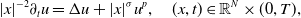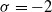1. Introduction
The goal of this short note is to establish some properties of solutions to the following non-homogeneous heat equation with a weighted source
in the range of exponents
![]() $\sigma \ge -2$
,
$\sigma \ge -2$
,
![]() $p\gt 1$
. More precisely, we consider radially symmetric solutions to (1.1), and we aim at establishing conditions on the exponents
$p\gt 1$
. More precisely, we consider radially symmetric solutions to (1.1), and we aim at establishing conditions on the exponents
![]() $p$
,
$p$
,
![]() $\sigma$
, and on the (radially symmetric) initial condition
$\sigma$
, and on the (radially symmetric) initial condition
implying either finite time blow-up of solutions to Eq. (1.1) or global existence and decay as
![]() $t\to \infty$
, and in the latter case giving a decay rate and (under suitable conditions) the large time behaviour as
$t\to \infty$
, and in the latter case giving a decay rate and (under suitable conditions) the large time behaviour as
![]() $t\to \infty$
. In order to ease the notation, we denote the radial variable by
$t\to \infty$
. In order to ease the notation, we denote the radial variable by
![]() $r=|x|$
, and we recall here for the readers’ convenience that, in this variable, Eq. (1.1) writes
$r=|x|$
, and we recall here for the readers’ convenience that, in this variable, Eq. (1.1) writes
where, as usual, the subscripts indicate derivatives.
Eq. (1.1) features a competition between a non-homogeneous heat equation with a weight (usually referred as density function by physical reasons)
![]() $\varrho (x)=|x|^{-2}$
and a source term also weighted with a power
$\varrho (x)=|x|^{-2}$
and a source term also weighted with a power
![]() $|x|^{\sigma }$
. Equations in the more general form
$|x|^{\sigma }$
. Equations in the more general form
for suitable functions
![]() $\varrho (x)$
(usually called density function) and
$\varrho (x)$
(usually called density function) and
![]() $q(x)$
have been proposed in several models in radial transport in confined plasma [Reference Kamin and Rosenau11, Reference Kamin and Rosenau12], in the theory of combustion with a power-law temperature depending on the source [Reference Kurdyumov, Kurkina, Malinetskii and Samarskii13, Reference Kurdyumov and Kurkina14], or (without the reaction term) in a kinetic model that describes the evolution of the probability density of the number of firms in a society [Reference Toscani26], just to give some examples. Such models justified a development of the mathematical theory of equations in the form (1.4), with or without a reaction term, and such equations are usually referred in literature under the name of non-homogeneous heat equation (if
$q(x)$
have been proposed in several models in radial transport in confined plasma [Reference Kamin and Rosenau11, Reference Kamin and Rosenau12], in the theory of combustion with a power-law temperature depending on the source [Reference Kurdyumov, Kurkina, Malinetskii and Samarskii13, Reference Kurdyumov and Kurkina14], or (without the reaction term) in a kinetic model that describes the evolution of the probability density of the number of firms in a society [Reference Toscani26], just to give some examples. Such models justified a development of the mathematical theory of equations in the form (1.4), with or without a reaction term, and such equations are usually referred in literature under the name of non-homogeneous heat equation (if
![]() $m=1$
) or non-homogeneous porous medium equation (if
$m=1$
) or non-homogeneous porous medium equation (if
![]() $m\gt 1$
).
$m\gt 1$
).
It has been thus noticed that densities
![]() $\varrho (x)$
either being exactly equal to
$\varrho (x)$
either being exactly equal to
![]() $|x|^{-2}$
or behaving as
$|x|^{-2}$
or behaving as
![]() $|x|^{-2}$
as
$|x|^{-2}$
as
![]() $|x|\to \infty$
are critical for the dynamic properties of (1.4). Indeed, restricting ourselves to our case of interest
$|x|\to \infty$
are critical for the dynamic properties of (1.4). Indeed, restricting ourselves to our case of interest
![]() $m=1$
, a number of works have addressed the mathematical analysis of solutions to Eq. (1.4), but the case
$m=1$
, a number of works have addressed the mathematical analysis of solutions to Eq. (1.4), but the case
![]() $\varrho (x)\sim |x|^{-2}$
has been avoided therein, see for example [Reference Li and Xiang16, Reference de Pablo, Reyes and Sánchez22, Reference Zheng and Wang27], where densities behaving like
$\varrho (x)\sim |x|^{-2}$
has been avoided therein, see for example [Reference Li and Xiang16, Reference de Pablo, Reyes and Sánchez22, Reference Zheng and Wang27], where densities behaving like
![]() $|x|^{-\sigma }$
are considered for either
$|x|^{-\sigma }$
are considered for either
![]() $\sigma \in (0,2)$
or
$\sigma \in (0,2)$
or
![]() $\sigma \gt 2$
. A similar criticality of
$\sigma \gt 2$
. A similar criticality of
![]() $\varrho (x)=|x|^{-2}$
has been observed also in the porous medium case
$\varrho (x)=|x|^{-2}$
has been observed also in the porous medium case
![]() $m\gt 1$
in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez7, Reference Kamin, Reyes and Vázquez10, Reference Kurdyumov, Kurkina, Malinetskii and Samarskii13, Reference Kurdyumov and Kurkina14, Reference Martynenko and Tedeev17–Reference Meglioli and Punzo20, Reference Reyes and Vázquez24], to quote but a few references dealing with the mathematical study of (1.4).
$m\gt 1$
in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez7, Reference Kamin, Reyes and Vázquez10, Reference Kurdyumov, Kurkina, Malinetskii and Samarskii13, Reference Kurdyumov and Kurkina14, Reference Martynenko and Tedeev17–Reference Meglioli and Punzo20, Reference Reyes and Vázquez24], to quote but a few references dealing with the mathematical study of (1.4).
Regarding the equation (1.4) with
![]() $\varrho (x)=|x|^{-2}$
, the authors established well-posedness and large time behaviour of solutions to (1.4) with
$\varrho (x)=|x|^{-2}$
, the authors established well-posedness and large time behaviour of solutions to (1.4) with
![]() $m=1$
and
$m=1$
and
![]() $q(x)=0$
in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez6] (generalizing then the technique also to the non-homogeneous porous medium equation without source term in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez7]), these properties being deduced by exploiting a transformation mapping its radially symmetric solutions to those of a standard heat equation. Afterwards, Toscani described in [Reference Toscani26] a kinetic model leading to a rather similar equation and employing an alternative transformation in its study. More recently, the authors considered in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez8] a general class of equations with two weights, namely
$q(x)=0$
in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez6] (generalizing then the technique also to the non-homogeneous porous medium equation without source term in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez7]), these properties being deduced by exploiting a transformation mapping its radially symmetric solutions to those of a standard heat equation. Afterwards, Toscani described in [Reference Toscani26] a kinetic model leading to a rather similar equation and employing an alternative transformation in its study. More recently, the authors considered in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez8] a general class of equations with two weights, namely
and established a number of qualitative properties of their solutions (such as Fujita-type exponents, second critical exponent limiting between finite time blow-up and global existence, classification of self-similar solutions) by introducing and then exploiting a number of transformations, at the level of radially symmetric solutions, mapping solutions to Eq. (1.5) to solutions to some other reaction–diffusion equations whose properties were well-established prior to this research. However, Eq. (1.1) (which is actually a limiting case for the ranges considered in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez8]) has been left out of the study in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez8] due to the fact that the main bunch of transformations therein were not applicable to it.
The present work is thus devoted to fill in this gap by establishing some qualitative properties related to the evolution of radially symmetric solutions to Eq. (1.1). This is done by means of a transformation detailed in Section 2 mapping such solutions to Eq. (1.1) to solutions to a generalised Fisher–KPP-type equation, which allows us to translate features of the latter equation to the former one by undoing the transformation. With the aid of it, we are able to give conditions on
![]() $p\gt 1$
and on the radially symmetric initial condition
$p\gt 1$
and on the radially symmetric initial condition
![]() $u_0$
such that the solution to the Cauchy problem (1.1)–(1.2) either blows up in a finite time
$u_0$
such that the solution to the Cauchy problem (1.1)–(1.2) either blows up in a finite time
![]() $T\in (0,\infty )$
or is global in time and decays to zero as
$T\in (0,\infty )$
or is global in time and decays to zero as
![]() $t\to \infty$
; in the latter, we also give the large time behaviour of such solutions.
$t\to \infty$
; in the latter, we also give the large time behaviour of such solutions.
In order to fix the notation employed throughout this short note, let us introduce here two critical exponents who will play a significant role in the forthcoming study,
the second being usually referred to as the Sobolev critical exponent in the context of the reaction–diffusion equation
see for example [Reference Filippas and Tertikas4, Reference Mukai and Seki21], both of them being equal by convention to
![]() $+\infty$
in dimension
$+\infty$
in dimension
![]() $N\in \{1,2\}$
. In particular, the analysis in Sections 3 and 4.1 shows that
$N\in \{1,2\}$
. In particular, the analysis in Sections 3 and 4.1 shows that
![]() $p_c(\sigma )$
is the Fujita-type exponent to Eq. (1.1) in dimension
$p_c(\sigma )$
is the Fujita-type exponent to Eq. (1.1) in dimension
![]() $N\geq 3$
, while
$N\geq 3$
, while
![]() $p_s(\sigma )$
appears in relation to the behaviour of a new explicit solution being a separatrix between global existence and blow-up, see Section 4.2.
$p_s(\sigma )$
appears in relation to the behaviour of a new explicit solution being a separatrix between global existence and blow-up, see Section 4.2.
Before passing to the precise statements and proofs, we stress that we do not aim at constructing a functional-analytic theory of Eq. (1.1) in this note. However, in the particular framework of radial symmetry, the well-posedness for Eq. (1.3) follows directly from the well-posedness property of the resulting Fisher–KPP-type equation by undoing the transformation in Section 2. We refrain here from entering the more detailed discussion of a notion of weak solution and the well-posedness, regularity and other properties of Eq. (1.1) without the assumption of radial symmetry.
2. The transformation
The following transformation, which is the main tool in our analysis, has been announced (but not employed in any form) in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez8]. We describe it below in more detail. Let
![]() $u$
be a radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1), that is, a solution to Eq. (1.3). In a first step, set
$u$
be a radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1), that is, a solution to Eq. (1.3). In a first step, set
After performing straightforward calculations, we deduce that
![]() $w(y,t)$
solves the equation
$w(y,t)$
solves the equation
with
Observe that, for
![]() $N\geq 3$
, the previous constants can be written in terms of the critical exponents (1.6) as
$N\geq 3$
, the previous constants can be written in terms of the critical exponents (1.6) as
In a second step, we introduce the function
![]() $\Psi$
as follows:
$\Psi$
as follows:
with
![]() $K$
defined in (2.3). Then, the function
$K$
defined in (2.3). Then, the function
![]() $\Psi$
solves the following one-dimensional generalised Fisher–KPP-type equation
$\Psi$
solves the following one-dimensional generalised Fisher–KPP-type equation
We may thus compose the transformations (2.1) and (2.4) to map (1.3) into (2.5). Let us also notice here that the initial conditions for the two equations are mapped in the following way
a fact that is useful when dealing with Cauchy problems. Since the well posedness of (2.5) is a standard property in the sense of classical solutions (for the uniqueness and comparison principle, even in more general cases, see for example [Reference Diaz and Kamin2, Reference Ducrot and Jin3]), and the transformations (2.1) and (2.4) preserve the order between two solutions at a fixed point
![]() $(r,t)$
, we obtain local existence and uniqueness for (1.3) by undoing the previous transformations (with solutions that remain classical except, in some cases, at
$(r,t)$
, we obtain local existence and uniqueness for (1.3) by undoing the previous transformations (with solutions that remain classical except, in some cases, at
![]() $r=0$
). The properties of solutions to (2.5) needed in the forthcoming analysis have been deduced by the authors (in a framework of a more general study) in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9]. We are thus in a position to translate these features into properties of solutions to Eq. (1.3) by undoing the previous changes of variable (2.1)–(2.4).
$r=0$
). The properties of solutions to (2.5) needed in the forthcoming analysis have been deduced by the authors (in a framework of a more general study) in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9]. We are thus in a position to translate these features into properties of solutions to Eq. (1.3) by undoing the previous changes of variable (2.1)–(2.4).
3. Finite time blow-up for
 $1\lt \boldsymbol{p}\lt \boldsymbol{p}_\boldsymbol{c}(\sigma )$
or
$1\lt \boldsymbol{p}\lt \boldsymbol{p}_\boldsymbol{c}(\sigma )$
or
 $\boldsymbol{N} \boldsymbol{\in \{1,2\}}$
$\boldsymbol{N} \boldsymbol{\in \{1,2\}}$
The result below, together with the one in the next Section 4, show that the exponent
![]() $p_c(\sigma )$
introduced in (1.6) plays the role of a Fujita-type exponent for Eq. (1.3).
$p_c(\sigma )$
introduced in (1.6) plays the role of a Fujita-type exponent for Eq. (1.3).
Theorem 3.1.
Let
![]() $\sigma \gt -2$
and either
$\sigma \gt -2$
and either
![]() $N\in \{1,2\}$
or
$N\in \{1,2\}$
or
![]() $N\geq 3$
and
$N\geq 3$
and
![]() $p\in (1,p_c(\sigma ))$
. Then any non-trivial, non-negative radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1) blows up in finite time.
$p\in (1,p_c(\sigma ))$
. Then any non-trivial, non-negative radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1) blows up in finite time.
Proof. Notice that any of the conditions
![]() $N\in \{1,2\}$
or
$N\in \{1,2\}$
or
![]() $N\geq 3$
and
$N\geq 3$
and
![]() $1\lt p\lt p_c(\sigma )$
implies
$1\lt p\lt p_c(\sigma )$
implies
![]() $K_0\lt 0$
, where
$K_0\lt 0$
, where
![]() $K_0$
is defined in (2.3). Thus, (2.5) features in this case a sum of reaction terms. It is rather obvious then that any solution to (2.5) blows up in finite time, but for the sake of completeness we give some details. Let
$K_0$
is defined in (2.3). Thus, (2.5) features in this case a sum of reaction terms. It is rather obvious then that any solution to (2.5) blows up in finite time, but for the sake of completeness we give some details. Let
![]() $\Psi$
be a non-negative, non-trivial solution to (2.5). Then, in particular,
$\Psi$
be a non-negative, non-trivial solution to (2.5). Then, in particular,
![]() $\Psi$
is a supersolution to the linear equation
$\Psi$
is a supersolution to the linear equation
Let
![]() $\underline {\Psi }$
be the solution to (3.1) with initial condition
$\underline {\Psi }$
be the solution to (3.1) with initial condition
![]() $\underline {\Psi }(z,0)=\Psi (z,0)$
and introduce
$\underline {\Psi }(z,0)=\Psi (z,0)$
and introduce
Then,
![]() $\Phi (z,0)=\underline {\Psi }(z,0)$
and
$\Phi (z,0)=\underline {\Psi }(z,0)$
and
![]() $\Phi$
are solutions to the classical one-dimensional heat equation. It then follows from standard results related to the heat equation that
$\Phi$
are solutions to the classical one-dimensional heat equation. It then follows from standard results related to the heat equation that
has at least an exponential time growth on compact subsets. By comparison, the same holds true for
![]() $\Psi$
. But, on the other hand,
$\Psi$
. But, on the other hand,
![]() $\Psi$
is also a supersolution to
$\Psi$
is also a supersolution to
and, since it has an exponential time growth, one can readily see that the energy
becomes negative for some
![]() $t_0\gt 0$
sufficiently large. Considering this
$t_0\gt 0$
sufficiently large. Considering this
![]() $t_0$
as initial time for comparison, finite time blow-up of
$t_0$
as initial time for comparison, finite time blow-up of
![]() $\Psi$
is then ensured by [Reference Quittner and Souplet23, Theorem 17.6] and the comparison principle. We end the proof by undoing the transformations (2.1)–(2.4).
$\Psi$
is then ensured by [Reference Quittner and Souplet23, Theorem 17.6] and the comparison principle. We end the proof by undoing the transformations (2.1)–(2.4).
4. Transition from decay to blow-up for
 $\boldsymbol{p} \boldsymbol{\gt} \boldsymbol{p}_\boldsymbol{c}\boldsymbol{(\sigma )}$
$\boldsymbol{p} \boldsymbol{\gt} \boldsymbol{p}_\boldsymbol{c}\boldsymbol{(\sigma )}$
In the range
![]() $p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, we observe that
$p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, we observe that
![]() $K_0\gt 0$
and thus (2.5) is a generalised Fisher–KPP type equation, featuring a competition between a (linear) absorption term and a source term. As established in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9], this fact leads to more interesting situations than in the previous section. Throughout this section, we fix
$K_0\gt 0$
and thus (2.5) is a generalised Fisher–KPP type equation, featuring a competition between a (linear) absorption term and a source term. As established in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9], this fact leads to more interesting situations than in the previous section. Throughout this section, we fix
![]() $N\geq 3$
and
$N\geq 3$
and
![]() $p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, the case
$p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, the case
![]() $p=p_c(\sigma )$
being considered in the next section.
$p=p_c(\sigma )$
being considered in the next section.
4.1 Decay and large time behaviour
Let us first remark that, for
![]() $p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, Eq. (1.1) admits a stationary solution (with a singularity at
$p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, Eq. (1.1) admits a stationary solution (with a singularity at
![]() $x=0$
),
$x=0$
),
In this section, we establish the decay rate as
![]() $t\to \infty$
and the large time behaviour of solutions whose initial condition lies below the singular stationary solution (4.1). Furthermore, we establish at least a class of solutions that remain bounded globally in time, completing the characterisation of
$t\to \infty$
and the large time behaviour of solutions whose initial condition lies below the singular stationary solution (4.1). Furthermore, we establish at least a class of solutions that remain bounded globally in time, completing the characterisation of
![]() $p_c(\sigma )$
as the Fujita-type exponent for Eq. (1.1).
$p_c(\sigma )$
as the Fujita-type exponent for Eq. (1.1).
Theorem 4.1.
Let
![]() $N\geq 3$
,
$N\geq 3$
,
![]() $\sigma \gt -2$
and
$\sigma \gt -2$
and
![]() $p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
. Let
$p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
. Let
![]() $u_0$
be an initial condition as in (1.2) such that
$u_0$
be an initial condition as in (1.2) such that
![]() $u_0(r)\lt S(r)$
for any
$u_0(r)\lt S(r)$
for any
![]() $r\in (0,\infty )$
. Then
$r\in (0,\infty )$
. Then
-
1. There exists
 $C=C(p,\sigma, u_0)\gt 0$
such that the solution
$C=C(p,\sigma, u_0)\gt 0$
such that the solution
 $u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
$u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
 $u_0$
satisfies
(4.2)
$u_0$
satisfies
(4.2) \begin{align} u(r,t)\leq Cr^{-(\sigma +2)/(p-1)}e^{-K_0t}, \quad (r,t)\in (0,\infty )\times (0,\infty ). \end{align}
\begin{align} u(r,t)\leq Cr^{-(\sigma +2)/(p-1)}e^{-K_0t}, \quad (r,t)\in (0,\infty )\times (0,\infty ). \end{align}
-
2. If, furthermore, the following weighted integral is finite
(4.3)then the large time behaviour of \begin{align} M(u_0) \,:\!=\, \int _0^{\infty }r^{(\sigma +2)/(p-1)-1}u_0(r)\,dr\lt \infty, \end{align}
\begin{align} M(u_0) \,:\!=\, \int _0^{\infty }r^{(\sigma +2)/(p-1)-1}u_0(r)\,dr\lt \infty, \end{align}
 $u$
as
$u$
as
 $t\to \infty$
is given by
(4.4)with uniform convergence over compact sets in
$t\to \infty$
is given by
(4.4)with uniform convergence over compact sets in \begin{align} \lim \limits _{t\to \infty }t^{1/2}\left [e^{K_0t}r^{(\sigma +2)/(p-1)}u(r,t)-G(r+Kt,t)\right ]=0, \end{align}
\begin{align} \lim \limits _{t\to \infty }t^{1/2}\left [e^{K_0t}r^{(\sigma +2)/(p-1)}u(r,t)-G(r+Kt,t)\right ]=0, \end{align}
 $(0,\infty )$
, where
$(0,\infty )$
, where
 $K_0$
,
$K_0$
,
 $K$
are defined in (2.3) and
is the Gaussian kernel.
$K$
are defined in (2.3) and
is the Gaussian kernel. \begin{align*} G(\zeta, t)=\frac {M(u_0)}{\sqrt {4\pi t}}e^{-\zeta ^2/4t}, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} G(\zeta, t)=\frac {M(u_0)}{\sqrt {4\pi t}}e^{-\zeta ^2/4t}, \end{align*}
-
3. If, moreover,
 $\textrm { supp}\,u_0\subset {\mathbb {R}}^N\setminus \{0\}$
is a compact set, then
$\textrm { supp}\,u_0\subset {\mathbb {R}}^N\setminus \{0\}$
is a compact set, then
 $u(0,t)=0$
for any
$u(0,t)=0$
for any
 $t\in (0,\infty )$
and in particular
$t\in (0,\infty )$
and in particular
 $u(t)\in L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}}^N)$
for any
$u(t)\in L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}}^N)$
for any
 $t\gt 0$
.
$t\gt 0$
.
Proof. Let
![]() $u_0$
be as in the statement. We infer from (2.6) that, by applying the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), the radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
$u_0$
be as in the statement. We infer from (2.6) that, by applying the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), the radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
![]() $u_0$
is mapped into the solution to (2.5) with an initial condition
$u_0$
is mapped into the solution to (2.5) with an initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
satisfying
$\Psi _0$
satisfying
We derive from (4.5) and [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9, Theorem 1] that the solution
![]() $\Psi$
to (2.5) with initial condition
$\Psi$
to (2.5) with initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
is global, decays to zero as
$\Psi _0$
is global, decays to zero as
![]() $t\to \infty$
and, more precisely, there is
$t\to \infty$
and, more precisely, there is
![]() $C\gt 0$
(depending on
$C\gt 0$
(depending on
![]() $\|\Psi _0\|_{\infty }$
) such that
$\|\Psi _0\|_{\infty }$
) such that
The decay estimate (4.2) follows then from the previous inequality by undoing (2.1)–(2.4). Assume next that (4.3) holds true. We infer from (2.1) to (2.4) that this condition entails
thus
![]() $\Psi _0\in L^1({\mathbb {R}})$
and
$\Psi _0\in L^1({\mathbb {R}})$
and
![]() $M(u_0)=\|\Psi _0\|_1$
. Then, [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9, Theorem 1] ensures that
$M(u_0)=\|\Psi _0\|_1$
. Then, [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9, Theorem 1] ensures that
with
We then deduce the large time behaviour (4.4) (with uniform convergence) from (4.6) by undoing the transformation (2.1)–(2.4). Finally, assume that the initial condition
![]() $u_0$
is compactly supported in a set contained in
$u_0$
is compactly supported in a set contained in
![]() ${\mathbb {R}}^N\setminus \{0\}$
, or, in terms of radial variables, in a compact interval of
${\mathbb {R}}^N\setminus \{0\}$
, or, in terms of radial variables, in a compact interval of
![]() $(0,\infty )$
. We then deduce from (2.6) that the initial condition
$(0,\infty )$
. We then deduce from (2.6) that the initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
to (2.5) is compactly supported in
$\Psi _0$
to (2.5) is compactly supported in
![]() $({-}\infty, \infty )$
. Let
$({-}\infty, \infty )$
. Let
![]() $\tilde {\Psi }$
be the solution to the Cauchy problem
$\tilde {\Psi }$
be the solution to the Cauchy problem
Since
![]() $\|\Psi _0\|_{\infty }\lt K_0^{1/(p-1)}$
, it readily follows by the comparison principle that
$\|\Psi _0\|_{\infty }\lt K_0^{1/(p-1)}$
, it readily follows by the comparison principle that
Moreover,
![]() $\tilde {\Psi }$
is a supersolution to (2.5). Indeed, taking into account (4.7) and (4.8), we compute
$\tilde {\Psi }$
is a supersolution to (2.5). Indeed, taking into account (4.7) and (4.8), we compute
for any
![]() $(z,t)\in {\mathbb {R}}\times (0,\infty )$
. It thus follows from the comparison principle applied to (2.5) that
$(z,t)\in {\mathbb {R}}\times (0,\infty )$
. It thus follows from the comparison principle applied to (2.5) that
![]() $\Psi (z,t)\leq \tilde {\Psi }(z,t)$
for any
$\Psi (z,t)\leq \tilde {\Psi }(z,t)$
for any
![]() $(z,t)\in {\mathbb {R}}\times (0,\infty )$
. Moreover, by standard results for the heat equation, there is a mapping
$(z,t)\in {\mathbb {R}}\times (0,\infty )$
. Moreover, by standard results for the heat equation, there is a mapping
![]() $t\mapsto z(t)$
and a positive constant
$t\mapsto z(t)$
and a positive constant
![]() $C(t)$
such that we have
$C(t)$
such that we have
whence, by undoing the transformations (2.1)–(2.4), we obtain that
![]() $u(0,t)=0$
for any
$u(0,t)=0$
for any
![]() $t\gt 0$
and that the solution
$t\gt 0$
and that the solution
![]() $u$
remains bounded in a neighbourhood of
$u$
remains bounded in a neighbourhood of
![]() $r=0$
. This fact, together with (4.2), ensures that
$r=0$
. This fact, together with (4.2), ensures that
![]() $u(t)\in L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}}^N)$
for any
$u(t)\in L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}}^N)$
for any
![]() $t\in (0,\infty )$
, completing the proof.
$t\in (0,\infty )$
, completing the proof.
4.1.1 Discussion
The previous statement does not take into account the behaviour of the function
![]() $t\mapsto u(r,t)$
at
$t\mapsto u(r,t)$
at
![]() $r=0$
when we start with data such that
$r=0$
when we start with data such that
![]() $u_0(0)\gt 0$
. Indeed, a priori, the result of Theorem4.1 stays true even when
$u_0(0)\gt 0$
. Indeed, a priori, the result of Theorem4.1 stays true even when
![]() $u(r,t)$
might blow-up in the sense of developing a vertical asymptote at
$u(r,t)$
might blow-up in the sense of developing a vertical asymptote at
![]() $r=0$
with a weaker singularity than
$r=0$
with a weaker singularity than
![]() $r^{-(\sigma +2)/(p-1)}$
while remaining bounded (and decaying in time as in the statement) at any point
$r^{-(\sigma +2)/(p-1)}$
while remaining bounded (and decaying in time as in the statement) at any point
![]() $x\in {\mathbb {R}}^N$
with
$x\in {\mathbb {R}}^N$
with
![]() $r=|x|\gt 0$
. This property is related, by the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), with the question of whether, if
$r=|x|\gt 0$
. This property is related, by the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), with the question of whether, if
![]() $\Psi$
is a solution to (2.5) such that
$\Psi$
is a solution to (2.5) such that
then its tail is preserved at later times, that is,
Up to our knowledge, there is no reference proving such a result for the precise decay (4.9), but it is established in [Reference Herraiz5] that tails of the form
![]() $\Psi (z)\sim A|z|^{-\alpha }$
as
$\Psi (z)\sim A|z|^{-\alpha }$
as
![]() $|z|\to \infty$
are preserved during the evolution for solutions to the reaction–diffusion equation
$|z|\to \infty$
are preserved during the evolution for solutions to the reaction–diffusion equation
and by comparison, the upper bound for the tail remains in force for (2.5). It is very likely (as suggested by the author of [Reference Herraiz5], who claims that the techniques therein apply for more general decays) that the same property holds true for initial conditions decaying with a precise exponential tail as
![]() $z\to -\infty$
(such as, for example, (4.9)). However, due to the very technical and lengthy character of the proofs in [Reference Herraiz5], we refrain from developing this subject in the present note.
$z\to -\infty$
(such as, for example, (4.9)). However, due to the very technical and lengthy character of the proofs in [Reference Herraiz5], we refrain from developing this subject in the present note.
4.2 A new explicit solution as a separatrix between decay and blow-up
In this section, we introduce a new explicit radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1) and show that it is a separatrix between decay and blow-up, in some conditions. As we shall see, the Sobolev critical exponent
![]() $p_s(\sigma )$
defined in (1.6) plays a significant role. We start from the following stationary solution to (2.5) obtained in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9, Section 2.1]
$p_s(\sigma )$
defined in (1.6) plays a significant role. We start from the following stationary solution to (2.5) obtained in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9, Section 2.1]
which, by undoing first the transformation (2.4), leads to
and finally, by undoing also (2.1), gives the following explicit radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1)
Observe that
![]() $U$
is an eternal solution to Eq. (1.1), in the sense that it is well defined for
$U$
is an eternal solution to Eq. (1.1), in the sense that it is well defined for
![]() $t\in ({-}\infty, \infty )$
. By employing the identity
$t\in ({-}\infty, \infty )$
. By employing the identity
we obtain from (4.11) that, for any
![]() $t\gt 0$
,
$t\gt 0$
,
where, as usual, the equivalence symbol
![]() $\sim$
means that the quotient between the two sides tends to one in the specified limit, and we recall that
$\sim$
means that the quotient between the two sides tends to one in the specified limit, and we recall that
![]() $K$
and
$K$
and
![]() $K_0$
are defined in (2.3). We observe that
$K_0$
are defined in (2.3). We observe that
![]() $U$
always decays as
$U$
always decays as
![]() $r\to \infty$
, but the local behaviour at
$r\to \infty$
, but the local behaviour at
![]() $r=0$
and the variation with respect to time are more interesting. Indeed, we notice on the one hand that
$r=0$
and the variation with respect to time are more interesting. Indeed, we notice on the one hand that
thus
![]() $p=p_s(\sigma )$
is critical with respect to the behaviour at
$p=p_s(\sigma )$
is critical with respect to the behaviour at
![]() $r=0$
. On the other hand, studying the variation with respect to time of the expression
$r=0$
. On the other hand, studying the variation with respect to time of the expression
we observe that it behaves in different ways in dynamic inner sets
![]() $\{0\lt r\lt e^{-Kt}\}$
and in dynamic outer sets
$\{0\lt r\lt e^{-Kt}\}$
and in dynamic outer sets
![]() $\{r\gt e^{-Kt}\}$
, for
$\{r\gt e^{-Kt}\}$
, for
![]() $t\gt 0$
. Gathering the previous analysis, we have:
$t\gt 0$
. Gathering the previous analysis, we have:
-
• if
 $p\in (p_c(\sigma ),p_s(\sigma ))$
, then
$p\in (p_c(\sigma ),p_s(\sigma ))$
, then
 $U$
is a singular solution, presenting a vertical asymptote at
$U$
is a singular solution, presenting a vertical asymptote at
 $r=0$
. Moreover, according to (4.12) and the negativity of
$r=0$
. Moreover, according to (4.12) and the negativity of
 $K$
in this range, the solution
$K$
in this range, the solution
 $U$
decays with respect to time in the inner set
$U$
decays with respect to time in the inner set
 $\mathcal {I}$
and increases with respect to time in the outer set
$\mathcal {I}$
and increases with respect to time in the outer set
 $\mathcal {O}$
defined below:(4.13)
$\mathcal {O}$
defined below:(4.13) \begin{align} \mathcal {I} \,:\!=\, \{(r,t)\in (0,\infty )^2\,:\, 0\lt r\lt e^{-Kt}\}, \quad \mathcal {O} \,:\!=\, \{(r,t)\in (0,\infty )^2\,:\, e^{-Kt}\lt r\}. \end{align}
\begin{align} \mathcal {I} \,:\!=\, \{(r,t)\in (0,\infty )^2\,:\, 0\lt r\lt e^{-Kt}\}, \quad \mathcal {O} \,:\!=\, \{(r,t)\in (0,\infty )^2\,:\, e^{-Kt}\lt r\}. \end{align}
-
• if
 $p=p_s(\sigma )$
, then we also observe that
$p=p_s(\sigma )$
, then we also observe that
 $K=0$
and thus
$K=0$
and thus
 $U$
is a stationary solution to Eq. (1.1) with
$U$
is a stationary solution to Eq. (1.1) with
 $U(0,t)=U(0)=[2K_0(p+1)]^{1/(p-1)}$
.
$U(0,t)=U(0)=[2K_0(p+1)]^{1/(p-1)}$
. -
• if
 $p\gt p_s(\sigma )$
, then we have
$p\gt p_s(\sigma )$
, then we have
 $U(0,t)=0$
for any
$U(0,t)=0$
for any
 $t\gt 0$
. Moreover, according to (4.12) and the positivity of
$t\gt 0$
. Moreover, according to (4.12) and the positivity of
 $K$
in this range, the solution
$K$
in this range, the solution
 $U$
increases with respect to time in the inner set
$U$
increases with respect to time in the inner set
 $\mathcal {I}$
and decreases with respect to time in the outer set
$\mathcal {I}$
and decreases with respect to time in the outer set
 $\mathcal {O}$
introduced in (4.13).
$\mathcal {O}$
introduced in (4.13).
In order to better illustrate the previous behaviour in inner and outer sets, for the readers’ convenience, we plot the solution
![]() $U$
at different times in Figure 1.
$U$
at different times in Figure 1.

Figure 1. The solution
![]() $U$
plotted at different times. Experiments for
$U$
plotted at different times. Experiments for
![]() $\sigma =1$
,
$\sigma =1$
,
![]() $N=4$
,
$N=4$
,
![]() $p=3.5$
, respectively,
$p=3.5$
, respectively,
![]() $p=4.5$
, where
$p=4.5$
, where
![]() $p_s(\sigma )=4$
.
$p_s(\sigma )=4$
.
The explicit solution
![]() $U$
plays the role of a separatrix between finite time blow-up and time decay. This is made precise in the following statement, where, as usual,
$U$
plays the role of a separatrix between finite time blow-up and time decay. This is made precise in the following statement, where, as usual,
![]() $U_0(r)=U(r,0)$
,
$U_0(r)=U(r,0)$
,
![]() $r\in [0,\infty )$
.
$r\in [0,\infty )$
.
Theorem 4.2.
Let
![]() $N\geq 3$
,
$N\geq 3$
,
![]() $p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
and
$p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
and
![]() $u_0$
be as in (1.2).
$u_0$
be as in (1.2).
-
(a) If
(4.14)then the radially symmetric solution \begin{align} \inf \limits _{r\in (0,\infty )}\frac {u_0(r)}{U_0(r)}=\kappa _0\gt 1, \end{align}
\begin{align} \inf \limits _{r\in (0,\infty )}\frac {u_0(r)}{U_0(r)}=\kappa _0\gt 1, \end{align}
 $u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
$u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
 $u_0$
blows up in finite time.
$u_0$
blows up in finite time.
-
(b) If
(4.15)then the radially symmetric solution \begin{align} \sup \limits _{r\in (0,\infty )}\frac {u_0(r)}{U_0(r)}=\kappa ^0\lt 1, \end{align}
\begin{align} \sup \limits _{r\in (0,\infty )}\frac {u_0(r)}{U_0(r)}=\kappa ^0\lt 1, \end{align}
 $u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
$u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
 $u_0$
decays to zero as
$u_0$
decays to zero as
 $t\to \infty$
on compact subsets in
$t\to \infty$
on compact subsets in
 ${\mathbb {R}}^N\setminus \{0\}$
and behaves as indicated in Theorem
4.1
.
${\mathbb {R}}^N\setminus \{0\}$
and behaves as indicated in Theorem
4.1
.
Proof. Let
![]() $\Psi$
be the solution to (2.5) obtained from
$\Psi$
be the solution to (2.5) obtained from
![]() $u$
through the transformation (2.1)–(2.4) and
$u$
through the transformation (2.1)–(2.4) and
![]() $\Psi _0(z)=\Psi (z,0)$
its initial condition. We deduce from (2.6) that the conditions (4.14), respectively (4.15), become
$\Psi _0(z)=\Psi (z,0)$
its initial condition. We deduce from (2.6) that the conditions (4.14), respectively (4.15), become
where we recall that
![]() $\overline {\Psi }$
is the explicit stationary solution to (2.5) introduced in (4.10). An application of [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9, Theorem 3.2], which states that
$\overline {\Psi }$
is the explicit stationary solution to (2.5) introduced in (4.10). An application of [Reference Iagar and Sánchez9, Theorem 3.2], which states that
![]() $\overline {\Psi }$
is a separatrix between finite time blow-up on the one hand and global existence and decay as
$\overline {\Psi }$
is a separatrix between finite time blow-up on the one hand and global existence and decay as
![]() $t\to \infty$
on the other hand, completes the proof.
$t\to \infty$
on the other hand, completes the proof.
5. The special cases
 $\boldsymbol{p} = \boldsymbol{p}_\boldsymbol{c} \boldsymbol{(\sigma )}$
and
$\boldsymbol{p} = \boldsymbol{p}_\boldsymbol{c} \boldsymbol{(\sigma )}$
and
 $\sigma =-2$
$\sigma =-2$
These two critical cases are connected by the common fact that, either if
![]() $\sigma \gt -2$
and
$\sigma \gt -2$
and
![]() $p=p_c(\sigma )$
or if
$p=p_c(\sigma )$
or if
![]() $\sigma =-2$
and
$\sigma =-2$
and
![]() $p\gt 1$
arbitrary, we have
$p\gt 1$
arbitrary, we have
![]() $K_0=0$
and thus (2.5) becomes the standard reaction–diffusion equation
$K_0=0$
and thus (2.5) becomes the standard reaction–diffusion equation
which is well understood nowadays (see, for example, the monograph [Reference Quittner and Souplet23] and references therein). The first case of this section, dealing with the exponent
![]() $p=p_c(\sigma )$
, is simpler and is to be considered more as a discussion, while we extend more the analysis of the second case,
$p=p_c(\sigma )$
, is simpler and is to be considered more as a discussion, while we extend more the analysis of the second case,
![]() $\sigma =-2$
.
$\sigma =-2$
.
Case 1.
![]() $\mathbf {p=p_c(\sigma )}$
. Observe that, in this case, an initial condition such that
$\mathbf {p=p_c(\sigma )}$
. Observe that, in this case, an initial condition such that
![]() $u_0(r)\gt 0$
for
$u_0(r)\gt 0$
for
![]() $r\in (0,\delta )$
is mapped by (2.6) into an initial condition
$r\in (0,\delta )$
is mapped by (2.6) into an initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
for (5.1) with an exponential tail as
$\Psi _0$
for (5.1) with an exponential tail as
![]() $z\to -\infty$
. Moreover, recalling the Fujita exponent
$z\to -\infty$
. Moreover, recalling the Fujita exponent
![]() $p_F=3$
of (5.1), we observe that
$p_F=3$
of (5.1), we observe that
We thus infer from the theory in [23, Chapter 18] that, if
![]() $\sigma \leq 2(N-3)$
, then
$\sigma \leq 2(N-3)$
, then
![]() $p_c(\sigma )\leq p_F$
and thus any non-trivial and non-negative solution to (5.1) blows-up in finite time, a property that is inherited by any non-trivial radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1) through the transformation (2.1)-(2.4). On the contrary, if
$p_c(\sigma )\leq p_F$
and thus any non-trivial and non-negative solution to (5.1) blows-up in finite time, a property that is inherited by any non-trivial radially symmetric solution to Eq. (1.1) through the transformation (2.1)-(2.4). On the contrary, if
![]() $\sigma \gt 2(N-3)$
, then
$\sigma \gt 2(N-3)$
, then
![]() $p_c(\sigma )\gt p_F$
and thus there are both solutions that blow-up in finite time and that exist globally. For example, [23, Theorem 20.1] ensures that small initial conditions
$p_c(\sigma )\gt p_F$
and thus there are both solutions that blow-up in finite time and that exist globally. For example, [23, Theorem 20.1] ensures that small initial conditions
![]() $\Psi _0$
will produce global solutions to (5.1) remaining below a Gaussian profile, whose decay rate as
$\Psi _0$
will produce global solutions to (5.1) remaining below a Gaussian profile, whose decay rate as
![]() $z\to -\infty$
is faster than the one given by (4.9) and by undoing the transformation (2.1)–(2.4) we obtain thus global solutions to Eq. (1.1). Moreover, the other results in [23, Chapter 20] can be readily translated into properties of radially symmetric solutions to Eq. (1.1).
$z\to -\infty$
is faster than the one given by (4.9) and by undoing the transformation (2.1)–(2.4) we obtain thus global solutions to Eq. (1.1). Moreover, the other results in [23, Chapter 20] can be readily translated into properties of radially symmetric solutions to Eq. (1.1).
Remark. Let us stress here that, contrary to the standard reaction–diffusion equations, the Fujita-type exponent
![]() $p=p_c(\sigma )$
for Eq. (1.1) is not always included in the range where any solution blows up in finite time, as explained above.
$p=p_c(\sigma )$
for Eq. (1.1) is not always included in the range where any solution blows up in finite time, as explained above.
Case 2.
![]() $\mathbf {\sigma =-2}$
and
$\mathbf {\sigma =-2}$
and
![]() $\mathbf {p\gt 1}$
. We observe that, in this case, (2.1) reduces to setting
$\mathbf {p\gt 1}$
. We observe that, in this case, (2.1) reduces to setting
![]() $r=e^y$
,
$r=e^y$
,
![]() $y\in {\mathbb {R}}$
. Then, according to the behaviour of the initial condition at
$y\in {\mathbb {R}}$
. Then, according to the behaviour of the initial condition at
![]() $r=0$
, we have the following result, slightly reminding of the properties of the non-homogeneous heat equation in [6] (where
$r=0$
, we have the following result, slightly reminding of the properties of the non-homogeneous heat equation in [6] (where
![]() $B(u_0)$
designs the blow-up set of the solution with initial condition
$B(u_0)$
designs the blow-up set of the solution with initial condition
![]() $u_0$
):
$u_0$
):
Theorem 5.1.
Let
![]() $u_0$
be as in (1.2).
$u_0$
be as in (1.2).
-
(a) If
 $u_0(0)=A\gt 0$
, then the solution
$u_0(0)=A\gt 0$
, then the solution
 $u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
$u$
to Eq. (1.1) with initial condition
 $u_0$
blows up in finite time. Moreover, if
$u_0$
blows up in finite time. Moreover, if
 $u_0$
is decreasing with respect to
$u_0$
is decreasing with respect to
 $r$
, then
$r$
, then
 $u$
blows up only at
$u$
blows up only at
 $r=0$
, that is,
$r=0$
, that is,
 $B(u_0)=\{0\}$
.
$B(u_0)=\{0\}$
. -
(b) Let
 $q_c=(p-1)/2$
and pick
$q_c=(p-1)/2$
and pick
 $q\geq \min \{1,q_c\}$
. Then, if
$q\geq \min \{1,q_c\}$
. Then, if
 $u_0$
satisfies
(5.2)for some
$u_0$
satisfies
(5.2)for some \begin{align} \int _{0}^{\infty }\frac {u_0^q(r)}{r}\,dr\lt \infty \end{align}
\begin{align} \int _{0}^{\infty }\frac {u_0^q(r)}{r}\,dr\lt \infty \end{align}
 $q\geq q_c$
, there exists a unique, classical, radially symmetric solution
$q\geq q_c$
, there exists a unique, classical, radially symmetric solution
 $u$
to Eq. (1.1) defined on a maximal time
$u$
to Eq. (1.1) defined on a maximal time
 $t\in (0,T(u_0))$
(where
$t\in (0,T(u_0))$
(where
 $T(u_0)\in (0,\infty ]$
) which also satisfies
(5.3)Moreover, if
$T(u_0)\in (0,\infty ]$
) which also satisfies
(5.3)Moreover, if \begin{align} \int _{0}^{\infty }\frac {u^q(r,t)}{r}\,dr\lt \infty, \quad t\in (0,T(u_0)). \end{align}
\begin{align} \int _{0}^{\infty }\frac {u^q(r,t)}{r}\,dr\lt \infty, \quad t\in (0,T(u_0)). \end{align}
 $u_0$
satisfies (5.2) and is non-decreasing for
$u_0$
satisfies (5.2) and is non-decreasing for
 $r\in (0,1)$
, then
$r\in (0,1)$
, then
 $u(0,t)=0$
for any
$u(0,t)=0$
for any
 $t\in (0,T(u_0))$
.
$t\in (0,T(u_0))$
.
Proof. (a) By applying (2.6), the initial condition
![]() $u_0$
is mapped into an initial condition
$u_0$
is mapped into an initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
to (5.1) such that
$\Psi _0$
to (5.1) such that
![]() $\lim \limits _{z\to -\infty }\Psi _0(z)=A\gt 0$
. It follows then from the classical work [Reference Lee and Ni15] that the solution
$\lim \limits _{z\to -\infty }\Psi _0(z)=A\gt 0$
. It follows then from the classical work [Reference Lee and Ni15] that the solution
![]() $\Psi$
to (5.1) with initial condition
$\Psi$
to (5.1) with initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
blows up in a finite time
$\Psi _0$
blows up in a finite time
![]() $T\in (0,\infty )$
. If, furthermore,
$T\in (0,\infty )$
. If, furthermore,
![]() $u_0$
is decreasing with respect to
$u_0$
is decreasing with respect to
![]() $r$
, then also
$r$
, then also
![]() $\Psi _0$
will be decreasing with respect to
$\Psi _0$
will be decreasing with respect to
![]() $z\in {\mathbb {R}}$
. We then readily deduce that the function
$z\in {\mathbb {R}}$
. We then readily deduce that the function
![]() $z\mapsto \Psi (z,t)$
is decreasing with respect to
$z\mapsto \Psi (z,t)$
is decreasing with respect to
![]() $z$
for any
$z$
for any
![]() $t\in (0,T)$
. Indeed, letting
$t\in (0,T)$
. Indeed, letting
![]() $w=\Psi _z$
, we differentiate with respect to
$w=\Psi _z$
, we differentiate with respect to
![]() $z$
in (5.1) and derive the equation satisfied by
$z$
in (5.1) and derive the equation satisfied by
![]() $w$
, that is,
$w$
, that is,
a linear equation solved by
![]() $w=0$
. By comparison, since
$w=0$
. By comparison, since
![]() $\Psi _{0,z}\leq 0$
, it follows that
$\Psi _{0,z}\leq 0$
, it follows that
![]() $\Psi _z(z,t)\leq 0$
for any
$\Psi _z(z,t)\leq 0$
for any
![]() $z\in {\mathbb {R}}$
,
$z\in {\mathbb {R}}$
,
![]() $t\in (0,T)$
. We then infer from [Reference Shimojo25, Theorem 1] that
$t\in (0,T)$
. We then infer from [Reference Shimojo25, Theorem 1] that
![]() $\Psi$
blows up only at
$\Psi$
blows up only at
![]() $-\infty$
, whence, by undoing the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), we conclude that
$-\infty$
, whence, by undoing the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), we conclude that
![]() $u$
blows up only at
$u$
blows up only at
![]() $r=0$
as
$r=0$
as
![]() $t\to T$
, as claimed.
$t\to T$
, as claimed.
(b) By applying the transformation (2.6) with
![]() $\sigma =-2$
, the initial condition
$\sigma =-2$
, the initial condition
![]() $u_0$
is mapped into an initial condition
$u_0$
is mapped into an initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
to (5.1), while the condition (5.2) becomes
$\Psi _0$
to (5.1), while the condition (5.2) becomes
thus
![]() $\Psi _0\in L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}})\cap L^q({\mathbb {R}})$
. Standard well-posedness results for (5.1) (see for example [Reference Quittner and Souplet23, Section 15]) ensure that there is a classical solution
$\Psi _0\in L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}})\cap L^q({\mathbb {R}})$
. Standard well-posedness results for (5.1) (see for example [Reference Quittner and Souplet23, Section 15]) ensure that there is a classical solution
![]() $\Psi$
to (5.1), defined on a maximal existence time
$\Psi$
to (5.1), defined on a maximal existence time
![]() $T(\Psi _0)=T(u_0)\in (0,\infty ]$
, such that
$T(\Psi _0)=T(u_0)\in (0,\infty ]$
, such that
![]() $t\mapsto \Psi (t)$
belongs to
$t\mapsto \Psi (t)$
belongs to
![]() $L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}})\cap L^q({\mathbb {R}})$
for any
$L^{\infty }({\mathbb {R}})\cap L^q({\mathbb {R}})$
for any
![]() $t\in (0,T(u_0))$
. By undoing the transformations (2.4) and
$t\in (0,T(u_0))$
. By undoing the transformations (2.4) and
![]() $r=e^y$
, we deduce the existence of a radially symmetric solution
$r=e^y$
, we deduce the existence of a radially symmetric solution
![]() $u$
to Eq. (1.1) defined on
$u$
to Eq. (1.1) defined on
![]() $(0,T(u_0))$
and satisfying (5.3), as claimed. Moreover, if
$(0,T(u_0))$
and satisfying (5.3), as claimed. Moreover, if
![]() $u_0$
is radially non-decreasing in
$u_0$
is radially non-decreasing in
![]() $(0,1)$
, then the initial condition
$(0,1)$
, then the initial condition
![]() $\Psi _0$
to (5.1) obtained by the transformation (2.6) belongs to
$\Psi _0$
to (5.1) obtained by the transformation (2.6) belongs to
![]() $L^q({\mathbb {R}})$
and is non-decreasing on
$L^q({\mathbb {R}})$
and is non-decreasing on
![]() $({-}\infty, 0)$
. It then follows that
$({-}\infty, 0)$
. It then follows that
![]() $\Psi _0(z)\to 0$
as
$\Psi _0(z)\to 0$
as
![]() $z\to -\infty$
and, by similar arguments as at the end of the proof of Part (a) above, the same property stays true for
$z\to -\infty$
and, by similar arguments as at the end of the proof of Part (a) above, the same property stays true for
![]() $t\in (0,T(u_0))$
. By undoing the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), we find that
$t\in (0,T(u_0))$
. By undoing the transformation (2.1)–(2.4), we find that
![]() $u(0,t)=0$
for any
$u(0,t)=0$
for any
![]() $t\in (0,T)$
, and the proof is complete.
$t\in (0,T)$
, and the proof is complete.
Remark.
-
(i) In particular, a very important aspect contained in Theorem 5.1 is the existence of non-trivial positive solutions to Eq. (1.1) with
 $\sigma =-2$
, a fact which is in stark contrast with the full non-existence of any non-trivial and non-negative solution to the equationobtained in [Reference Abdellaoui, Colorado and Peral1, Theorem 4.7] (with
$\sigma =-2$
, a fact which is in stark contrast with the full non-existence of any non-trivial and non-negative solution to the equationobtained in [Reference Abdellaoui, Colorado and Peral1, Theorem 4.7] (with \begin{align*} \partial _tu=\Delta u+|x|^{-2}u^p, \quad p\gt 1, \end{align*}
\begin{align*} \partial _tu=\Delta u+|x|^{-2}u^p, \quad p\gt 1, \end{align*}
 $\gamma =0$
in the notation therein). It thus appears that the presence of the critical density function
$\gamma =0$
in the notation therein). It thus appears that the presence of the critical density function
 $|x|^{-2}$
in front of
$|x|^{-2}$
in front of
 $u_t$
is the decisive feature that guarantees the existence of positive solutions.
$u_t$
is the decisive feature that guarantees the existence of positive solutions.
-
(ii) The outcome of Part (b) in Theorem 5.1 is also in strong contrast with the evolution of the standard heat equation starting from similar initial conditions
 $u_0$
, for which the solutions become positive at every point immediately. This difference is another effect of the singular density
$u_0$
, for which the solutions become positive at every point immediately. This difference is another effect of the singular density
 $|x|^{-2}$
at
$|x|^{-2}$
at
 $x=0$
, a fact also noticed in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez6] in the absence of a reaction term. As a particular case of part (b), we also infer that, if there is
$x=0$
, a fact also noticed in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez6] in the absence of a reaction term. As a particular case of part (b), we also infer that, if there is
 $\delta \gt 0$
such that
$\delta \gt 0$
such that
 $u_0(r)=0$
for
$u_0(r)=0$
for
 $r\in (0,\delta )$
, then
$r\in (0,\delta )$
, then
 $u(0,t)=0$
for any
$u(0,t)=0$
for any
 $t\in (0,T(u_0))$
, similarly to what we proved for
$t\in (0,T(u_0))$
, similarly to what we proved for
 $\sigma \gt -2$
and
$\sigma \gt -2$
and
 $p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
in Theorem 4.1.
$p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
in Theorem 4.1. -
(iii) The case
 $\sigma =-2$
is of special interest in some models in the theory of combustion in [Reference Kurdyumov, Kurkina, Malinetskii and Samarskii13], but with a porous medium-type diffusion instead of the heat equation. Moreover, this case has not been included in the study performed in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez8].
$\sigma =-2$
is of special interest in some models in the theory of combustion in [Reference Kurdyumov, Kurkina, Malinetskii and Samarskii13], but with a porous medium-type diffusion instead of the heat equation. Moreover, this case has not been included in the study performed in [Reference Iagar and Sánchez8].
6. Conclusion
In this article, we have studied a number of properties of solutions to Eq. (1.1), which presents as main feature a critical density function
![]() $|x|^{-2}$
pondering the time derivative. On the one hand, we have shown that the critical exponent
$|x|^{-2}$
pondering the time derivative. On the one hand, we have shown that the critical exponent
![]() $p_c(\sigma )$
plays the role of a Fujita-type exponent, limiting between the range of blow-up for any non-trivial solution and possible existence of global solutions to the equation. On the other hand, in the range
$p_c(\sigma )$
plays the role of a Fujita-type exponent, limiting between the range of blow-up for any non-trivial solution and possible existence of global solutions to the equation. On the other hand, in the range
![]() $p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, we have introduced a new explicit solution which serves as a separatrix between solutions presenting finite time blow-up and solutions decaying to zero as
$p\gt p_c(\sigma )$
, we have introduced a new explicit solution which serves as a separatrix between solutions presenting finite time blow-up and solutions decaying to zero as
![]() $t\to \infty$
. Moreover, we provide the large time behaviour of such solutions, towards a profile related to the Gaussian kernel. Finally, we show local existence of solutions for
$t\to \infty$
. Moreover, we provide the large time behaviour of such solutions, towards a profile related to the Gaussian kernel. Finally, we show local existence of solutions for
![]() $\sigma =-2$
, in contrast with the equation with a singular potential alone which is known for non-existence of any solution. The fundamental tool employed in all these proofs is a new transformation mapping solutions to Eq. (1.1) into solutions to a generalised Fisher–KPP equation which is also itself of interest. We believe that our work contributes to improve the understanding of equations involving singular potentials and densities.
$\sigma =-2$
, in contrast with the equation with a singular potential alone which is known for non-existence of any solution. The fundamental tool employed in all these proofs is a new transformation mapping solutions to Eq. (1.1) into solutions to a generalised Fisher–KPP equation which is also itself of interest. We believe that our work contributes to improve the understanding of equations involving singular potentials and densities.
Acknowledgements
R. G. I. and A. S. are partially supported by the Project PID2020-115273 GB-I00 and by the Grant RED2022-134301-T funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033 (Spain).
Competing interest
The authors declare that there is no competing interest.
Data availability
Our manuscript has no associated data.