caused by scFOS is also localised in the colon. The Ussing chamber experiments showed that dietary Ca and scFOS did not influence colonic permeability via alterations in faecal water.
The consistent finding that dietary Ca beneficially influences colonic permeability is very interesting. In the first place, it is intriguing that intestinal permeability apparently can be improved in a healthy situation. Secondly, an increased permeability is suggested to be a primary causative factor contributing to inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis(Reference Arrieta, Bistritz and Meddings2, Reference Arnott, Kingstone and Ghosh23, Reference Wyatt, Vogelsang and Hubl24). It is generally accepted that the gut microbiota and its intimate contact with an over-reactive immune system in the intestinal epithelium is the driving force behind the chronic inflammation(Reference Sartor25). As intestinal bacteria reside mainly in the colon(Reference Guarner and Malagelada26), decreasing of colonic permeability by a high-Ca diet might be a highly attractive nutritional intervention for inflammatory bowel disease patients. Moreover, in a previous study, we showed that supplemental Ca attenuated some important aspects of colitis development in HLA-B27 transgenic rats(Reference Schepens, Schonewille and Vink11).
Based on the individual lactulose results, dietary Ca does not influence small-intestinal permeability. The fact that Meddings & Gibbons(Reference Meddings and Gibbons16) could not detect any lactulose and mannitol in the colon underlines the specificity of both lactulose and mannitol as markers for small-intestinal permeability. Therefore, Ca supplementation might only be worthwhile when targeting the colon for health improvement. The reason for the difference in localisation is unknown, but we hypothesise that Ca influences intestinal permeability by modulating the colonic microbiota or its metabolites. For example, Salmonella typhi and Escherichia coli, being members of the enterobacteria, are able to induce an increase in intestinal permeability(Reference Mangell, Nejdfors and Wang27). In agreement with these results, dietary Ca decreased faecal enterobacteria in the present study (control: 9·1 (se 0·2); Ca: 7·3 (se 0·1) and scFOS: 9·1 (se 0·1) log10 colony-forming units/g faeces). Effects of both Ca and scFOS on the intestinal microbiota have been shown before(Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink8, Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink13, Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink14, Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Wissink and Wouters28).
Also, the increase in total permeability caused by dietary scFOS is shown to be localised in the colon. This was hypothesised, as these carbohydrates, or prebiotics, are rapidly hydrolysed and metabolised in the colon by the endogenous microbiota(Reference Andersson, Ellegard and Bosaeus29). In this way, scFOS change the bacterial composition, which is often assumed to be beneficial(Reference Gibson and Roberfroid30). In the present study, scFOS were supplemented, which have a degree of polymerisation ranging from 2 to 8. Supplementation with long-chain FOS (degree of polymerisation between 2 and 60) alters the microbiota differently from supplementation with scFOS, because of differences in fermentation rate(Reference Roberfroid, Van Loo and Gibson31) and amount and pattern of SCFA production(Reference Macfarlane and Macfarlane32). However, Ten Bruggencate et al. (Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink8) showed that scFOS and inulin (mix of short-chain and long-chain FOS; average degree of polymerisation between 10 and 12) both impaired resistance to intestinal infection in rats. On the contrary, Petersen et al. (Reference Petersen, Heegaard and Pedersen33) only observed increased translocation of Salmonella in mice supplemented with scFOS, and not in mice supplemented with inulin. The decreased food intake of the rats fed scFOS might be due to rapid and extensive fermentation of scFOS causing bloating and abdominal cramps(Reference Briet, Achour and Flourie34). These unpleasant feelings decrease appetite. As the permeability marker data are expressed as percentage of intake, the differences in food intake do not influence the outcome measurements. The Cr-EDTA excretion increased gradually with time in the scFOS group. This might reflect relatively slow gut microbiota adaptations due to scFOS. The change in the intestinal permeability by supplemental scFOS has previously been associated with a decreased resistance to intestinal infections(Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink14).
Paracellular permeability in the small intestine, determined by individual lactulose excretion, was not significantly influenced by the supplementation of scFOS to the diet. A similar site-specific effect of scFOS has been observed in previous studies in our laboratory. In one study, dietary scFOS increased mucosal inflammation in the caecum and colon after oral infection with Salmonella enteritidis, but not in the ileum(Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Ten Bruggencate and Lettink-Wissink12). In another study, scFOS supplementation increased mucin concentration and stimulated mucosal lactobacilli and enterobacteria in the caecum and colon, but again not in the ileum(Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink14). scFOS therefore clearly have region-specific effects in rats: in the colon they may exert undesirable effects, while in the small intestine no such effects were observed. Results fit with the idea that the physiological effects of scFOS are microbiota mediated and these mainly reside in the caecum and colon. Furthermore, although fermentation in the rat takes place in both the caecum and colon, the similarity of the effects of scFOS in both these organs supports the use of the rat as an appropriate model for human colonic fermentation.
Interestingly, most adverse effects of scFOS on intestinal infection, which are mentioned in this paper(Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Ten Bruggencate and Lettink-Wissink12–Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink14), were inhibited when Ca was supplemented to the diet(Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink8). The Ca content of the control diet in these studies and the present investigation matches with the lower limit of the human intake range, while the Ca-supplemented diet provided more than the general habitual dietary Ca intake(Reference Schepens, Schonewille and Vink11, Reference Alaimo, McDowell and Briefel35). The dose of scFOS used in the present study (6 %) is high, but probably realistic for the human situation. Daily intake of fructose-based non-digestible carbohydrates has been estimated up to 10 g(Reference Coussement36). This corresponds to 2 % in the diet, assuming a total food intake of 500 g dry weight/d. This estimation does not take into account consumption of specific meals and products supplemented with fructose-based carbohydrates, typically 3–10 g/portion(Reference van Loo, Coussement and de Leenheer37). As the human diet still contains other non-digestible carbohydrates, supplementation with 6 % is high, but certainly not unrealistic. When scFOS are fermented, SCFA are produced, which lead to acidification of the intestinal lumen. Subsequently, the protective effect of supplemental Ca might be due to formation of the insoluble calcium phosphate complex in the small intestine. In the colon, solubilisation of this complex increases the buffering capacity of the intestinal lumen, which may counteract the adverse effects of acidic fermentation of scFOS(Reference Remesy, Levrat and Gamet38). Indeed, the pH of faecal water of the rats fed the high-Ca diet was higher than that of the rats fed the low-Ca control diet. It will be interesting to investigate the effect on intestinal permeability when both Ca and scFOS are supplemented to the diet. This will be further explored in following studies. Finally, when studying the effects of non-digestible carbohydrates, Ca content of the diet should be taken into account.
Since the individual lactulose and mannitol excretion in urine were not influenced by the different diets, the relevance of the lactulose:mannitol ratio is questionable. Bijlsma et al. (Reference Bijlsma, Peeters and Groot39) suggested that the individual lactulose and mannitol excretion values provide more information than the ratio of the two sugars. In fact, mannitol excretion in urine depends mainly on the magnitude of solvent drag caused by villus tip hyperosmolality, while urinary lactulose results truly represent paracellular permeability. By combining the two probes in a ratio, the information is lost and wrong conclusions can be drawn. For example, in the case of coeliac disease, mannitol excretion is clearly decreased because of villus atrophy, while urinary lactulose recovery is increased(Reference Ukabam and Cooper40). These findings are more informative than a ratio. In the present study, the ratio indicates that dietary effects exist, while the individual lactulose and mannitol results are not affected by the diet. Based on these findings, we conclude that small-intestinal permeability is not changed by Ca or scFOS.
In the Ussing chamber experiments, we did not observe any effect of the different faecal waters, prepared from faeces of the nutritional study, on permeability. Nevertheless, the pH of the faecal waters was different due to the diets. This demonstrates that fermentation of scFOS indeed influenced colonic contents, supporting the use of faecal water to study the potential scFOS effects. These Ussing chamber results suggest that the effect of Ca and scFOS on colonic permeability is not mediated by differences in faecal water composition. Although we observed a change in cytotoxicity of faecal water by Ca and scFOS in previous studies(Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Termont and Weerkamp7, Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Ten Bruggencate and Lettink-Wissink12, Reference Ten Bruggencate, Bovee-Oudenhoven and Lettink-Wissink13, Reference Govers and Van der Meer41), apparently luminal cytotoxicity is not responsible for the effects on colonic permeability. However, it should be kept in mind that, for example, SCFA produced by scFOS fermentation are rapidly absorbed by the colonic mucosa and therefore are largely absent in faecal waters(Reference Alles, Hautvast and Nagengast42), although they might have been capable of influencing the gut wall in vivo and thus the permeability. Additionally, exposure time of the colonic tissue to the faecal water in the Ussing chamber is much shorter than that occurs in vivo. Nevertheless, we hypothesise that other mechanisms, which cannot be mimicked in the Ussing chamber, may play a role in the effects of Ca and scFOS on permeability. A possible hypothesis is that Ca influences the viscosity of the mucus layer, thereby altering intestinal permeability(Reference Crowther, Marriott and James43). Handling the colonic tissue for use in the Ussing chambers results in partial loss of this layer, hence this effect may be missed. Moreover, as mentioned earlier and described in other papers, both Ca and scFOS modulate the intestinal microbiota(Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Ten Bruggencate and Lettink-Wissink12, Reference Bovee-Oudenhoven, Wissink and Wouters28), and these microbes are not present in the Ussing chambers or in the different faecal waters used in the experiments.
Although extracellular Ca is crucial for the maintenance of intestinal tight junction function in cell studies(Reference Gonzalez-Mariscal, Contreras and Bolivar44), no direct effect of Ca on permeability in Ussing chambers was observed when colonic tissue was exposed to Ca-free Ringer solution on the luminal side. These differences in observation suggest that the effect of Ca on permeability as observed in vivo is either indirect or long term or both.
In conclusion, the present study shows that dietary Ca decreases, while scFOS increase the permeability of the rat colon. We hypothesise that modulation of mucins and/or microbiota is important for the permeability effects of both Ca and scFOS, since in vivo results could not be mimicked in Ussing chambers. The results of the present study emphasise that nutrition can play an important role in the modulation of gut epithelial integrity.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the biotechnicians at the Small Animal Centre (Wageningen University and Research Centre, The Netherlands) for their expert assistance. The present study was supported by TI Food and Nutrition (Wageningen, The Netherlands). None of the authors has conflicts of interest. M. A. A. S. contributed to study design, experimental procedures, data analysis, data interpretation and manuscript writing. A. R. contributed to study design, experimental procedures and data interpretation. A. J. S. and C. V. assisted in experimental procedures and data analysis. R.-J. M. B. contributed to data interpretation and assisted in manuscript writing. L. E. M. W. contributed to data interpretation and manuscript writing. R. v. d. M. and I. M. J. B.-O. contributed to study design, data interpretation and manuscript writing.





