Introduction
Mortality due to childhood diarrhoea has decreased over the recent decades due to improved detection, preventive and proper treatment; nonetheless, acute gastroenteritis is still a major concern especially in low-income countries including sub-Saharan Africa [Reference Vasco1]. Diarrhoea is the eighth leading cause of mortality accounting for about 1.6 million deaths in 2016 among children of all ages and the fifth leading cause of death in children less than 5 years old [2]. Globally, acute gastroenteritis accounts for 10% of hospitalizations and 19% of deaths in children under 5 years [Reference Adadey and Quaye3]. It is said to be predominantly caused by viruses; with Rotavirus accounting for about 20% of fatal diarrhoea globally, though they are also associated with bacteria and some protozoans [Reference Adadey and Quaye3–Reference Webb and Starr5].
Clinical investigation of diarrhoeal aetiology can be expensive and time consuming and the results seldom directly affect patient treatment [Reference Fauci and Morens6]. However, it is important to determine aetiology because it is a key determinant in diarrhoeal disease prevention and treatment. For example, Rotavirus which is the single leading aetiologic pathogen for gastroenteritis now has an effective vaccine [Reference Goldman7, Reference Wittenberg8].
This systematic review accessed the aetiology of gastroenteritis in sub-Saharan Africa using multiple studies across different sub-regions in order to have a clearer picture of the true etiologic pathogens to serve as a reliable source of information in tackling the burden of gastroenteritis.
Materials and methods
This systematic review followed the guidelines provided in the Cochrane Collaboration and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). The PRISMA checklist is included in Supporting Information.
Search strategy for identification of studies
A systematic search of three electronic databases (Pubmed, Google Scholar and Wiley Online Library) was conducted using a range of search strings (Etiology of gastroenteritis in Africa, Aetiology of Diarrhoea, Gastroenteritis in children under 5 years, Diarrhoea Disease in children, Acute Diarrhoea in Africa, Diarrhoea in Africa, Gastrointestinal Diseases children, Causes of Diarrhoea in children) and was limited to studies published from 2007 to 2019 in the English language.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Articles had to report original data on the aetiology of viruses, bacteria and parasites associated with gastrointestinal diseases with a particular emphasis on diarrhoea before they could be included in this study. Articles were excluded if they focused on only one pathogen (being it a virus, bacteria or parasite) or focused on participants above 5 years. Included articles were also restricted to those conducted in Sub-Saharan Africa according to the United Nation's demarcations and reported clinically tested results of faecal samples to arrive at results. Articles were again excluded if quantitative data was not available or accessible. The process of data search and inclusion is summarised in Figure 1.
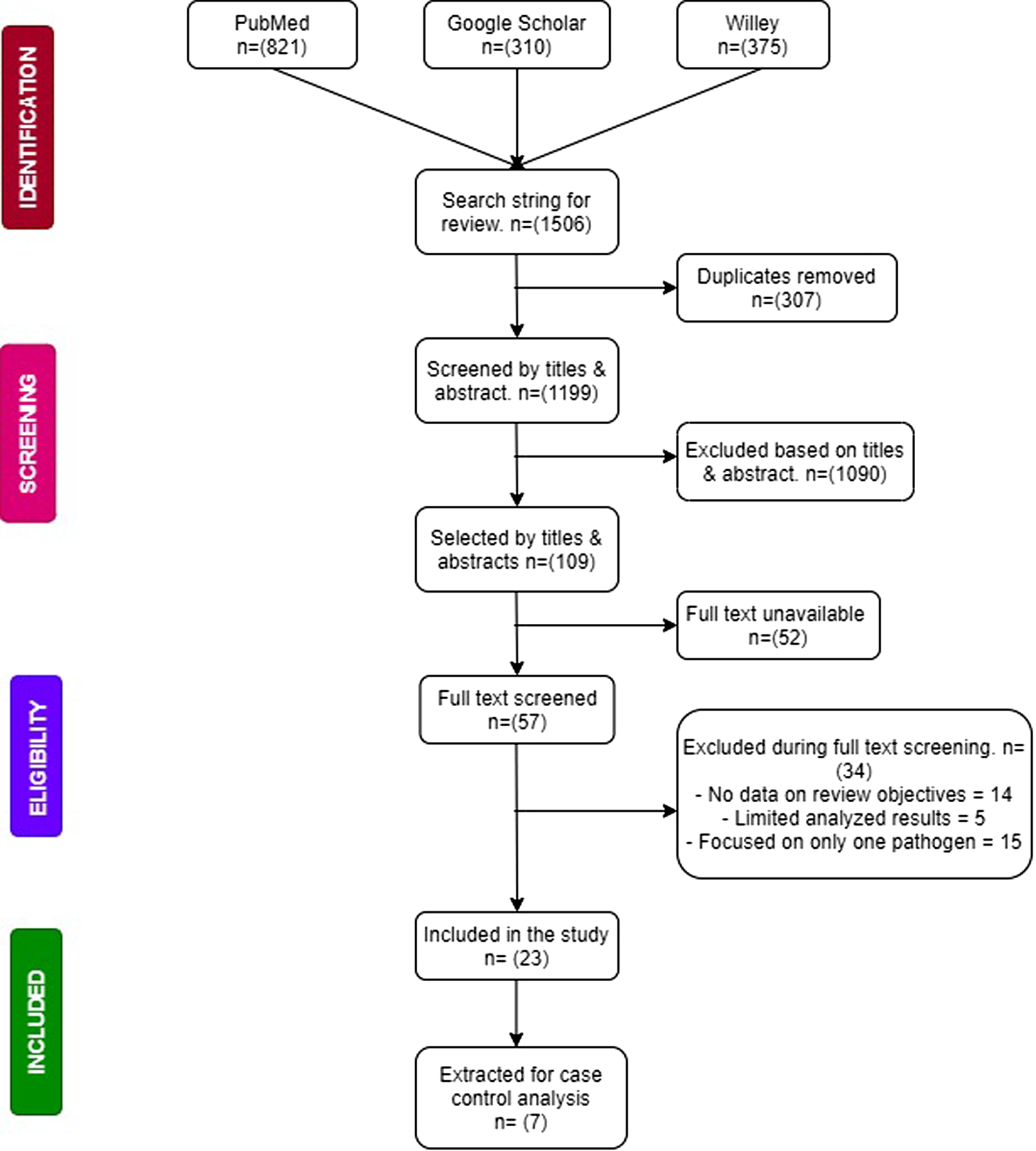
Fig. 1. Flow chart of study selection and criteria.
Data selection
Data was extracted from full-text articles and were reviewed by three independent researchers after their titles and abstracts had been screened for relevance. During the screening process, an additional researcher was on standby to resolve any discrepancies that may arise with study selection. Relevant data such as the following were collected: characteristics of the study (study period, setting, design, country and sub region in which the study was conducted), etiological agents (viruses, bacteria and parasites), study population (age of participants, case definition, sample size) and analysed data (frequencies, percentages, odds ratios, confidence intervals).
Risk of bias assessment
The study adapted a customised checklist used by Oordt-Speets et al., which is based on the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) and on criteria relevant to the designs of studies included in the systematic review to assess study quality/risk of bias in individual studies. The checklist included eight questions that could be answered ‘yes’, ‘no’ or ‘cannot tell/not applicable’. Each question was given a weight of 10 or 15 points based on relevance. Each study was given an overall quality assessment score based on answers to the eight questions; 100 points were scored if all eight responses were positive. Overall study quality was categorised as ‘high’ (scores ≥80 points), ‘moderate’ (scores >50 to <80 points) or ‘low’ (scores ⩽50 points).
Data was categorised into four sub geographical regions according to the United Nation's demarcation of Sub Saharan Africa: West African Region, East African Region, Middle African Region and South African Region. Publication bias also assessed.
Statistical analysis
Analysis was performed when data on age and region were available in studies that reported frequencies of two or more pathogens. Meta-analysis was performed using proportions of the pathogens that were identified among studies to be associated with gastroenteritis among children under 5 years old including: viruses (Rotavirus, Norovirus, Astrovirus and Adenovirus), bacteria (E. coli, Salmonella species, Shigella species and Campylobacter species) and parasites (Giardia species, Entamoeba histolytica and Trichomonas intestinalis). Separate analysis was also done for pathogens with the highest frequencies stratified by case control studies. Pooled proportions were calculated using the DerSimonian and Laird method of the random effects model [Reference DerSimonian and Laird9] with results depicted on the forest plot. Heterogeneity was accessed by the Cochran's Q test and quantified by the Higgins I 2 test. The resultant heterogeneity was considered as low (I 2 of 0–30%), moderate (30–60%), substantial (60–90%) or high (90–100%). P-Values were obtained by comparing the statistic with the χ 2 distribution with k-1 degrees of freedom, with 0.10 considered the cut-off for statistically significant heterogeneity. Publication bias was also assessed using Egger's test. All statistical analyses were performed in STATA version 12.0.
Results and discussion
Study characteristics
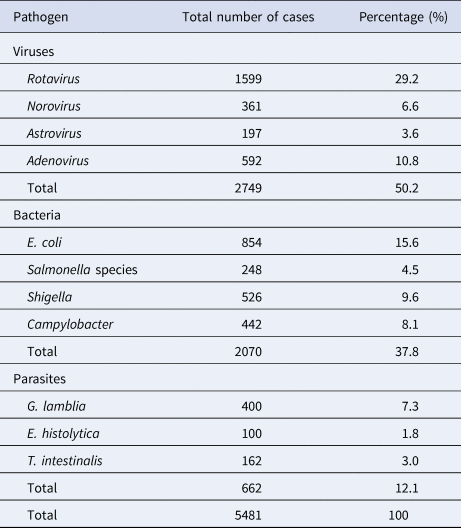
Out of the 1251 results pooled from unique searches, 23 [Reference Aminu10–Reference Nitiema26] of them met the criteria for the selection of studies. Of the 23 studies that were included, ~69.6% (16/23) were cross-sectional studies while 30.4% (7/17) [Reference Ouédraogo12, Reference Swierczewski19–Reference Randremanana22, Reference Breurec24, Reference Bonkoungou27] were case control studies but only five [Reference Ouédraogo12, Reference Swierczewski19, Reference Randremanana20, Reference Randremanana22, Reference Breurec24] reported the necessary data to be added to the case-control analysis. The majority of the included studies were from the East and West African Regions (10/23 and 9/23 respectively). Only two studies came from both the South and Middle African Regions. The majority of the studies received a moderate quality assessment score (11/17). Six studies received a ‘low’ assessment score because of inadequate case definitions and the lack of adjustment for possible confounding factors, in addition to the lack of representativeness of some of the study populations. A detailed description of the study characteristics is presented in Table 1. A total of 5481 cases of gastroenteritis were recorded in all the 23 studies reviewed. Included studies identified participants from hospitals. Only four studies specified outpatients as their source participants. Viruses accounted for 50.2% of the cases whereas bacteria and parasites accounted for 37.8% and 12.1% of the cases respectively. Table 2 shows the types of pathogens and the number of infections they caused.
Table 1. Study characteristics

Table 2. Distribution of pathogens and the total number of detections in diarrhoeal cases
Aetiology of gastroenteritis
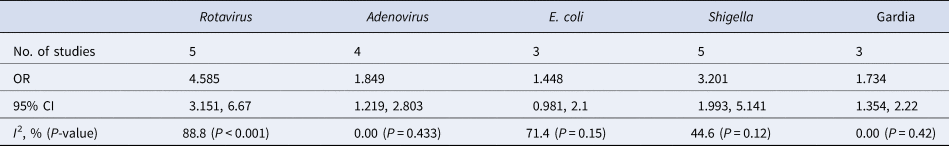
Meta-analysis of the 23 studies showed that the most prevalent virus associated with gastroenteritis across all the geographical regions was Rotavirus (pooled estimates from 3.8% to 38.5%) with an overall estimate of 26.% (95% CI 25.9–27.9) followed by Norovirus (pooled estimates between 5.1% and 29.5%) with an overall estimate of 8.4% (95% CI 7.5–9.2). Rotavirus detection was highest in the West African region and lowest in South Africa. Adenovirus and Astrovirus were the least detected viruses with an overall pooled estimate of 1.3% and 4.8% respectively. The most prevalent bacteria were E. coli (pooled estimates between 10.8% and 40.8%) with an overall estimate of 33.8% (95% CI 32.7–34.9). E. coli detection was highest in the East African region and lowest in middle Africa. The most prevalent parasite was T. intestinalis with an overall estimate of 12.6% (95% CI 11.4–13.7) pooled from only the west and east African regions. Generally, the Middle and South African regions contributed limited articles to this study, resulting in small detection rates of all pathogens in both sub-regions. A visual show of all the pathogens associated with gastroenteritis in all the regions is provided in Table 3. Viruses were predominant in gastrointestinal illness in sub Saharan Africa with the frequency of 1878 cases out of a total of 3712 cases. A distribution of cases and the type of pathogen can be seen in Table 2 above. Rotavirus was detected most frequently in all the regions with 1599 cases out of the 2749 cases associated with enteric viruses. The frequency of Rotavirus was highest in East Africa (899/1599), followed by West Africa (471/1599). Forest plots from the meta-analysis of the most prevalent virus, bacteria and parasite stratified by the region are included in Figures 2–4. A separate meta-analysis for diarrhoeal pathogens in the West, Middle and East African Regions stratified by case control studies (Table 4) also resulted in Rotavirus having the highest odds ratio compared to the detection of other enteric pathogens in diarrhoea cases (OR 4.585), followed by Giardia (OR 1.448) and E. coli (OR 1.734).
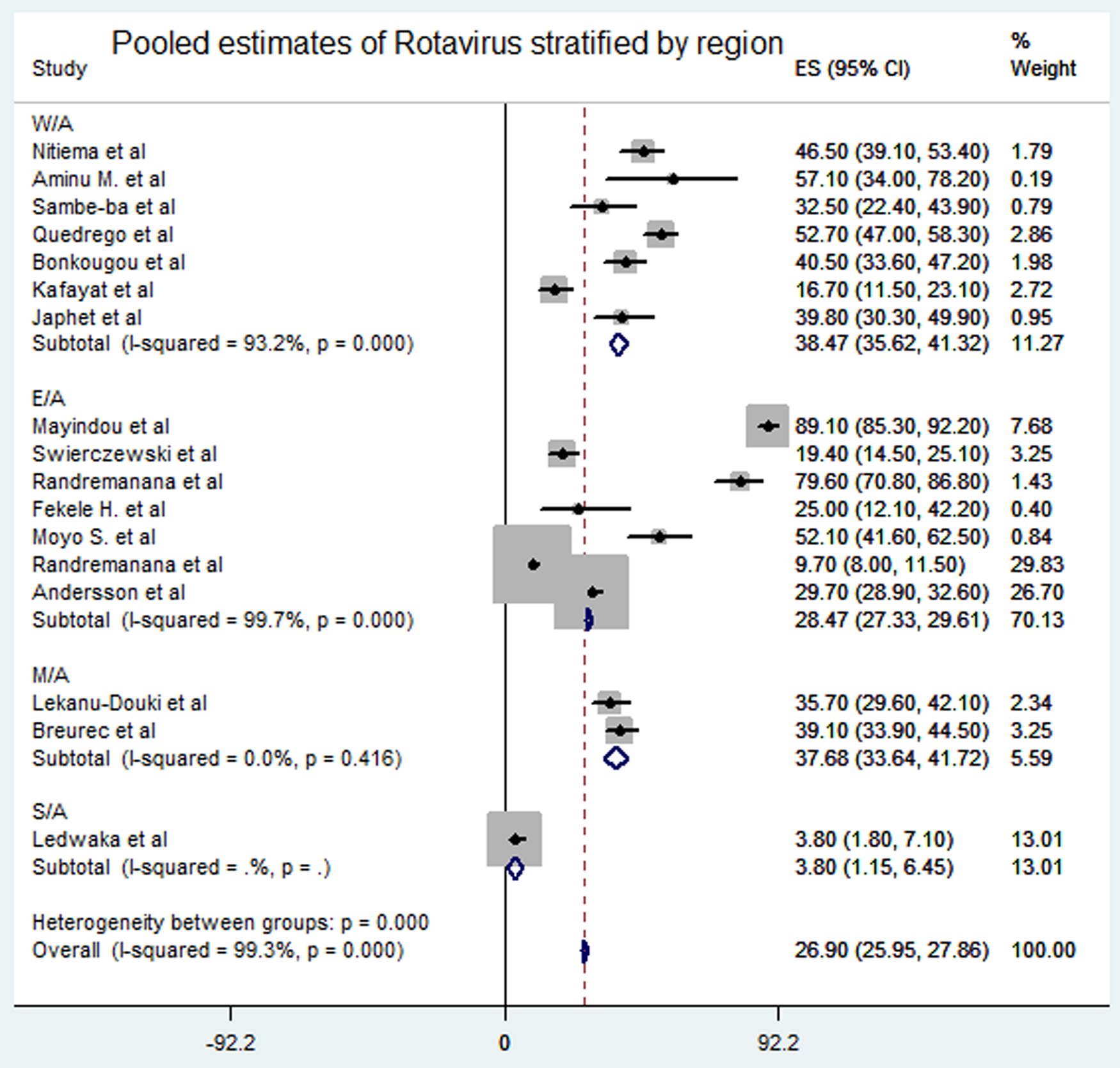
Fig. 2. Pooled estimates of Rotavirus stratified by region.
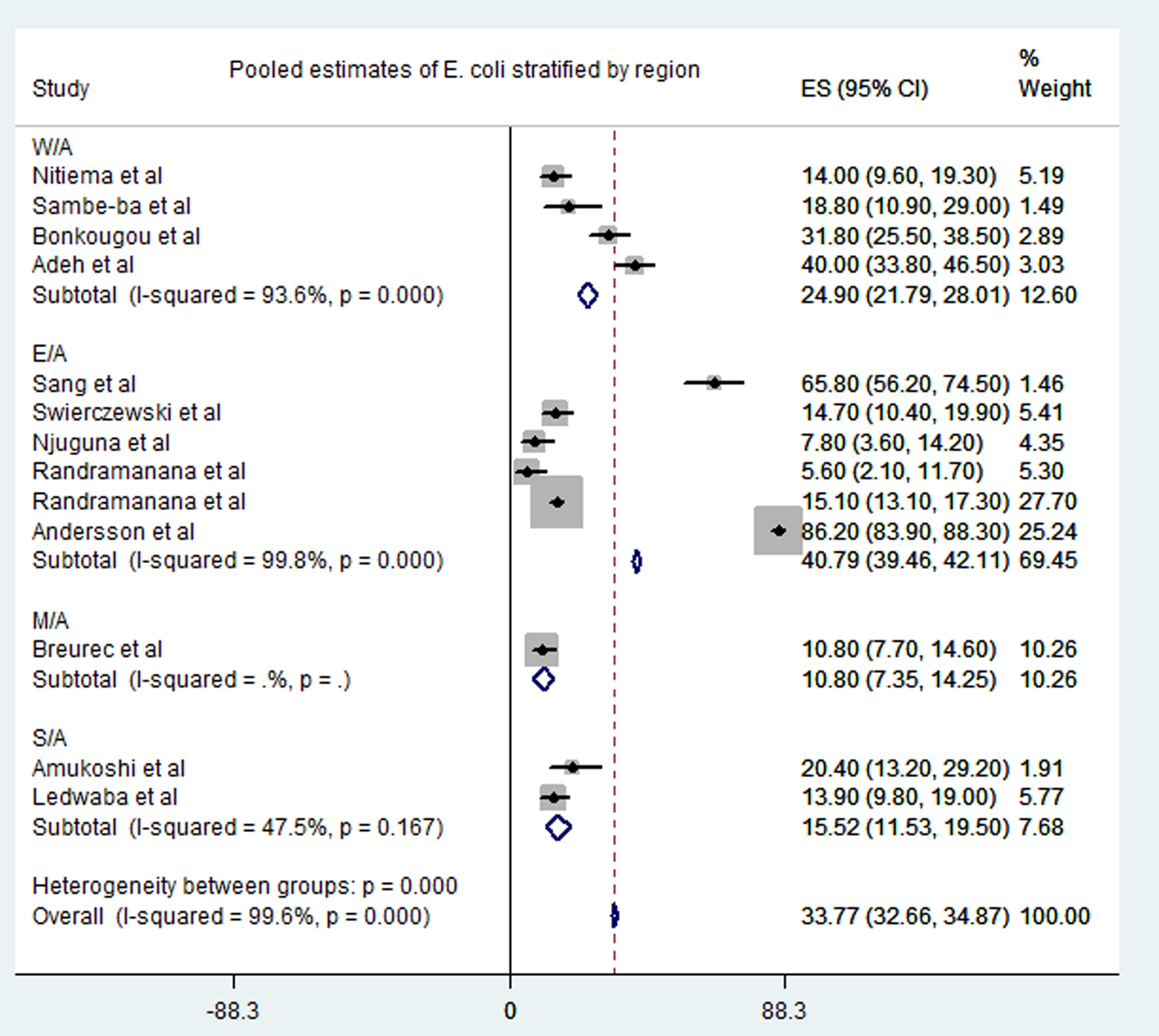
Fig. 3. Pooled estimates of E. coli stratified by region.
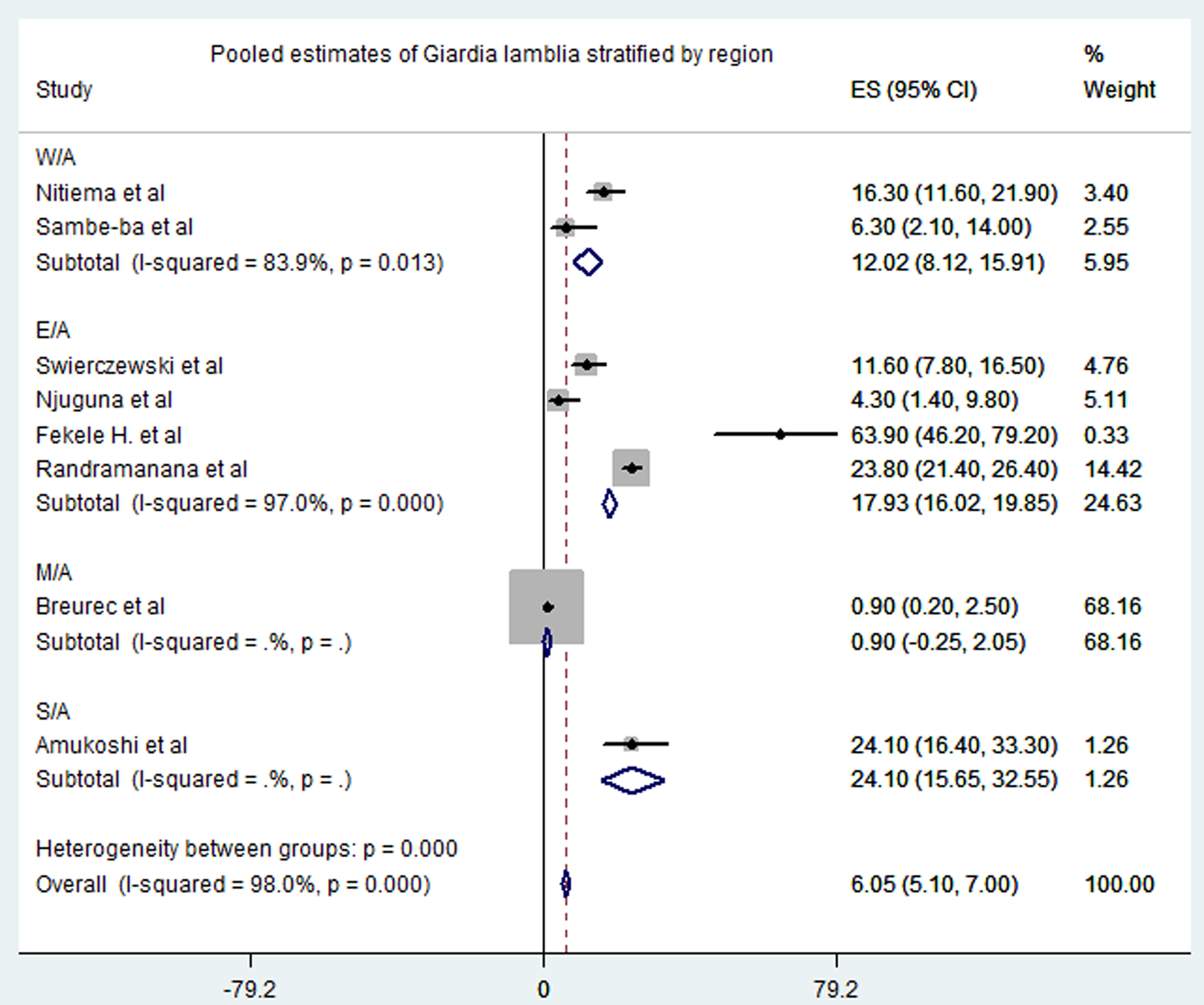
Fig. 4. Pooled estimates of Giardia lamblia stratified by region.
Table 3. Overview of pathogens that caused gastrointestinal diseases from all studies stratified by regions
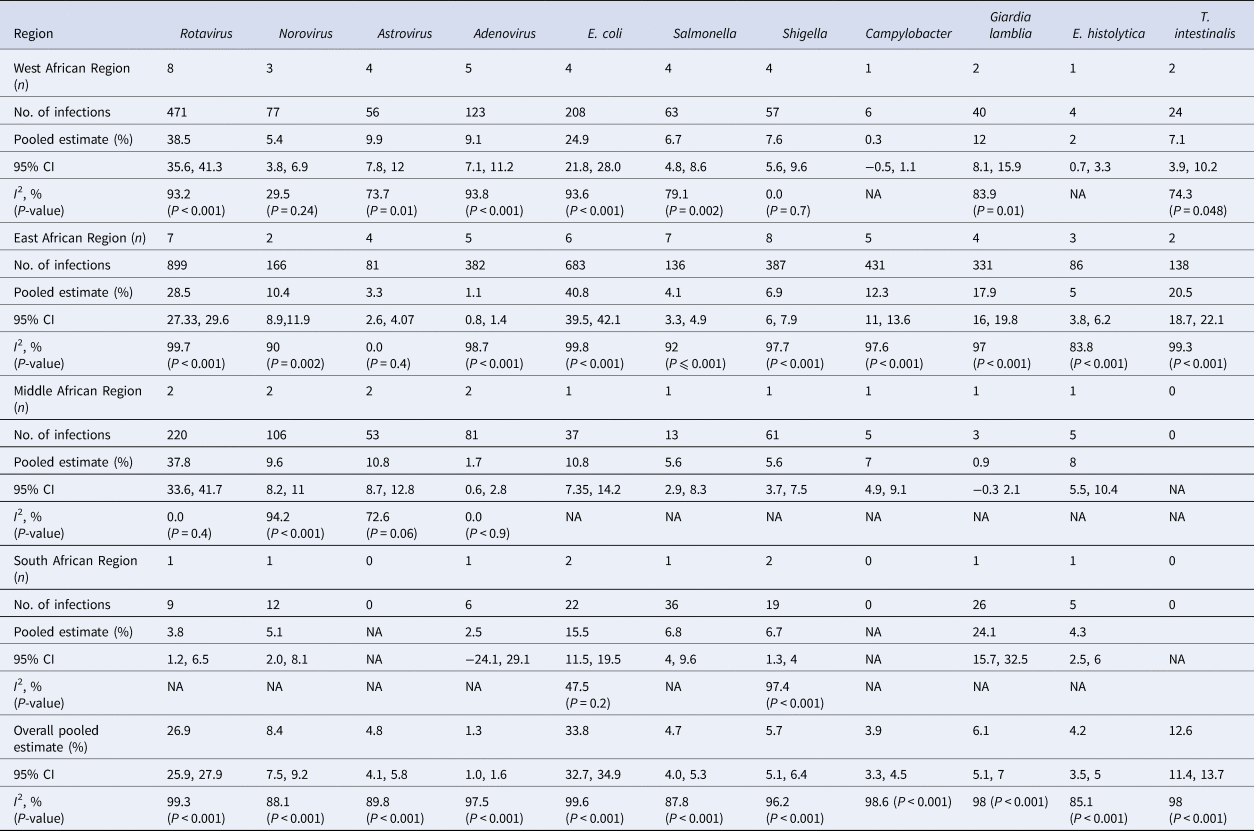
Table 4. Meta-analysis of odds ratios of case control studies
Publication bias and source of heterogeneity
Egger's test of publication bias was not significant (P = 0.085 at 95% CI); supporting the hypothesis that there was no publication bias. Large heterogeneity was found among the included studies. Heterogeneity could partly be attributed to large variation in sampling. Some studies investigated large samples while others investigated small samples. Again, the number of pathogens reported by the different studies also varied greatly. The average number of pathogens reported by included studies was ~5 out of the 11 pathogens examined in this study. Lastly, heterogeneity could also be attributed to the diagnostic methods used to detect the diarrhoeal pathogens since different methods may have different sensitivities, specificities, positive predictive and negative predictive values
Discussion
This study investigated the aetiology of enteric pathogens associated with gastroenteritis in children under 5 years. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis covering the frequency of enteric pathogens associated with gastroenteritis in children less than 5 years in sub-Saharan Africa. This systematic review indicated that viruses are the most common pathogens associated with gastroenteritis in children less than 5 years old; accounting for about 50.2% of the cases analysed (Table 2). This confirms the existing knowledge that viruses are accountable for over 70% of all gastroenteritis in infants [Reference Chow, Leung and Hon4, Reference Webb and Starr5]. The Global Enteric Multicenter Study (GEMS) identified Rotavirus, Cryptosporidium, Shigella and certain strains of E. coli (particularly ST-only or LT/STST-ETEC strains) as the most predominant enteric pathogens associated with diarrhoeal diseases with Rotavirus having the highest attributable fraction in all their sites [Reference Kotloff28]. Even though the GEMS study included only four sites in Africa, their outcome pertaining to the most common pathogens associated with diarrhoeal diseases is comparable to this study except Cryptosporidium, which is not included in this analysis because it is not often reported in the region; an assertion the GEMS agrees on. In this review, Rotavirus accounted for 32.7% of cases which confirms that Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe gastroenteritis in children worldwide, accounting for 30% to 72% in all hospitalisations and 4% to 24% in acute gastroenteritis at the community level [Reference Chow, Leung and Hon4, Reference Wilhelmi, Roman and Sánchez-Fauquier29]. Even though some studies [Reference Randremanana22, Reference Desselberger and Goodfellow30] assert that the introduction of Rotavirus vaccine has changed this trend, we found that Rotavirus is still the leading cause of acute diarrhoea in sub-Saharan Africa except in south Africa which had a relatively low estimate (3.8%). In fact, Randremanana et al., revealed that despite the introduction of Rotavirus vaccine in the year prior to their study, Rotavirus was still the leading cause of gastroenteritis in Madagascar [Reference Randremanana22]. This assertion is however not a measure of the impact of Rotavirus vaccine in the region as we did not include a pre- and post-analysis of Rotavirus infections in this study.
A relatively limited decline in Rotavirus cases in an area may be due to multiple factors including: reduced vaccine effectiveness (vaccine efficacy reported to be around 60% in low-income countries and up to about 90% high-income countries), failure to vaccinate resulting in low vaccine coverage, breastfeeding, malnutrition, co-administration of OPV and the kind of Rotavirus strain causing the infections [Reference Lekana-Douki23, Reference Burnett31]. Our meta-analysis showed that the odds of Rotavirus being associated with gastroenteritis was more than four times in cases (OR 4.58 at 95% CI) as compared to other known etiologic pathogens like Shigella (OR 3.201), E. coli (OR 1.849) and Adenoviruses (OR 1.448) (Table 4). Adenovirus, Astrovirus and Norovirus have also been identified as important etiologic factors of gastroenteritis [Reference Desselberger and Goodfellow30, Reference Wilhelmi, Roman and Sánchez-Fauquier29].
Even though viruses are the most common causes of gastroenteritis, bacteria and parasites are also a serious concern especially in low-income countries in sub-Saharan Africa [Reference Webb and Starr5]. It has been noted that Salmonella, Campylobacter and Shigella species are most common bacteria in gastroenteritis [Reference Chow, Leung and Hon4]. This contradicts our results as the meta-analysis of this study revealed that E. coli cases (overall pooled estimate 33.8%) was the most prevalent bacteria associated with gastroenteritis in the regions of sub-Saharan Africa.
Parasitic infections causing gastroenteritis are common; for example, giardia is detected in about 5% to 30% of infectious gastroenteritis in low-income countries and is thought to be associated with poverty [Reference Minetti32, Reference Nkrumah and Nguah33]. This is consistent with this review which revealed that about 7.2% (Table 2) of the cases in our study were by Giardia lamblia. A study in Ghana indicated an overall incidence of Giardia lamblia to be 144 per 1000 persons with the parasite commonly detected (89.5%) in the population under study [Reference Nkrumah and Nguah33]. Among the three parasites included in this review, Giardia lamblia was most detected in cases (400/662). T. intestinalis followed with 162 cases out of the 662 parasites detected. These parasites are more frequent in low-income countries with poor sanitation, indicating that parasitic infections can be prevented by improving sanitation [Reference Chow, Leung and Hon4].
The major limitation we encountered with this review is that fewer studies from the Middle and South African Regions met the study criteria. Some studies lacked the necessary data for analysis. Again, most of the included studies did not report on all of the pathogens under review. This limits the ability to access the true impact of those pathogens not reported.
Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis showed notable variations in the proportions of etiological pathogens associated with gastroenteritis in different regions across sub-Saharan Africa. Our study has also identified various enteric pathogens associated with gastroenteritis. We recommend that future aetiology studies focus on all known enteric pathogens associated with diarrhoea and not limited to only one pathogen. This will help know the true aetiology of diarrhoeal disease and allow design of prevention and treatment strategies. It is further recommended that Rotavirus vaccination should be intensified across sub-Saharan Africa.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268820000618.
Author contributions
All authors made substantial contribution to the study. TBO designed and conceived the study. HY supervised and edited the manuscript. CAB and EKDK conducted electronic search, extracted data and analysed it. TA and DG wrote the initial manuscript. TBO and GO revised manuscript. HY, TBO and GO critically analysed the manuscript. All authors gave final approval for manuscript to be submitted for publication.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
This study is a systematic review and meta-analysis using secondary data already published in 17 articles, all of which have been duly cited.










