Introduction
Morbidity and death in all age groups are considerably increased by poor diets. One in five fatalities worldwide are caused by poor nutrition. In 2017, 11 million deaths were attributable to dietary risk factors, with 3 million deaths each due to high salt intake and poor whole grain intake, and 2 million due to low fruit intake(Reference Murray1).
Promoting healthy eating habits is a recognised strategy to lessen the impact of malnutrition. Since doctors are usually the gatekeepers in the healthcare system, they play an important role in encouraging people to eat healthy and live a healthy lifestyle. Doctors can assist individuals by giving nutrition counselling, nutrition assessments or identifying and recommending patients to seek professional dietetic care, all of which are referred to as nutrition care.
Doctors are typically seen as trustworthy sources of nutrition by the general public and are expected to provide nutrition care. The Behavioural Risk Factor Surveillance System study revealed a roughly threefold increase in patients’ attempts to treat their nutrition issues following physician advice(Reference Rutledge, Groesz and Linke2). Thus, it should come as no surprise that the majority of professional bodies in a number of countries list nutrition care as one of the responsibilities that doctors should take on when delivering healthcare(Reference Crowley, Ball and Hiddink3).
Nonetheless, physicians worldwide continue to underutilise this opportunity to render nutrition care to their clients. Doctors struggle to provide nutrition care due to a lack of training in nutrition counselling, limited expertise and low confidence(Reference Crowley, Ball and Hiddink3,Reference Mogre, Stevens and Aryee4) . The vast majority of practicing doctors, medical students and incoming interns frequently report being dissatisfied and unwilling to counsel patients with nutritional issues(Reference Mogre, Stevens and Aryee4,Reference Hark, Deen and Morrison5) .
Some nutrition education interventions (NEIs) have been carried out over the years to improve medical students’ nutrition education experiences, with results published in the literature, in order to promote effective nutrition care provision. However, there has been a scarcity of critical systematic reviews of the literature to help inform the design and development of these interventions on the competencies and dietary habits of medical students and residents. There have been three previous reviews of this phenomenon(Reference Crowley, Ball and Hiddink3,Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6,Reference Sunguya, Poudel and Mlunde7) . Mogre et al. (Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) conducted a realist review of the literature to determine what types of educational interventions work, how, for whom, why and under what conditions to improve doctors’ and other healthcare professionals’ competencies and nutrition care delivery. Crowley et al. (Reference Crowley, Ball and Hiddink3) conducted a critical review of the literature in 2019 and reported on the types of nutrition education provided to medical students, but did not report on their impact on medical students’ and residents’ competencies. Sunguya et al. (Reference Sunguya, Poudel and Mlunde7) reported on the effectiveness of in-service nutrition training programmes on health workers’ nutrition knowledge, counselling skills and child undernutrition management practices. Although the review by Mogre et al. (Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) reported on the impact of NEIs on medical students’ competencies, it did not extensively evaluate the impact of NEIs on medical students’ own dietary habits, only included studies published until 2014, and has not been updated since. Crowley et al. (Reference Crowley, Ball and Hiddink3) conducted a review that included both interventional and non-interventional studies, as well as studies published up to 2018.
This scoping review aims to map current literature and provide a summary of the impact of NEIs on nutrition care competencies, self-efficacy and dietary habits of medical students and residents as a prelude to conducting a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. This will provide information that both academics and practitioners may find useful.
Methods
The study followed the scoping review guidelines proposed by Arksey and O'Malley(Reference Arksey and O'Malley8) and the recommendations of Levac et al.(Reference Levac, Colquhoun and O'Brien9). We used these guidelines to screen data from existing databases and then reported in accordance with the PRISMA extension for scoping review(Reference Tricco, Lillie and Zarin10).
Eligibility criteria
Studies were chosen based on the following eligibility criteria.
Participants: Medical students and residents.
Outcomes: Eligible studies included those that reported on nutrition knowledge, attitudes towards nutrition care, self-efficacy, nutrition counselling skills, dietary and lifestyle practices, and readiness to provide nutrition care. Intervention studies aimed at changing the dietary and lifestyle habits of medical students and residents were also considered.
Study design: Randomised control trials, quasi-experimental studies and prospective studies.
Time frame: From January 2010 to June 2021. Only published studies were considered.
Language: Only English-language publications were considered.
Exclusion criteria
All systematic reviews and one-time studies were excluded. Interventions aimed at medical doctors or family physicians were also excluded from the study. Furthermore, commentaries, case studies, conference proceedings, non-peer-reviewed papers, opinion pieces, letters to the editor and abstracts were not accepted.
Information sources and search strategy
We searched four electronic databases, including PubMed, ProQuest, Cochrane and Google Scholar, to find relevant literature (for grey literature). From 28 May 2021 to 29 June 2021, the literature was searched, and email alerts were set up to notify of newly published articles. BYA developed the search strategy based on the study's main research question, which was then reviewed by VM. Keywords and databases pertinent to the study were identified by BYA, VM and a librarian. Appropriate MESH terms as well as free text of keywords were identified and used as needed. Keywords included ‘nutrition care’, ‘nutrition care competency’, ‘knowledge’, ‘attitudes’, ‘nutrition counselling’, ‘nutrition education’ and ‘medical students’ (undergraduate students or trainees or future doctors). The appropriate Boolean operators were used. The search strategy was developed first for PubMed and then applied to the other databases.
Selection of relevant studies
All search results were exported into EndNote X9 reference manager for de-duplication and selection. BYA and VM independently screened the titles and abstracts against the eligibility criteria. Full-text screening was used for articles with insufficient information in the title and abstract to justify their inclusion. BYA and VM discussed the results of the screening process with the rest of the review team, highlighting areas of disagreement that were resolved through discussion. The reference list of the selected articles was searched for additional relevant articles to include.
Data extraction/charting
We extracted data on population (i.e. medical students or interns or residents or student doctor or trainee doctor), sample size, study design, focus or objective of the study, educational level of participants, methods of teaching and learning, type of intervention (e.g. workshop, curriculum design), duration of intervention, outcome of intervention and study location. Components of the data extraction form was based on previous research(Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6,Reference Steinert, Mann and Centeno11) . Each full text was reviewed using this format, and the data were extracted into an Excel spreadsheet. BYA extracted the data, and the results were discussed with VM and the other team members. We did not assess the methodological quality of the included studies because we were scoping the literature for a more comprehensive systematic review.
Data analysis and synthesis
The data were analysed in Microsoft Excel 2013. Descriptive analysis was performed and presented in the form of frequencies, percentages and narrative format. Furthermore, we classified the included studies based on the type of outcomes reported, NEI and study designs.
Patient and public involvement
Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, conduct, reporting or dissemination plans for this study.
Results
The four databases yielded 1807 articles. After de-duplication, there were 1787 articles left for screening. After removing 1750 studies based on title and abstract screening, the remaining 37 studies were subjected to full-text screening, with 23 articles found eligible and included in the analysis. The flowchart of the selection process is shown in Fig. 1.
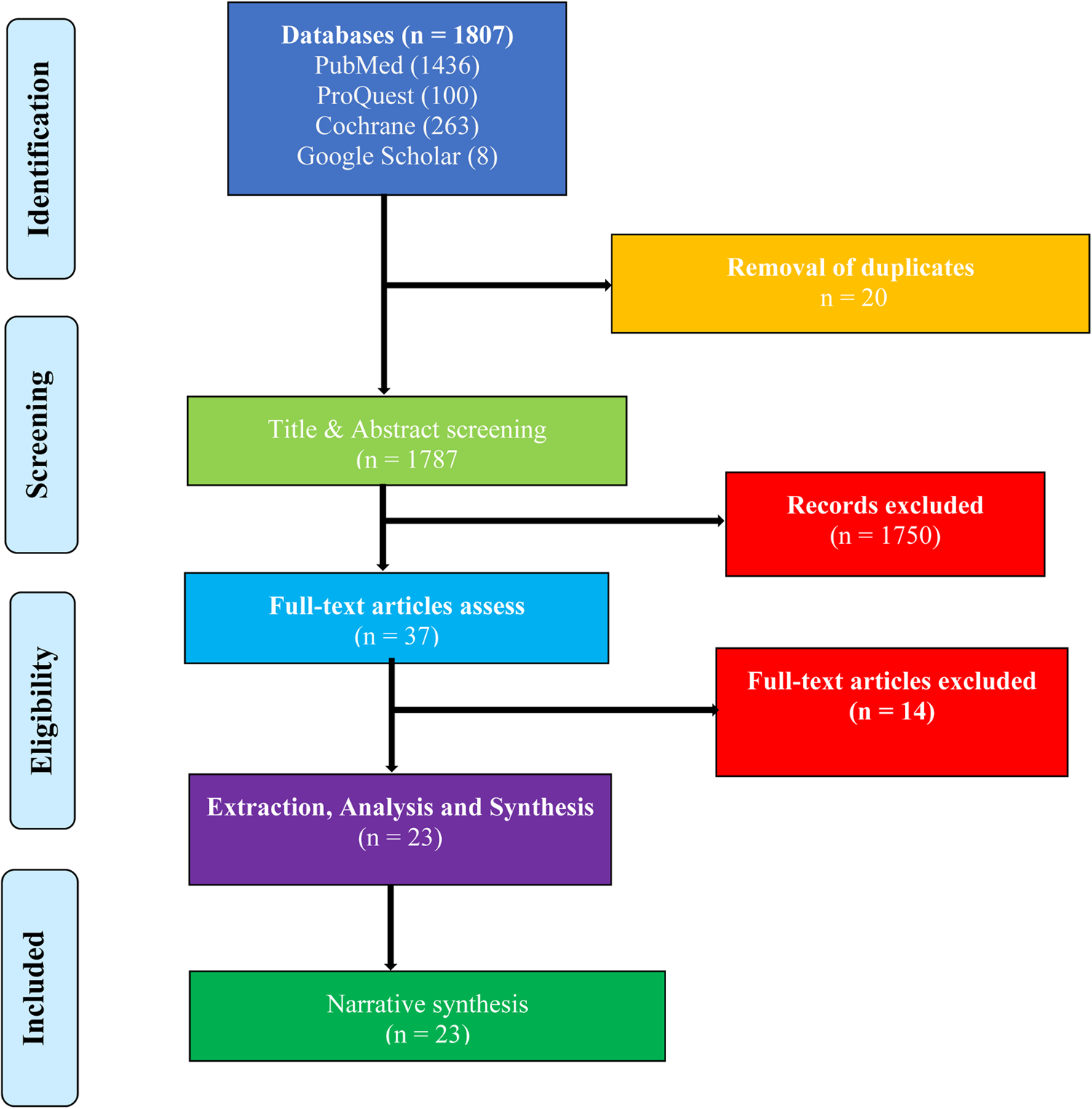
Fig. 1. A PRISMA flowchart of the study selection process.
Eighteen of the studies (78⋅3 %) were conducted in the United States of America (USA), while the remaining articles were conducted in the Netherlands, Indonesia, Iran, New Zealand and Portugal (shown in Table 1).
Table 1. Characteristics of the included studies (n 23)
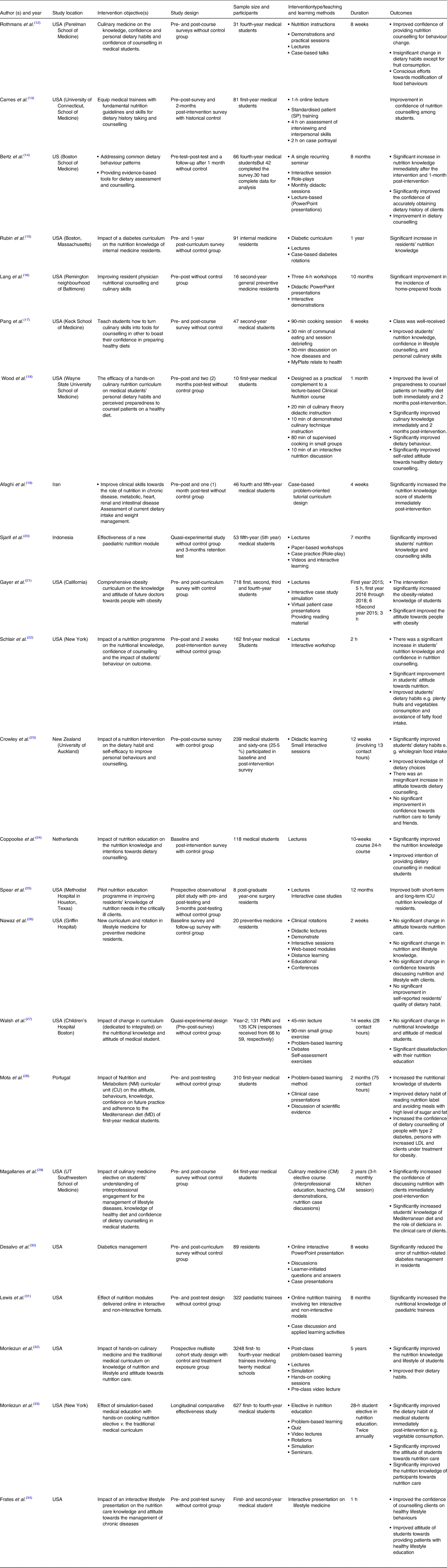
Table 2 summarises the study designs, methodological approaches and the format of intervention of the included studies. The articles used a variety of study designs, with the majority (n 15, 65⋅2 %) using a quasi-experimental design. The included studies had a total sample size of 6621 participants (median = 81 participants; interquartile range (IQR): 25⋅5 and 252⋅5). The studies with integrated participation (a combination of preclinical and clinical year students) had the largest sample size (median = 718, IQR: 672⋅5 and 1983). Slightly more than three-quarters of the studies (n 18, 78⋅3 %), used only survey questionnaires and a few studies (n 5, 21⋅7 %) combined surveys and open-ended questions. The majority of the surveys (n 14, 60⋅9 %) were conducted using validated questionnaires adapted from previous research. Eighteen (78⋅3 %) of the studies used a quantitative method, while the remaining (n 5, 21⋅7 %) used mixed methods (quantitative and qualitative methods combined). Mixed method approaches were used in studies that reported on participants’ feedback about the intervention (n 5, 21⋅7 %). The interventions were delivered through a variety of methods, including problem-based learning sessions, demonstrations, interactive case presentations, interactive case studies, interactive workshops, paper-based workshops, debates, hands-on experience self-assessment, visual patient presentation, culinary sessions, case-based presentations, video lecture and rotations in lifestyle medicine.
Table 2. Study designs, format of intervention and data collection methods
Nutrition-related knowledge
Almost all the studies (n 21, 91⋅3 %) assessed changes in study participants’ nutrition-related knowledge(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12,Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14–Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28,Reference Lewis, Frank and Nagel31–Reference Magallanes, Sen and Siler35) . Eighteen of these studies (85⋅7 %)(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12,Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14–Reference Spear, Sim and Moore25,Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28,Reference Lewis, Frank and Nagel31–Reference Monlezun, Leong and Joo33,Reference Magallanes, Sen and Siler35) found a significant positive change in knowledge immediately following intervention. Three studies (n 3, 14⋅3 %) reported no change in knowledge or improvement without specifying whether the change was statistically significant(Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26,Reference Walsh, Ziniel and Delichatsios27,Reference Frates, Xiao and Simeon34) . Nawaz et al. found a slight but insignificant increase in residents’ knowledge on various lifestyle components after following a lifestyle medicine curriculum that included didactics, distance learning, educational conferences and a newly developed lifestyle medicine rotation programme in a study of twenty preventive medicine residents(Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26).
The qualitative feedback of study participants demonstrates that students learned about nutrition-related disorders, and how to encourage the adoption of healthy dietary practices(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12). Except for four studies(Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14,Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18,Reference Sjarif, Yuliarti and Wahyuni20,Reference Spear, Sim and Moore25) , which had a two-time measurement and a follow-up (or third time measurement) assessment post-intervention, all the studies had two-time measurements (i.e. baseline and post-intervention). Two of these studies reportedly conducted a 3-month follow-up assessment(Reference Sjarif, Yuliarti and Wahyuni20,Reference Spear, Sim and Moore25) . One study each, included 1-month(Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14) and 2-month(Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18) post-intervention follow-up measurements. Except for one study, all the studies that had follow-up assessments reported a decrease in the mean knowledge scores of the participants at follow-up compared with immediately post-intervention but higher than the baseline score. For example, Wood et al. (Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18) discovered that first-year medical students’ baseline mean knowledge score was 5⋅3 out of a possible 10⋅0 points, which increased significantly (P = 0⋅001) to 8⋅8 points immediately following the intervention and declined to 6⋅9 points 2 months later(Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18). In addition, Berz et al. (Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14) discovered a baseline score of 4⋅3 that significantly increased to 5⋅8 immediately post-intervention but declined to 5⋅2 at the 1-month follow-up assessment. In an observational prospective study, Spear et al. (Reference Spear, Sim and Moore25) implemented nutrition education among surgery residents, with mean knowledge scores increasing from 45 % at baseline to 82 % immediately post-intervention and declining by 65 % 3 months later. Sjarif et al. (Reference Sjarif, Yuliarti and Wahyuni20) found a knowledge score of 23⋅7 % at baseline that increased to 61⋅7 % post-intervention and 63 % at 3-months post-intervention using a quasi-experimental design.
Attitude towards nutrition care
Of the twenty-three studies, 47⋅8 % (n 11) investigated changes in study participants’ attitudes. Four (36⋅4 %) studies(Reference Gayer, Weiss and Clearfield21,Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22,Reference Monlezun, Dart and Vanbeber32,Reference Monlezun, Leong and Joo33) reported a significant change in attitude after the intervention, while seven (63⋅6 %) studies(Reference Lang, Jennings and Lam16,Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18,Reference Coppoolse, Seidell and Dijkstra24,Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26–Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28) reported no significant change. Schlair et al. (Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22) observed medical students developing the attitude that patients are more likely to lose weight if they are counselled by physicians about weight and obesity management immediately following the intervention compared with baseline. Two studies found statistically significant increases in the odds of medical students reporting that nutrition counselling should be made a routine practice in medical care(Reference Monlezun, Dart and Vanbeber32,Reference Monlezun, Leong and Joo33) , as well as the belief that physician counselling could increase the odds of patients wanting to improve their diet(Reference Monlezun, Leong and Joo33). A study conducted in the United States with 718 first- to fourth-year medical students discovered a significant reduction in their perception of obese people having low intelligence and sexual attractiveness after intervention when compared with baseline(Reference Gayer, Weiss and Clearfield21). Another study found that after intervention, participants’ attitudes towards reading and understanding nutrition labels for healthy food choices improved(Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28). The seven studies that did not report a significant change in attitude post-intervention reported positive attitudes towards nutrition at baseline that were maintained post-intervention. Wood et al. (Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18) discovered that at baseline, participants were both highly motivated (mean = 8⋅2 points) and excited (mean = 8⋅2 points) to counsel patients on healthy lifestyle choices, which was sustained post-intervention. Similarly, at the outset of three other studies(Reference Coppoolse, Seidell and Dijkstra24,Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26,Reference Frates, Xiao and Simeon34) , almost all students believed that talking to patients about healthy lifestyles was important, and some believed that nutritional counselling could lead to improved dietary behaviours.
Self-efficacy in nutrition care
More than half of the studies (n 13, 56⋅5 %) examined study participants’ self-efficacy(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12–Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14,Reference Lang, Jennings and Lam16–Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18,Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22–Reference Coppoolse, Seidell and Dijkstra24,Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26,Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28,Reference Frates, Xiao and Simeon34,Reference Magallanes, Sen and Siler35) . Immediately following the intervention, eleven of the included studies found a significant improvement in participants’ self-efficacy to provide nutrition care(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12–Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14,Reference Lang, Jennings and Lam16–Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18,Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22,Reference Coppoolse, Seidell and Dijkstra24,Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28,Reference Frates, Xiao and Simeon34,Reference Magallanes, Sen and Siler35) . The aspects that were improved were increased efficacy in using the plate dietary method, making appropriate referrals, and confidence in providing dietary counselling in the treatment of people with obesity, elevated LDL-cholesterol and type 2 diabetes. Following a qualitative approach, Rothmans et al. reported that some of the students who participated in their intervention commented that, unlike before, they are now confident in their dietary care prowess and thus willing to provide nutrition care(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12). In terms of follow-up assessments, Berz et al. reported a 1-month follow-up self-efficacy assessment, and while the score decreased from 4⋅1 to 3⋅9, it remained higher than the baseline score of 3⋅3.
The two studies that did not report significant improvements in self-efficacy either reported a significant decrease in participants’ confidence in providing nutrition care and health-related counselling to family/friends(Reference Crowley, Ball and Leveritt23) or reported a non-significant increase in confidence in discussing lifestyle issues with patients(Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26). Crowley et al. explained that students’ confidence dropped as a result of the intervention's emphasis on the physiological aspects of nutrition rather than behaviour counselling(Reference Crowley, Ball and Leveritt23).
Dietary and lifestyle habits of medical students and residents participating in NEIs
Nine (39⋅1 %) of the included studies(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12,Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18,Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22,Reference Crowley, Ball and Leveritt23,Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26,Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28,Reference Monlezun, Dart and Vanbeber32,Reference Monlezun, Leong and Joo33,Reference Magallanes, Sen and Siler35) ) looked at the impact of nutrition education on the dietary and lifestyle habits of medical students and residents. Except for one(Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26), all of these studies (n 8, 89 %) improved participants’ dietary habits post-intervention(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12,Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18,Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22,Reference Crowley, Ball and Leveritt23,Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28,Reference Monlezun, Dart and Vanbeber32,Reference Monlezun, Leong and Joo33,Reference Magallanes, Sen and Siler35) . Some of the improvements included increased fruit consumption, increased consumption of homemade food over restaurant and pre-prepared meals, avoidance of fatty foods, increased frequency of wholegrain food intake and decreased consumption of processed meat, avoiding the consumption of high sugar and fat foods, decreased odds of daily soft drink consumption and decreased odds of believing that healthy eating is expensive and time-consuming. The remaining study, Nawaz et al., reported an insignificant change in the eating habits of their study participants with a statistically significant improvement in their ability to manage their own stress(Reference Nawaz, Petraro and Via26).
Preparedness of medical students and residents to provide nutrition care
Three studies looked into how prepared participants were to provide nutrition care(Reference Lang, Jennings and Lam16,Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18,Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28) . In the study by Woods et al., participants’ self-rated level of preparedness increased significantly both immediately post-intervention (coefficient = 2⋅8 points; 95 % CI 1⋅6, 4⋅0 points; P = 0⋅001) and 2 months later (M: 2⋅2, 95 % CI 1⋅0, 3⋅4, P = 0⋅002). Mota et al. investigated the proportion of medical students who believed they could provide dietary counselling as a preventive measure before and after taking a nutrition and metabolism course during a semester. The authors discovered that the percentage of students who agreed they felt capable of providing dietary counselling increased significantly from 31⋅6 % at baseline to 73⋅3 % immediately post-intervention(Reference Mota, Castelo and Morais28). Lang et al. (Reference Lang, Jennings and Lam16) examined preventive medicine residents’ self-rated level of feeling as a competent cook and discovered that 50 % perceived themselves as competent cooks, which increased significantly to 67 % immediately post-intervention.
Participants’ assessments of NEIs
Bert et al. and Rothmans et al. reported in their evaluation of participants’ experiences with the interventions that participants identified the need for the intervention to be extended to all medical students, the nutrition education programme being their best experience over their 4 years of medical education, and rating of the programme as their most preferred course since coming to medical school(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12,Reference Berz, Donovan and Eyllon14) .
Discussion
We conducted a scoping review of the literature and summarised the effects of NEIs on the nutrition-related knowledge, attitude, self-efficacy, dietary and lifestyle habits, and preparedness to provide nutrition care among medical students and residents. We examined twenty-three studies that reported various interventions to improve the nutrition education experiences of medical students and residents, with significant improvements in the outcome variables reported. NEIs, in particular, were effective in improving participants’ nutrition-related knowledge, attitudes and self-efficacy following intervention. Furthermore, as reported in a number of the included studies, the personal dietary and lifestyle habits of medical students and residents improved post-intervention. Finally, the NEIs improved medical students’ and residents’ readiness to provide effective nutrition care in the future. These findings show that by implementing appropriate NEIs, it is possible to address the problem of inadequate nutrition education in the medical curriculum.
The twenty-three included studies in this review demonstrate the growing recognition of the need to improve medical students’ nutrition education experiences. Furthermore, critical stakeholders such as medical educators and researchers are showing an interest in finding solutions to the long-standing issue of inadequate nutrition education in the medical curriculum. It is also worth noting that almost all the interventions were designed to improve important competency outcomes such as nutrition-related knowledge, self-efficacy and attitudes, and personal dietary habits, all of which are required competencies for medical students and residents to provide effective nutrition care.
Nutrition-related knowledge is an important component of providing effective nutrition care, but it is not the only factor or attribute required. It is thus commonplace to find that twenty-one of the included studies designed studies aimed at improving participants’ nutrition-related knowledge, with more than 70 % (n 18) of those studies reporting significant improvements. This finding is consistent with the findings of the realist review reported by Mogre et al. (Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6), in which the majority of the included studies reported improvements in participants’ nutrition-related knowledge. Similarly, Sunguya et al. (Reference Sunguya, Poudel and Mlunde7) discovered in their systematic review that eighteen of the twenty-five included studies reported significant post-nutrition training improvements in health workers’ nutrition knowledge. Despite these gains in knowledge, it is important to note that increased nutrition knowledge alone is insufficient to promote effective nutrition care delivery. This is supported by the findings of Mogre et al. (Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) who found that interventions aimed solely at increasing knowledge were less likely to change nutrition practice behaviour.
Another significant finding of this scoping review was that the included studies demonstrated that medical students and residents had a positive attitude towards nutrition education and saw nutrition care as an important responsibility prior to intervention. The majority of the reviewed studies did not report significant changes in participants’ attitudes towards nutrition care because the authors of the included studies reported that the participants already had positive and favourable attitudes towards nutrition care at the baseline measurements. It is commendable that the NEIs maintained the participants’ positive attitudes, as this is an important determinant of doctors’ ability to provide effective nutrition care(Reference Crowley, Ball and Hiddink3,Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) .
Self-efficacy is an important predictor of nutrition care, so it is not surprising that some of the interventions were designed to improve participants’ nutrition self-efficacy. Previous reviews also discovered a substantial number of included studies that designed interventions to improve this phenomenon or conducting cross-sectional surveys to investigate this phenomenon(Reference Crowley, Ball and Hiddink3,Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) . Eleven of the thirteen studies that looked into this phenomenon found that participants’ nutrition self-efficacy improved significantly after the intervention. This is generally laudable, given that increased self-efficacy is likely to result in increased nutrition care provision. Mogre et al. (Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) reported in their realist review of identifying the mechanisms that demonstrate why some NEIs succeed in improving nutrition care practice that interventions were more likely to result in improving nutrition care practice if they reportedly improved the participants’ nutrition self-efficacy.
In a realist review, Mogre et al. (Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) discovered that doctors will feel more at ease and more likely to provide nutrition care if they themselves practice healthy dietary and lifestyle habits. Several studies included in this review also investigated this concept. Following this concept, nine of the included studies designed interventions to improve the participants’ personal dietary and lifestyle habits, with the majority of them reporting post-intervention improvements in this phenomenon. These findings highlight the importance of improving nutrition education, as it will not only improve the competencies of medical students and residents, but will also help them change their dietary habits, lowering their risk of developing non-communicable diseases.
We also discovered that studies with post-intervention follow-up assessments/measurements found a decrease in knowledge and self-efficacy. This finding is concerning because the majority of the interventions included in this scoping review were single required courses delivered as a one-time event primarily during the preclinical level (some as early as the first and second years of medical school) with no opportunity for reinforcement(Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22). Even though these interventions reported significant changes of the outcomes, the sustainability of these acquired competencies till practice will be difficult in the absence of opportunities for reinforcement. Furthermore, as demonstrated in a previous review, the majority of these interventions focused on increasing participants’ knowledge, which does not always translate into practice(Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6). Nutrition self-efficacy and nutrition care expectations, as noted by Schlair et al.(Reference Schlair, Hanley and Gillespie22) may be difficult to address in the early preclinical years due to a lack of clinical exposure. Integration of nutrition content throughout the entire medical programme, with opportunities for clinical exposure and reinforcement, may be more effective and should be recommended.
Except for one, all the included studies used multiple teaching and learning strategies to achieve the interventions’ intended outcomes. This is consistent with the findings of the systematic reviews published by Mogre et al. (Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6) and Sunguya(Reference Sunguya, Poudel and Mlunde7). The use of multiple teaching and learning strategies is most likely informed by the fact that the studies had multiple outcomes that necessitated the use of various approaches. There is also evidence that interventions that used multiple approaches to meet participants’ educational needs were more likely to report significant changes(Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6). In the findings of a previous review(Reference Mogre, Scherpbier and Stevens6), the use of multiple, non-traditional teaching and learning strategies was found to improve nutrition care competencies as well as nutrition practice behaviour(Reference Mogre, Stevens and Aryee4). Simulated patient cases, group work, role-plays, hands-on demonstrations, group practice, panel discussions, case-based learning, problem-based learning tutorials, computer or web-based cases, student-led debates, self-assessment exercises, interactive lectures and clinical case presentations were some of the non-traditional approaches used in the included studies in this scoping review.
Culinary medicine is a new and innovative approach to nutrition education that has gained popularity in recent years. Six of the included studies used this teaching model, which resulted in significant improvements in students’ confidence in nutrition counselling, home meal preparation, nutrition-related knowledge, personal cooking skills and dietary behaviour(Reference Rothman, Bilici and Mergler12,Reference Lang, Jennings and Lam16,Reference Wood, Gleit and Levine18) . Its success may be due to its ability to provide hands-on, experiential learning opportunities that encourage active participation and strong interprofessional collaboration(Reference Aspry, Van Horn and Carson36,Reference Crawford and Aspry37) . Thus, culinary medicine adds to the toolbox of approaches that could be used to improve the nutrition education experience of medical students and residents.
The strength of this review lies in the use of a comprehensive and extensive search strategy to identify relevant nutrition education interventional studies to provide an evidence account of the impact of the interventions. Despite its strengths, there are some significant limitations to consider. The majority of the included studies provided a limited description of the processes of intervention implementation relating to the ‘what’, ‘why’ and ‘how’ outcomes of the interventions were achieved, making it difficult for successful interventions to be repeated and adopted in other contexts and settings. Furthermore, because we only included articles in English, articles in other languages that may contain very rich information relevant to the purpose of this study may be overlooked. Only a few of the studies included studies had follow-up surveys, which provided limited information about the long-term impact of nutrition education on participants’ competencies, dietary and lifestyle habits.
Conclusion
We found a diverse range of NEIs that used a variety of teaching and learning approaches, as well as a relatively large number of studies that could support a systematic review and meta-analysis, while taking into account the various designs and instruments, and advocating for nutrition education researchers to develop uniform instruments for assessing intervention outcomes. Despite this, the interventions showed promise in improving nutrition-related knowledge, self-efficacy, attitudes and preparedness to provide nutrition care among medical students and residents. The interventions also demonstrated their potential for improving the personal dietary and lifestyle habits of medical students and residents, which is required to potentially provide them with confidence to support individuals in adopting healthy dietary practices. Future NEIs should aim to follow-up with doctors beyond medical school, in order to assess how they use the acquired nutrition care competencies and skills in patient care to improve clinical outcomes.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the University Library for assisting them in locating relevant databases.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
B. Y. A. conceptualised and managed the project, collected, curated, analysed and visualised the data, and wrote the original and revised drafts. V. M. is the supervisor, who accepts full responsibility for the work and/or the study's conduct, has access to the data, and has final say on whether to publish. P. K. G. designed the project and reviewed the draft.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.