Cocoa (Theobroma cacao) has been consumed since 600 BC, when the Mayans and Aztecs considered it to be a divine food(Reference Hurst, Tarka and Powis1). Nowadays, cocoa is consumed as chocolate and other confectionery products throughout the world. Cocoa has become of increasing interest due to its high content of polyphenolic compounds, particularly flavonoids – mainly flavanols, including ( − )-epicatechin, (+)-catechin and polymeric procyanidins(Reference Gu, House and Wu2).
Cocoa flavonoids have been linked to beneficial health effects, mainly in chronic diseases such as CVD(Reference Grassi, Desideri and Croce3), but also preventing certain kinds of cancer(Reference Visioli, Bernaert and Corti4), improving brain function(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Casadesus and Lee5) and modulating immune response(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Perez-Cano and Ramirez-Santana6, Reference Ramiro-Puig, Perez-Cano and Ramos-Romero7). The effects of cocoa on the immune system are less well known and most of the studies are performed in vitro showing the modulatory effects of cocoa extracts and its isolated polyphenols on stimulated macrophages(Reference Ono, Takahashi and Kamei8) and lymphocytes(Reference Mao, van de Water and Keen9, Reference Ramiro, Franch and Castellote10). However, these in vitro effects from cocoa cannot be extrapolated to in vivo function since the bioavailability and metabolism of its polyphenols must be taken into account. Monomeric flavanols are stable during gastric transit(Reference Rios, Bennett and Lazarus11), although controversial data in the degradation or not of procyanidin oligomers in the stomach have been reported(Reference Rios, Bennett and Lazarus11, Reference Spencer, Chaudry and Pannala12). After gastric transit, flavanols are absorbed from the jejunal lumen into the epithelial cell layer and metabolised in the intestine in methyl and glucuronide conjugates, with an additional glucuronidation, methylation and sulfation in the liver, both in rats and humans(Reference Urpi-Sarda, Monagas and Khan13, Reference Tomas-Barberan, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos and Marin14). Consequently, flavanol conjugates are found in the plasma and urine of experimental animals after their intake(Reference Baba, Osakabe and Natsume15). Therefore, studies on the bioavailability of flavonoids and their metabolites are now playing a crucial role in the understanding of the health-promoting properties of flavonoids.
We previously found that long-term cocoa intake by healthy young rats enhances antioxidant status in lymphoid organs. Certainly, cocoa intake promotes the progression of immature thymocytes towards more mature T cell stages in the thymus, and modulates lymphocyte functionality in both intestinal and systemic compartments(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Perez-Cano and Ramirez-Santana6, Reference Ramiro-Puig, Urpi-Sarda and Perez-Cano16). Taking into account the effects of a cocoa diet on the immune function, the aim of the present study was to investigate which are the specific epicatechin metabolites from regular 10 % cocoa diet consumption, and their distribution and concentration in young rat lymphoid organs. Furthermore, we have considered the accumulation of metabolites in the testes as a specific target organ since previous studies have shown that flavonoids such as quercetin affect sperm quality(Reference Taepongsorat, Tangpraprutgul and Kitana17).
Methods
Materials
Reagents and standards were obtained from the following sources: methanol and acetonitrile (HPLC grade) from Scharlau (Barcelona, Spain); formic acid, ( − )-epicatechin and ethyl gallate from Sigma-Aldrich-Fluka (St Louis, MO, USA); taxifolin from Extrasynthèse (Genay, France). Standards of epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide, 3′-O-methylepicatechin and 4′-O-methylepicatechin were chemically synthesised and characterised as previously published(Reference Gonzalez-Manzano, Gonzalez-Paramas and Santos-Buelga18, Reference Dueñas, Gonzalez-Manzano and Gonzalez-Paramas19). Ultrapure water (Milli-Q) was obtained from Millipore (Bedford, MA, USA). The extraction cartridge plates were Waters Oasis® Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance (HLB) (3 ml, 60 mg; Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA).
Animals and experimental design
Wistar rats of 2 weeks of age (50 % male, 50 % female), with their dam, were obtained from Harlan (Barcelona, Spain). They were housed in cages of one dam with ten pups on a 12 h light–dark schedule. At the age of 3 weeks, pups were weaned and randomly distributed in two different groups (n 10) receiving, over a period of 3 weeks, (a) chow containing 10 % (w/w) natural cocoa or (b) control chow, and both groups had free access to water. The chow used in the present study was an American Institute of Nutrition (AIN)-93G formulation. The 10 % (w/w) cocoa diet was produced from modified AIN-93G containing 100 g cocoa per kg as described previously(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Urpi-Sarda and Perez-Cano16). Studies were performed in accordance with the institutional guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals, and experimental procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Experimentation of the University of Barcelona (reference 3131).
Phenolic content of chow containing 10 % (w/w) natural cocoa
The determination and quantification of individual phenolic compounds (mg/g) in chow containing 10 % (w/w) natural cocoa were analysed by HPLC as previously described(Reference Andres-Lacueva, Monagas and Khan20) and were found to be 0·34 (sd 0·01) mg ( − )-epicatechin/g, 0·10 (sd 0·004) mg (+)-catechin/g and 0·23 (sd 0·01) mg procyanidin B2/g(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Urpi-Sarda and Perez-Cano16).
Sample preparation
After 3 weeks of the cocoa or control diet, 6-week-old rats were anesthetised and the thymus, spleen, liver, lymphoid nodes and testes were excised. Organs were immediately frozen in liquid N2, and then stored at − 80°C until analysis. Flavan-3-ol metabolites were extracted three times (0·75 ml × 3) with an ice-cold solution of 1·5 m-formic acid with 5 % of methanol, using a Mixer Mill (Retsch MM 300, Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) at 20 Hz during 0·5 min and centrifuged each time at 14 000 rpm. Solid-phase extraction was carried out using HLB cartridges (Waters Corp.). Pooled supernatant fractions were loaded into preconditioned cartridges with the internal standard (ethyl gallate) and washed with 2 ml of 1·5 m-formic acid in water and with 2 ml of 5 % methanol in water. Elution was performed with 2 ml of 0·1 % formic acid in methanol. Eluate was evaporated under an N2 stream and reconstituted with 100 μl of taxifolin, as an additional external standard, dissolved in mobile phase A (0·1 % formic acid in water). Recoveries of the metabolites were 85 (sd 13) % for epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide, 84 (sd 15) % for 3′-O-methylepicatechin, 84 (sd 15) % for 4′-O-methylepicatechin and 88 (sd 10) % for epicatechin aglycone.
Liquid chromatography–tandem MS
Liquid chromatography analyses were performed using an Agilent 1200 (Agilent Technologies, Waldbronn, Germany) equipped with a quaternary pump and a refrigerated autosampler. A triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (API 3000) from Applied Biosystems (PE Sciex, Concord, ON, Canada), equipped with a Turbo IonSpray source operated in the negative-ion mode, was used to obtain the MS/MS data. Liquid chromatography–MS/MS methodology was performed as previously published(Reference Urpi-Sarda, Monagas and Khan13). Optimum MS/MS parameters were optimised for each compound by infusion experiments. Data were collected under the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode, tracking the transition of parent and product ions specific for each compound. The MRM monitored the following transitions in each analysis: epicatechin (289/245), epicatechin glucuronide (465/289), epicatechin sulfate (369/289), epicatechin sulfoglucuronide (545/289), methylepicatechin (303/137), methylepicatechin glucuronide (479/303), methylepicatechin sulfate (383/303), methylepicatechin sulfoglucuronide (559/303), ethyl gallate as an internal standard (197/169) and taxifolin (303/285) as an additional external standard. For quantification purposes, calibration curves were prepared in control tissues, in the range of expected concentrations, by supplementation with known concentrations of epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide: 0, 0·2, 1, 2 and 4 μmol/l. As no other glucuronide conjugates were available, both epicatechin and methylepicatechin glucuronides were quantified and expressed as epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide equivalents. The concentration of metabolites was expressed as mean values with their standard errors of the mean (nmol/g tissue).
Results
After regular 3-week consumption of a 10 % (w/w) cocoa diet, epicatechin metabolites were identified in rat tissue samples. As shown in Fig. 1, one epicatechin glucuronide (MRM 465/289) and two methylepicatechin glucuronides (MRM 479/303) were identified in all tissues after the administration of cocoa. Because the concentrations of these metabolites were in the order of nmol/g tissue, identification was achieved by the product ion scan of the deprotonated molecules in the urine samples of the rats, as previously published(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Urpi-Sarda and Perez-Cano16). Free methyl derivatives of epicatechin and sulfate and sulfoglucuronide conjugates were not detected in these tissues. No epicatechin metabolites were found in animals fed the control diet.

Fig. 1 Representative multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) chromatograms of epicatechin metabolites in the testicles of rats after regular cocoa consumption. (a) Epicatechin-7-O-glucuronide (tentatively) at peak 1 (MRM 465/289). (b) Methylepicatechin glucuronides 1 and 2 at peaks 2 and 3, respectively (MRM 479/303). cps, Counts per s.
The identified metabolites were quantified in the testicles, liver, and in lymphoid tissues including the thymus, spleen and lymphatic nodes (Table 1) by comparison with calibration curves of epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide obtained in control tissues. As far as we know, this is the first time that epicatechin glucuronides have been quantified using an actual standard of epicatechin glucuronide. Previously, metabolites were quantified with regard to the corresponding aglycone(Reference Urpi-Sarda, Monagas and Khan13, Reference Roura, Andres-Lacueva and Estruch21) or after sample hydrolysis(Reference Baba, Osakabe and Natsume15). The highest concentrations of total metabolites, including glucuronide conjugates of epicatechin and methylepicatechin, were found in the thymus, testicles and liver in about 2-fold higher concentrations than in lymphatic nodes and spleen.
Table 1 Distribution of epicatechin metabolites in lymphoid organs and testes after a 10 % (w/w) cocoa diet
(Mean values with their standard errors)
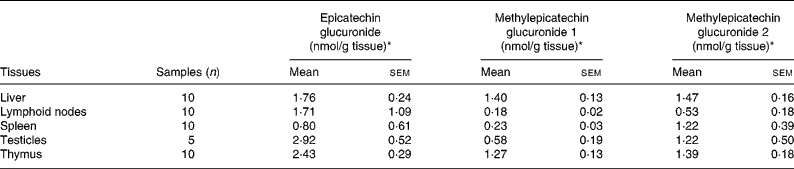
* Expressed as epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide equivalents.
Taking into account the predominant metabolites in these tissues, epicatechin glucuronide was found in the testicles and thymus in higher concentrations than in the liver and lymphoid nodes (about 1·5-fold). Moreover, the liver and thymus were the organs with major amounts of total methylepicatechin glucuronides. Methylepicatechin glucuronide 2 was the major methylepicatechin glucuronide in all the tissues. A significantly lower concentration of this compound was observed in lymphoid nodes with respect to the liver and thymus (about 2·7-fold lower). Methylepicatechin glucuronide 1 was found in the liver and thymus at significantly higher concentrations than in the lymphoid nodes and spleen (about 7- and 6-fold, respectively), while significantly higher concentrations (of only about 2-fold) were observed in the testicles when compared with the liver.
Discussion
The present study shows for the first time that epicatechin metabolites are distributed in young rat lymphoid tissues, testes and liver after exposure to a 10 % (w/w) cocoa diet over 3 weeks. The cocoa used in the present study contained mainly ( − )-epicatechin as the major flavanol. This compound, which is stable during gastric transit(Reference Rios, Bennett and Lazarus11) or comes from the degradation of procyanidin oligomers(Reference Spencer, Chaudry and Pannala12), is absorbed in the jejunal part of the intestine, where it is methylated and glucuronidated, and then, in the liver, undergoes further conjugation(Reference Urpi-Sarda, Monagas and Khan13, Reference Tomas-Barberan, Cienfuegos-Jovellanos and Marin14). In the present study, glucuronide conjugates of epicatechin and methylepicatechin are the main metabolites found in rat tissues. Positive identification of the methyl and glucuronide metabolites of epicatechin detected in the sample tissues was not possible as no standards of all of them are available. In the present study, the glucuronide standard used (epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide) showed shorter retention time than the glucuronide conjugate found in the rat tissues. Natsume et al. (Reference Natsume, Osakabe and Oyama22) purified and elucidated the structure of epicatechin metabolites in human and rat urine after oral administration of ( − )-epicatechin as ( − )-epicatechin-3′-O-glucuronide, 4′-O-methyl-( − )-epicatechin-3′-O-glucuronide, and 4′-O-methyl-( − )-epicatechin 5 or 7-O-glucuronide in human urine, and 3′-O-methyl-( − )-epicatechin, ( − )-epicatechin-7-O-glucuronide, and 3′-O-methyl-( − )-epicatechin-7-O-glucuronide in rat urine. In accordance with Natsume's findings, we tentatively identified the glucuronide conjugate found in tissues of the present study as ( − )-epicatechin-7-O-glucuronide, which is also coherent with its late elution as compared with the epicatechin-5-O-glucuronide standard(Reference Gonzalez-Manzano, Gonzalez-Paramas and Santos-Buelga18). The HPLC elution behaviour of epicatechin-glucuronides found in human subjects and rats reported by Natsume et al. (Reference Natsume, Osakabe and Oyama22) would also be in accordance with our previous results in which, after cocoa consumption, a major glucuronide with higher retention time in human subjects than in rats was found(Reference Urpi-Sarda, Monagas and Khan13). Furthermore, following Natsume's observations, we tentatively identified the major methyl-glucuronide derivative (peak 3, Fig. 1) as 3′-O-methyl-( − )-epicatechin-7-O-glucuronide.
The present results are also consistent with previous studies. Thus, one epicatechin glucuronide and one 3′-O-methylepicatechin glucuronide were found in rat brain tissue after the administration of 100 mg( − )-epicatechin/kg per d over 10 d(Reference El Mohsen, Kuhnle and Rechner23). Furthermore, the metabolites detected in rat tissues in the present study matched the findings of other authors who detected epicatechin-glucuronide and methylepicatechin glucuronide in the plasma, gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidneys of rats after feeding with grapeseed extract(Reference Tsang, Auger and Mullen24). Predominant metabolites in rat plasma and bile after oral administration of ( − )-epicatechin were found to be glucuronide conjugates of 3′-O-methyl-( − )-epicatechin at concentrations about 7-fold higher than other ( − )-epicatechin conjugates that were secondary metabolites(Reference Okushio, Suzuki and Matsumoto25).
There are no studies about the accumulation of epicatechin metabolites in tissues after cocoa intake but the presence of catechins after tea consumption has been reported in several tissues. After maternal exposure to green tea extracts, tea catechins were detected in most of the fetal rat organs (brain, eyes, heart, lungs, kidneys and liver), catechin gallates being more readily taken up than catechins(Reference Chu, Wang and Chu26). Tea catechins and theaflavins were found in the small and large intestine, liver and prostate in conjugated and free forms after administration of black tea to mice(Reference Henning, Aronson and Niu27). After administration of 10 μmol [3H]epicatechin to rats, major amounts of radioactivity were observed in the large intestine and caecum at 24 h, and little radioactivity was observed in the stomach, plasma, small intestine, blood and testes(Reference Abrahamse, Kloots and van Amelsvoort28).
As shown here, epicatechin metabolites were accumulated in concentrations 2-fold higher in the thymus, testes and liver than in lymphoid nodes and spleen. The high amounts of epicatechin metabolites accumulated in the thymus correlate well with previous findings demonstrating an increase in thymus superoxide dismutase and catalase activities after cocoa consumption in rats(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Urpi-Sarda and Perez-Cano16). Furthermore, the fact that the activity of these antioxidant enzymes is not affected in the liver or spleen(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Urpi-Sarda and Perez-Cano16) might be explained by the minor concentration found in the spleen and lower epicatechin glucuronide levels in the liver.
The accumulation of epicatechin metabolites in the thymus could affect lymphocyte composition in this tissue, because a cocoa diet in rats seems to favour T cell development(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Urpi-Sarda and Perez-Cano16). Moreover, although the tissue accumulation was less, rats fed cocoa also exhibited modifications in spleen cell composition and, interestingly, changes in lymphocyte functionality, increasing proliferation rate and decreasing IL-4 secretion(Reference Ramiro-Puig, Perez-Cano and Ramirez-Santana6).
In addition, epicatechin metabolites have also been observed in mesenteric lymph nodes, which belong to gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) compartments. Ramiro-Puig et al. (Reference Ramiro-Puig, Perez-Cano and Ramos-Romero7) demonstrated changes in GALT lymphocyte composition in young rats, such as decreases in the Th percentage and increases in γδ T cell percentage. These changes observed in mesenteric lymph nodes and in lymphocyte composition could result from epicatechin metabolites accumulated in these tissues.
The relatively high concentration of epicatechin metabolites found in the testes, mainly epicatechin glucuronide, shows that an accumulation could occur. To our knowledge, there are not many studies about the accumulation of epicatechin metabolites and their effect on the testes. Previously, a diet containing 0·5 to 2 % cocoa-rich flavanols given to male rats over a period of 2 weeks showed a dose-dependent reduction in oxidative DNA damage in rat testes, as concluded from the decrease of levels in a marker of DNA oxidation, 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine(Reference Orozco, Wang and Keen29). This reduction in oxidative damage in the testes after cocoa intake could be due to the accumulation of epicatechin metabolites in the testes. To our knowledge, only low activities for epicatechin metabolites have been described until now. With regards to structure–activity, it has been shown that substitution of the hydroxyls in the catechol B-ring of catechins results in a decrease of the antioxidant activity(Reference Dueñas, Gonzalez-Manzano and Gonzalez-Paramas19). Flavonoids containing an unsubstituted catechol B-ring do not inhibit NADPH oxidase, but scavenge the superoxide radical(Reference Steffen, Gruber and Schewe30, Reference Natsume, Osakabe and Yasuda31), suggesting that the o-dihydroxy catechol structure in the B-ring is the most important factor for protecting against oxidation(Reference Natsume, Osakabe and Yasuda31). The O-methylation of catechol arrangement in the B-ring converts the flavonoid to an NADPH oxidase inhibitor(Reference Steffen, Gruber and Schewe30), affording a plausible explanation for the improvement of endothelial function and bioavailability of NO in human subjects after the intake of epicatechin products(Reference Heiss, Schroeter and Balzer32).
In conclusion, in the present study we show that epicatechin is absorbed from the complex matrix that is cocoa, it is metabolised in glucuronide and methylated forms and distributed in the testicles, liver and lymphoid organs (thymus, spleen and lymphoid nodes). Further studies should be done to evaluate the bioactivity of these metabolites, which could contribute to explain whether that accumulation is related to the biological activity associated with flavanol consumption.
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by national grants: Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología (CICYT; projects AGL 2004-08378-C02-01, AGL 2005-002823, AGL 2009-13906-C02-01 and AGL 2007-66108-C04-02) and Grupo Consolider-Ingenio 2010 Fun-C-Food (CSD2007-063). M. U.-S. and S. R.-R. are thankful for a Ph.D student FPI fellowship, N. K. is thankful for a Ph.D student FPU fellowship and R. L. is thankful for a postdoctoral programme Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (FIS; no. CD06/00161) from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation.
The authors' contributions were as follows: M. C. and C. A.-L., conception and design; M. U.-S., N. K., R. L., C. S.-B. and S. G.-M., analysis and interpretation of the data; M. U.-S., E. R.-P., N. K. and S. R.-R., drafting of the article; M. U.-S., E. R.-P., N. K., S. R.-R., M. C., R. L., C. S.-B., S. G.-M. and C. A.-L., critical revision and final approval; M. C. and C. A.-L., initiation and design of the study and obtaining the funding.
The authors are not aware of any personal, financial, political or academic conflict of interest.




