The use of antidepressant medication to treat acute bipolar type II depression remains a controversial issue. Reference Bond, Noronha, Kauer-Sant'Anna, Lam and Yatham1 Most practice guidelines recommend treating acute bipolar II depression with either mood stabiliser monotherapy or combined mood stabiliser plus antidepressant therapy. Antidepressant monotherapy is almost universally eschewed. Reference Fountoulakis, Vieta, Sanchez-Moreno, Kaprinis, Goikolea and Kaprinis2,Reference Altshuler, Post, Leverich, Mikalauskas, Rosoff and Ackerman3 The reluctance to use antidepressants for bipolar II depression is because of concerns over manic switch episodes, primarily derived from findings of studies on tricyclic antidepressants in patients with bipolar I depression Reference Ghaemi, Lenox and Baldessarini4,Reference Ghaemi, Klara, Ko, Baldassano, Kontos and Baldessarini5 or from studies of mixed populations of bipolar I, II and schizoaffective disorder. Reference Ghaemi, Lenox and Baldessarini4–Reference Sachs, Nierenberg, Calabrese, Marangell, Wisniewski and Gyulai7 In contrast, controlled trials of antidepressant monotherapy in bipolar II depression have reported good effectiveness and a low manic switch rate. Reference Amsterdam and Shults8–Reference Parker, Tully, Olley and Hadzi-Pavlovic14 Parker et al Reference Parker, Tully, Olley and Hadzi-Pavlovic14 have even argued that some selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors may function as mood stabilisers in bipolar II disorder.
We present results from the first prospective, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, safety and effectiveness trial of antidepressant monotherapy v. mood stabiliser monotherapy for the treatment of acute bipolar II major depressive episodes (trial registration number: NCT00602537). Based upon observations from our preliminary studies, Reference Amsterdam and Shults11–Reference Amsterdam, Wang and Shults13 we hypothesised that short-term venlafaxine monotherapy would be superior to lithium monotherapy in terms of its effects on symptoms of depression and that a similar, and low, manic switch rate would be observed during both treatments.
Method
Participants
This study contained a new cohort of participants distinct from that of prior bipolar II depression studies conducted by our group. Participants were recruited via radio and print advertisements approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Pennsylvania. Approximately 1200 respondents were screened for possible inclusion in the study over a 4.5-year period. Out-patients ⩾18 years old with a DSM-IV-TR diagnosis 15 of bipolar II disorder and current major depressive episode with a 17-item Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) Reference Williams16 score ⩾16 were enrolled. Exclusion criteria were: history of prior mania or psychosis, substance misuse or dependence within the preceding 3 months, non-response to venlafaxine or lithium within the current episode, sensitivity to venlafaxine or lithium, presence of an unstable medical condition, pregnant or nursing, renal or hepatic insufficiency, dementia, malignancy, or concurrent use of antidepressant or mood stabiliser medication.
Procedures
After a description of the study was provided to participants, written informed consent was obtained in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Review Board of the University of Pennsylvania. The study was conducted using good clinical practice guidelines with oversight by the local office of human research and an independent data and safety monitoring board.
A psychiatric diagnosis was verified using the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I disorders (SCID-I). Reference First, Spitzer, Gibbon and Williams17 Medical history, physical examination (including weight and blood pressure), and laboratory tests (including urea nitrogen, creatinine, thyroid panel, pregnancy test in women, screen for drugs of misuse and electrocardiogram) were performed. Best estimates of the number of prior major depressive and hypomanic episodes (as defined by DSM-IV criteria) that occurred since the onset of the disorder were obtained from participants at their initial interview using the SCID interview format.
Structured 28-item HRSD and Young Mania Rating Scale (YMRS) Reference Young, Biggs, Ziegler and Meyer18 measures were obtained by a study clinician masked to treatment condition. Symptom ratings were obtained with attribution as to the origin of the symptom. For example, insomnia could be recorded on the HRSD scale as a depressive symptom; or recorded on the YMRS as a hypomanic symptom; or simultaneously recorded on both the HRSD and YMRS as a mixed hypomanic and depressive episode symptom (if the evaluator attributed the insomnia to both conditions). This ‘real-world’ rating method sometimes resulted in baseline YMRS scores that were above zero. This procedure has been successfully employed in prior bipolar II depression trials as a means of distinguishing hypomanic from depressive symptoms. Reference Amsterdam and Shults8–Reference Amsterdam, Wang and Shults13
Randomisation
Blocked randomisation with varying block sizes was performed in two stages. A block size was randomly selected from among a small set of possible block sizes. Group numbers were then randomly permuted within each block. This procedure was continued until all participants were randomised within each treatment condition. Random numbers were generated and permuted using the random number generator and use written code in Stata Version 13.1 statistical software. All participants, treating clinicians, research coordinators and data managers were masked to the treatment condition. Treatment allocation codes for emergency un-masking were maintained by the investigational drug service at the medical centre. Assurance of masked treatment allocation was obtained from each participant and by each of the two study clinicians at the completion of treatment.
Treatment
Venlafaxine was initiated at 37.5 mg daily and increased to 75 mg daily during week 1 of treatment. The dose was titrated upward in 37.5 mg or 75 mg increments every week (as tolerated) to a maximum dose of 375 mg daily by week 4 of treatment. This dose was then maintained for an additional 8 weeks of therapy. Venlafaxine could be reduced to a minimum of 75 mg daily based upon tolerability and response. Participants unable to tolerate a venlafaxine dose of 75 mg daily were discontinued from the trial.
Lithium was initiated at 300 mg daily and increased to 600 mg daily during week 1 of treatment. A serum lithium level was obtained. Based upon clinical response, tolerability and a serum lithium level of 0.8–1.5 mmol/L, the dose of lithium could be increased to 900 mg daily during week 2 of therapy. Another lithium level was then obtained, and the dose increased to 1200 mg daily during week 3 of therapy based upon clinical response and serum lithium level. This procedure was repeated until a serum lithium level between 0.8 and 1.5 mmol/L was achieved. We anticipated that the majority of patients would attain a therapeutic lithium dose and plasma level by week 4 of therapy. Lithium was then maintained at the maximum tolerated dose for the remaining 8 weeks of the trial. Participants unable to tolerate a dose of 300 mg daily or maintain a sustained minimum lithium level of 0.5 mmol/L were discontinued from the trial. Steady state serum lithium levels were drawn approximately 12 h after the last dose of lithium.
To maintain masked treatment conditions for venlafaxine v. lithium, blood samples for ‘true’ lithium levels (for participants taking double-blind lithium, the lithium group) or ‘sham’ lithium levels (for participants taking double-blind venlafaxine, the venlafaxine group) were obtained from all participants. An unmasked study doctor provided the masked study clinicians with a written report of either a ‘true’ lithium level (for the lithium group) or a ‘sham’ lithium level (for the venlafaxine group). For the latter group, ‘sham’ lithium levels were provided in a fashion that mimicked ‘true’ lithium levels. This allowed the masked clinician to maximise medication dosing of both treatment conditions in a safe and clinically appropriate fashion (whereby only occasional serum lithium levels fell outside the therapeutic range). Short-term zolpidem (⩽10 mg) or trazodone (⩽75 mg) were permitted for severe insomnia up to study week 4 (but rarely employed).
Frequency of treatment-emergent syndromal and subsyndromal hypomania symptoms were assessed via participant telephone reports and clinician-elicited information of mood conversion symptoms during the preceding treatment period performed at each study visit using the YMRS rating. Reference Amsterdam, Luo and Shults10–Reference Amsterdam, Wang, Schwarz and Shults12 As a result of an emerging consensus in the field that bipolar II disorder may be characterised by the presence of frequent subsyndromal hypomania with <4 symptoms lasting <4 days, Reference Nivoli, Colom, Murru, Pacchiarotti, Castro-Loli and González-Pinto19 treatment-emergent hypomania was defined in four ways: (a) syndromal hypomania meeting DSM-IV criteria; (b) type I subsyndromal hypomania with ⩾4 symptoms lasting ⩽3 days; (c) type II subsyndromal hypomania with ⩽3 symptoms lasting ⩾4 days; and (d) type III subsyndromal hypomania with ⩽3 symptoms lasting ⩽3 days. If warranted, participants experiencing hypomania or subsyndromal hypomania underwent double-blind rescue therapy via upward or downward adjustment of medication within the allowable dosage (and lithium level) parameters.
Outcome measures
Outcome measures were obtained at baseline and after treatment weeks 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12. The protocol-designated primary outcome was the frequency of response, defined as a ⩾50% reduction in baseline 17-item HRSD score plus a final clinical global impression severity (CGI/S) Reference Guy20 score of 1 (not depressed), 2 (borderline depressed) or 3 (mildly depressed). Protocol-designated secondary outcomes included the frequency of remission (defined as a final 17-item HRSD score ⩽8 plus a final CGI/S rating score of 1 or 2; change over time in HRSD scores; change over time in clinical global impression change (CGI/C) score; Reference Guy20 change over time in CGI/S score; change over time in YMRS score; frequency of increase in YMRS score over baseline; frequency of increase in YMRS score ⩾8; frequency of syndromal and subsyndromal hypomanic episodes; and change over time in weight and blood pressure. 21
Sample size justification
The study was powered to generate a sufficient sample size to test the hypothesis that venlafaxine monotherapy would result in a significantly greater response rate relative to lithium monotherapy. Based upon estimates of response rates of 60% for venlafaxine v. 30% for lithium monotherapy, there was 85% power to detect a difference this large or larger, with sample sizes of 56 participants per treatment condition.
Statistical procedures
Analyses were conducted on double data entered results under masked conditions according to the intent-to-treat principle on a sample size of 129, with two-sided tests of hypotheses. Descriptive statistics were performed on baseline clinical and demographic variables on all participants and by treatment condition. Significant differences between treatment conditions for specific variables were explored using Fisher's exact test for categorical variables, t-tests for comparisons of means of continuous variables and independent samples median tests for comparisons of continuous variables with outliers. Kappa coefficients were determined to assess the adequacy of masked treatment allocation.
Differential response between treatment groups was ascertained using Fisher's exact test. Differential effects of treatment on continuous measures of change over time for the HRSD, CGI/S, CGI/C and YMRS, respectively, were assessed using generalised estimating equations (GEE) analyses with an autoregressive correlation matrix (AR(1)). In these models, the respective continuous variables were regressed on time (the log of the number of weeks from baseline +1), condition (−0.5 lithium, 0.5 venlafaxine) and the condition×time interaction, which served as the test for differential change on these variables. These models also included, as covariates, the baseline score on the respective variable, as well as the baseline score×time interaction. GEE models were also used to examine changes in weight and blood pressure as a function of condition. Analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS v. 21.
Results
Enrolment
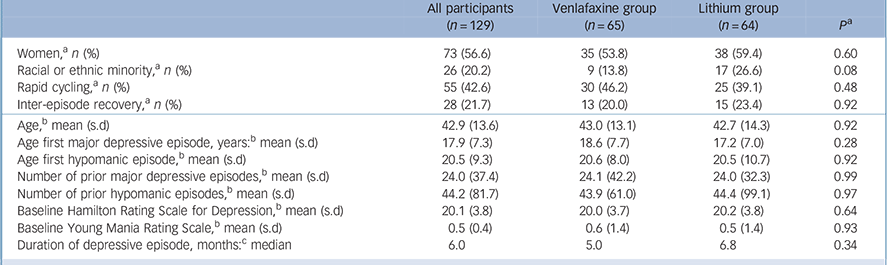
A total of 129 participants were enrolled between 2009 and 2013: 73 (57%) women with mean age of 41.3 years (s.d. = 12.8), range 18–77 and 56 (43%) men with a mean age of 44.9 years (s.d. = 14.6), range 19–71. There were 103 (80%) non-Hispanic White participants, 20 (16%) African American and 6 (4.7%) were Asian- or Latino-American. Sixty-five participants were randomised to venlafaxine and 64 to lithium monotherapy (Fig. 1). There were no significant differences between treatment conditions in baseline demographic or clinical characteristics (Table 1).
Table 1 Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics of study participants
| All participants (n = 129) |
Venlafaxine group (n = 65) |
Lithium group (n = 64) |
P a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Women, a n (%) | 73 (56.6) | 35 (53.8) | 38 (59.4) | 0.60 |
| Racial or ethnic minority, a n (%) | 26 (20.2) | 9 (13.8) | 17 (26.6) | 0.08 |
| Rapid cycling, a n (%) | 55 (42.6) | 30 (46.2) | 25 (39.1) | 0.48 |
| Inter-episode recovery, a n (%) | 28 (21.7) | 13 (20.0) | 15 (23.4) | 0.92 |
| Age, b mean (s.d) | 42.9 (13.6) | 43.0 (13.1) | 42.7 (14.3) | 0.92 |
| Age first major depressive episode, years: b mean (s.d) | 17.9 (7.3) | 18.6 (7.7) | 17.2 (7.0) | 0.28 |
| Age first hypomanic episode, b mean (s.d) | 20.5 (9.3) | 20.6 (8.0) | 20.5 (10.7) | 0.92 |
| Number of prior major depressive episodes, b mean (s.d) | 24.0 (37.4) | 24.1 (42.2) | 24.0 (32.3) | 0.99 |
| Number of prior hypomanic episodes, b mean (s.d) | 44.2 (81.7) | 43.9 (61.0) | 44.4 (99.1) | 0.97 |
| Baseline Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression, Reference Amsterdam, Wang and Shults13 mean (s.d) | 20.1 (3.8) | 20.0 (3.7) | 20.2 (3.8) | 0.64 |
| Baseline Young Mania Rating Scale, Reference Altshuler, Post, Leverich, Mikalauskas, Rosoff and Ackerman3 mean (s.d) | 0.5 (0.4) | 0.6 (1.4) | 0.5 (1.4) | 0.93 |
| Duration of depressive episode, months: c median | 6.0 | 5.0 | 6.8 | 0.34 |
a. P-values are from Fisher's exact test.
b. P-value for comparison of means from independent samples t-test
c. P-value for comparison of medians from independent samples.
Assurance of masked condition
A correct guess of the masked treatment was made by participants 47% of the time (κ = 0.28) and by the two study clinicians 43% (κ = 0.26) and 33% (κ = 0.16) of the time, respectively. Thus, participants and clinicians were adequately masked to treatment allocation.
Masked study drug dosing
The mean maximum venlafaxine dose was 256.55 mg/day (s.d. = 101.07, range 75–375) and 1180.85 mg/day (s.d. = 399.14, range 300–1800) for lithium. The mean maximum lithium level for participants in the lithium group was 0.94 mmol/L (s.d. = 0.38, range 0.30–2.40).
The mean maximum sham venlafaxine dose (i.e. for participants in the lithium group) was 260.11 mg/day (s.d. = 97.11, range 75–375); whereas the mean maximum sham lithium dose (i.e. for those in the venlafaxine group) was 1140 mg/day (s.d. = 299.44, range 300–1500). The average maximum sham lithium level was 1.04 mmol/L (s.d. = 0.24, range 0.40–1.50). Thus, masked drug dosing was uniformly prescribed between treatment conditions (all P>0.10).
Premature treatment discontinuation
In total, 38 participants (30%) who completed the baseline measurement discontinued treatment prematurely: 10 (15.4%) in the venlafaxine group and 28 (43.8%) in the lithium group (P = 0.0004; Fisher's exact test). Although more participants in the lithium group prematurely withdrew from treatment for lack of effectiveness, there were no statistically significant differences between groups for the reasons for premature discontinuation (P<0.34) (Fig. 1).
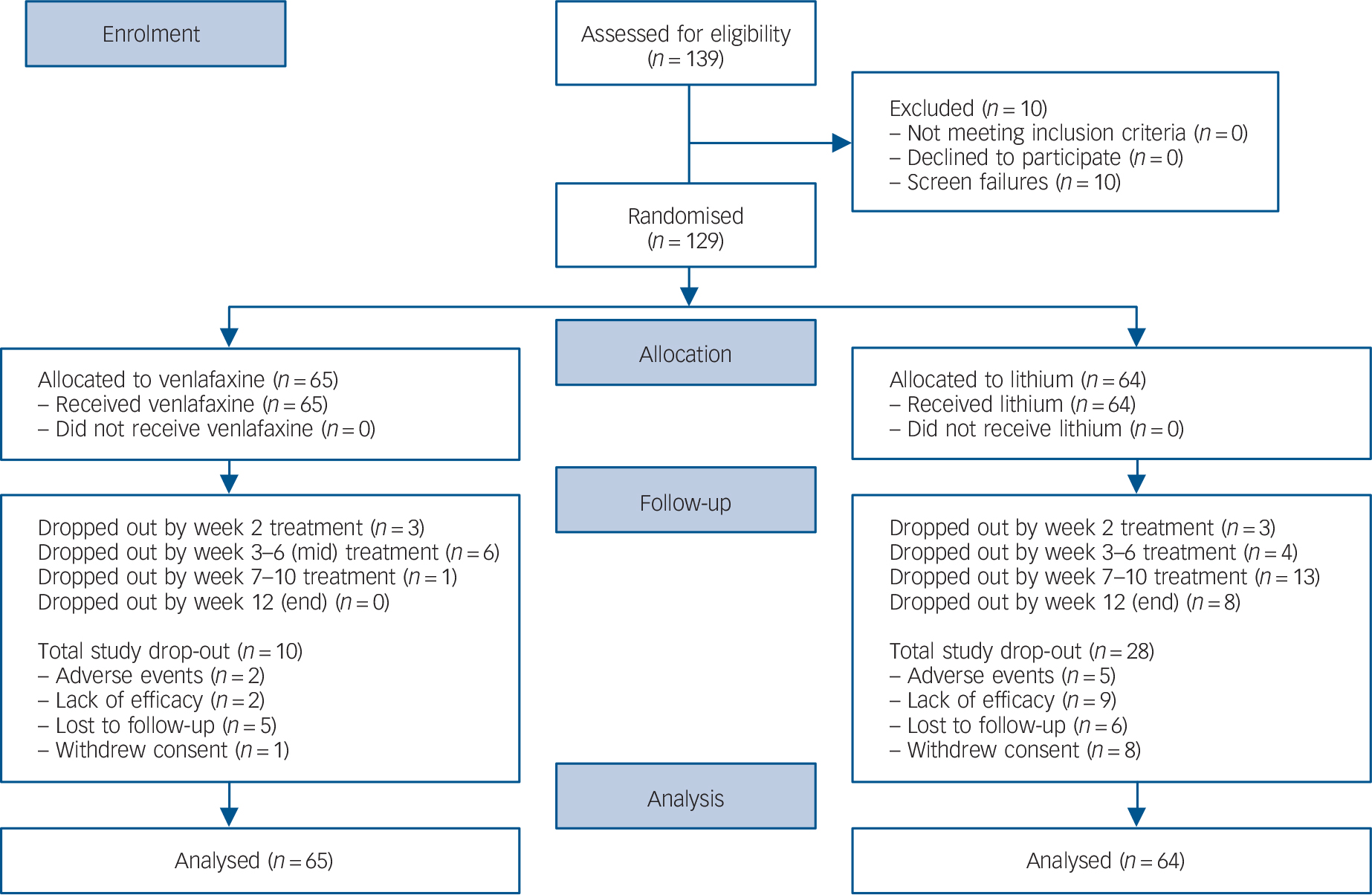
Fig. 1 CONSORT diagram of participants with bipolar II major depression randomised to venlafaxine or lithium.
Primary and secondary outcome measures
A total of 66 participants (51.2%) met criteria for response: 44 (67.7%) in the venlafaxine group v. 22 (34.4%) in the lithium (P = 0.0002; Fisher's exact test).
A total of 56 participants (43.4%) met criteria for remission: 38 (58.5%) in the venlafaxine group v. 18 (28.1%) in the lithium group (P = 0.0007, Fisher's exact test). Relative to lithium, venlafaxine produced a greater reduction in HRSD scores over time (β = −5.32, s.e. = 1.16, 95% CI −7.59 to −3.06, χ2 = 21.19, P<0.0001) (Fig. 2), a greater decline in CGI/S scores (β = −1.05, s.e. = 0.22, 95% CI −1.48 to 0.61), χ2 = 22.33, P<0.0001) and a greater improvement in CGI/C scores (β = −1.31, s.e. = 0.32, 95% CI −1.94 to −0.69, χ2 = 16.95, P<0.0001).
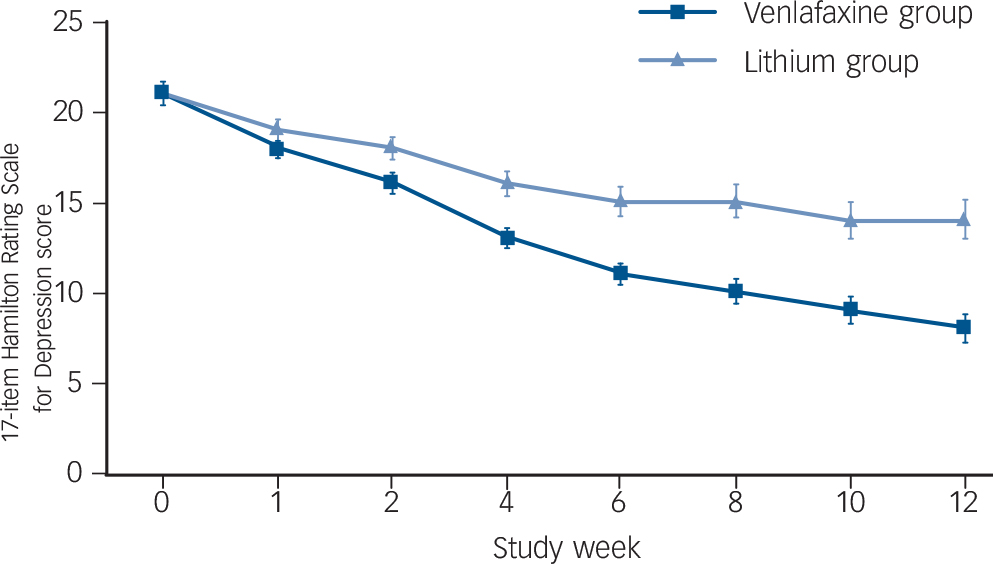
Fig. 2 Estimated change over time in HRSD scores during venlafaxine (n = 65) or lithium (n = 64).
Bars are standard errors of prediction when controlling for baseline severity.
Treatment-emergent hypomanic symptoms
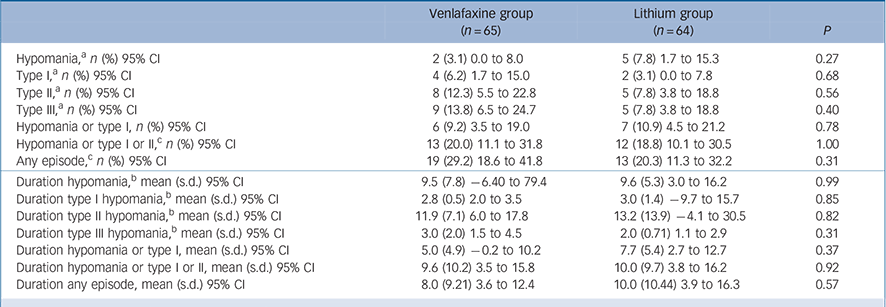
There were no group differences in the change over time in YMRS scores (β = −0.07, s.e. = 0.23, 95% CI −0.52 to 0.39, χ2 = 0.08, P = 0.77). There were also no differences between treatment conditions in the proportion of participants with a YMRS score ⩾8 (P = 0.74843, Fisher's exact test) or the proportion of participants with any increase in YMRS score over baseline score (P = 0.85591, Fisher's exact test). There were no statistically significant differences between treatment conditions in the frequency or duration of treatment-emergent syndromal or subsyndromal hypomanic episodes. The proportion of participants meeting criteria for ‘any’ kind of subsyndromal hypomanic episode was slightly higher (albeit not statistically significant) in the venlafaxine (29.2%; n = 19) v. the lithium group (20.3%; n = 13) (p = 0.31), which translates to a negligible effect size (ϕ = 0.10). Moreover, we note that this modest group difference was not clinically meaningful given that these participants experienced only the briefest and least severe types of subsyndromal hypomanic episodes (Table 2).
Table 2 Frequency and duration (in days) of treatment-emergent hypomanic symptoms
| Venlafaxine group (n = 65) |
Lithium group (n = 64) |
P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypomania, a n (%) 95% CI | 2 (3.1) 0.0 to 8.0 | 5 (7.8) 1.7 to 15.3 | 0.27 |
| Type I, a n (%) 95% CI | 4 (6.2) 1.7 to 15.0 | 2 (3.1) 0.0 to 7.8 | 0.68 |
| Type II, a n (%) 95% CI | 8 (12.3) 5.5 to 22.8 | 5 (7.8) 3.8 to 18.8 | 0.56 |
| Type III, a n (%) 95% CI | 9 (13.8) 6.5 to 24.7 | 5 (7.8) 3.8 to 18.8 | 0.40 |
| Hypomania or type I, n (%) 95% CI | 6 (9.2) 3.5 to 19.0 | 7 (10.9) 4.5 to 21.2 | 0.78 |
| Hypomania or type I or II, c n (%) 95% CI | 13 (20.0) 11.1 to 31.8 | 12 (18.8) 10.1 to 30.5 | 1.00 |
| Any episode, c n (%) 95% CI | 19 (29.2) 18.6 to 41.8 | 13 (20.3) 11.3 to 32.2 | 0.31 |
| Duration hypomania, b mean (s.d.) 95% CI | 9.5 (7.8) −6.40 to 79.4 | 9.6 (5.3) 3.0 to 16.2 | 0.99 |
| Duration type I hypomania, b mean (s.d.) 95% CI | 2.8 (0.5) 2.0 to 3.5 | 3.0 (1.4) −9.7 to 15.7 | 0.85 |
| Duration type II hypomania, b mean (s.d.) 95% CI | 11.9 (7.1) 6.0 to 17.8 | 13.2 (13.9) −4.1 to 30.5 | 0.82 |
| Duration type III hypomania, b mean (s.d.) 95% CI | 3.0 (2.0) 1.5 to 4.5 | 2.0 (0.71) 1.1 to 2.9 | 0.31 |
| Duration hypomania or type I, mean (s.d.) 95% CI | 5.0 (4.9) −0.2 to 10.2 | 7.7 (5.4) 2.7 to 12.7 | 0.37 |
| Duration hypomania or type I or II, mean (s.d.) 95% CI | 9.6 (10.2) 3.5 to 15.8 | 10.0 (9.7) 3.8 to 16.2 | 0.92 |
| Duration any episode, mean (s.d.) 95% CI | 8.0 (9.21) 3.6 to 12.4 | 10.0 (10.44) 3.9 to 16.3 | 0.57 |
a. P-value for comparison of proportion using Fisher's exact test.
b. Comparison of means using Student's t-test.
c. Some of the same patients who experienced type I or hypomanic episodes also experienced type II or type III episodes.
Tolerability and safety
Here was a modest, albeit not clinically meaningful venlafaxine-induced increase in sitting (β = 4.62, s.e. = 2.15, 95% CI 0.40 to 8.84, χ2 = 4.61, P = 0.032) but not standing (β = 3.58, s.e. = 2.06, 95% CI −0.46 to 7.62, χ2 = 3.02, P = 0.08) diastolic blood pressure. There were no significant treatment effects over time on sitting (β = 0.79, s.e. = 2.35, 95% CI −3.82 to 5.39, χ2 = 0.11, P = 0.74) or standing (β = 0.01, s.e. = 2.43, 95% CI −4.74 to 4.77, χ2 = 0.00, P = 1.00) systolic blood pressure.
There was a modest, albeit statistically significant, difference in weight change during monotherapy among treatment conditions (β = −3.45, s.e. = 1.20, 95% CI −5.80 to −1.10, χ2 = 8.20, P = 0.004). Controlling for baseline weight, GEE models predicted an average end of treatment weight of 82.26 kg (s.e. = 0.41, 95% CI 81.46–83.06) for the venlafaxine group and 83.78 kg (s.e. = 0.30, 95% CI 83.18–84.40) for the lithium group. This difference was because of a small weight loss in the venlafaxine group (observed: mean −1.31, s.d. = 3.85, range −14.97 to 9.98 kg; predicted: −1.20, s.e. = 0.42, 95% CI −2.02 to −0.37) relative to the lithium group (observed: mean −0.24, s.d. = 2.49, range −7.26 to 5.90 kg; predicted: 0.37, s.e. = 0.31, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.98).
A total of 6 participants prematurely discontinued treatments for adverse events: three in the venlafaxine group (facial flushing, nausea, sedation, agitation, tachycardia) and three in the lithium group (jitteriness, headache, weight gain, tremor). No serious adverse events occurred.
Discussion
The use of antidepressant monotherapy in bipolar II depression continues to engender controversy. Most expert consensus panels recommend avoiding antidepressant medications and prescribing mood stabiliser monotherapy or prescribing a combination of mood stabiliser plus antidepressant therapy for short-term therapy. However, for bipolar II depression, these recommendations have not been validated and the evidence base supporting them is limited. Reference Fountoulakis, Vieta, Sanchez-Moreno, Kaprinis, Goikolea and Kaprinis2,Reference Pacchiarotti, Bond, Baldessarini, Nolen, Grunze and Licht22
The reluctance to use antidepressants for bipolar II depression is because of concerns over treatment-emergent mania. Manic switch episodes have been reported in studies of tricyclic antidepressants in bipolar I depression or in studies of mixed populations of bipolar I, II, and schizoaffective disorder. Reference Ghaemi, Lenox and Baldessarini4–Reference Sachs, Nierenberg, Calabrese, Marangell, Wisniewski and Gyulai7 For example, one randomised study of patients with bipolar I and II depression reported adequate antidepressant efficacy, but more manic conversions during venlafaxine relative to sertraline or bupropion as adjuncts to a mood stabiliser. Reference Leverich, Altshuler, Frye, Suppes, McElroy and Keck23 A comparative trial of adjunctive bupropion v. desipramine found a higher manic conversion rate during desipramine, but only modest antidepressant effectiveness resulting from both compounds. Reference Sachs, Nierenberg, Calabrese, Marangell, Wisniewski and Gyulai24 A retrospective study of bipolar I and II depression found that 44% of patients with a history of prior mood conversions had at least one mood conversion during antidepressant therapy, and that adjunctive mood stabiliser therapy provided little protection against antidepressant-induced manic symptoms. Reference Kupfer, Chengappa, Gelenberg, Hirschfeld, Goldberg and Sachs25 Vieta et al Reference Vieta, Martinez-Arán, Manuel Goikolea, Torrent, Colom and Benabarre26 reported a higher manic switch rate with venlafaxine relative to paroxetine as adjuncts to mood stabilisers. Finally, Viktorin et al Reference Viktorin, Lichtenstein, Thase, Larsson, Lundholm and Magnusson27 reported a higher manic switch rate in a mixed bipolar I and II population treated with antidepressant monotherapy v. antidepressant plus mood stabiliser therapy. Thus, findings regarding antidepressant use and treatment-emergent manic symptoms in bipolar populations are mixed.
In contrast, controlled trials of antidepressant monotherapy in bipolar II depression have consistently reported good effectiveness and a low manic switch rate. For example, Kupfer et al Reference Kupfer, Carpenter and Frank28 found that patients with bipolar II depression were no more likely than patients with unipolar depression to develop hypomania during acute imipramine monotherapy. Similarly, low manic switch rates have been reported by our group Reference Amsterdam and Shults8–Reference Amsterdam, Luo and Shults10,Reference Amsterdam, Garcia-España, Schweizer, Fawcett, Quitkin and Reimherr29,Reference Amsterdam and Shults30 and others Reference Parker, Tully, Olley and Hadzi-Pavlovic14 during fluoxetine monotherapy relative to lithium and/or placebo. Furthermore, prior studies by our group of venlafaxine monotherapy in bipolar II depression have consistently shown good effectiveness and low manic switch rates. Reference Amsterdam and Shults11–Reference Amsterdam, Wang and Shults13,Reference Amsterdam31 For example, one 6-week study found venlafaxine to be similarly effective in 17 participants with bipolar II disorder and 31 participants with unipolar depression with a more rapid onset of antidepressant activity among the bipolar II group and no manic episodes observed. Reference Amsterdam31 A subsequent 12-week, open-label, randomised study of venlafaxine v. lithium monotherapy showed superior antidepressant effect for venlafaxine relative to lithium with no significant difference in treatment-emergent manic symptom rates. Reference Amsterdam and Shults11 These findings were also supported by a subsequent analysis of individuals with bipolar II depression who were non-responders to lithium crossed-over to venlafaxine monotherapy. Reference Amsterdam, Wang and Shults13
Although in the current study lithium appeared to be less effective than venlafaxine in treating acute depressive symptoms, we would note that there may also be room for other mood stabiliser therapies for the management of bipolar II depression. For example, there is some evidence that lamotrigine monotherapy may be helpful in the treatment of bipolar II depression. Reference Parker and McCraw32
Limitations and future directions
Several caveats should be considered in the interpretation of the present findings. The lack of a placebo comparison group constrains our ability to determine the true efficacy and mood conversion rate of venlafaxine and lithium monotherapy in people with bipolar II depression. It is possible that the effectiveness of lithium may have been higher had the dose of lithium been adjusted in such a fashion as to maintain higher steady-state serum levels at the lower therapeutic range. However, those individuals who continued in treatment and were maintained at lower therapeutic serum lithium levels in both the lithium and sham lithium (i.e. venlafaxine) conditions did so because they demonstrated clinical improvement in their symptoms or they would have been discontinued from the trial as per protocol.
It is possible that the relatively low mood conversion rates seen in both treatment conditions represented background frequency of manic symptoms as a result of the illness rather than true drug-induced phenomena. It is also possible that the lack of difference in the rate of treatment-emergent hypomanic symptoms between treatment conditions it the result of small sample sizes and insufficient statistical power to detect group differences. Thus, findings from this study should not be construed as endorsing a change in recommended clinical practice. Nevertheless, we would note that the estimated change by the end of week 12 in YMRS scores was minimal for both venlafaxine and lithium, with change values that were not clinically meaningful. We also note that this study was not specifically powered to detect a difference in YMRS scores between treatment groups. Failure to identify significant differences in YMRS scores between groups is not proof that such differences do not exist. In fact, when considering ‘any’ subsyndromal episodes occurring during the study, the number of participants experiencing a subsyndromal hypomanic episode was not significantly higher during venlafaxine v. lithium (P = 0.31).
It is possible that the frequency and severity of mood conversion episodes would have been greater in the venlafaxine group if a longer treatment duration had been employed. However, observations from prior studies of antidepressant monotherapy in bipolar II depression showed that most mood conversion episodes occur early in treatment, if they occur at all, and they do not appear to interfere with treatment outcome. Reference Amsterdam and Shults11–Reference Amsterdam, Wang and Shults13 Longer follow-up periods will be needed to confirm these observations. The frequency and severity of manic symptoms in both treatment conditions may also have been greater had symptoms been rated without attribution as to cause, as it is possible that the clinicians underrecognised hypomanic symptoms and overdiagnosed depressive symptoms.
It is also possible that the low mood conversion rate resulted from the selection of a more mildly ill patient population with a low propensity for venlafaxine-induced hypomania, and that the rate of manic symptoms would have been greater in participants with more severe bipolar II disorder. If this were the case, it could account for the low baseline YMRS scores and the low hypomanic switch rate during treatment. We note, however, that the estimated frequencies of hypomanic episodes prior to study enrolment were similar for the venlafaxine and lithium groups and did not differ substantially from those observed in previous bipolar II depression studies. Reference Amsterdam and Shults8–Reference Amsterdam, Wang and Shults13,Reference Amsterdam, Garcia-España, Schweizer, Fawcett, Quitkin and Reimherr29–Reference Amsterdam31 It is possible that certain types of patients (for example, those with a prior history of mood conversions) are most vulnerable to hypomanic switches. Thus, moderator analyses are also needed. Finally, we acknowledge that the results of the current study are preliminary and limited by a modest sample size and that larger comparative trials of antidepressant v. lithium monotherapy in bipolar II depression are needed to confirm the present findings.
Implications
This study demonstrates a significantly greater effectiveness of venlafaxine v. lithium monotherapy for the acute treatment of bipolar II depression with no statistically significant or clinically meaningful difference in the proportion of participants with an increase in YMRS score or treatment-emergent manic symptoms. These findings are in line with those of prior studies in which good effectiveness and low manic switch rates during antidepressant monotherapy of bipolar II depression have been observed. Although not definitive, the present results warrant further investigation and replication by other research groups studying larger bipolar II cohorts.







eLetters
No eLetters have been published for this article.