Introduction
Levels of self-recruitment within and connectivity among populations are key factors influencing marine population persistence and stock sustainability (Hastings & Botsford, Reference Hastings and Botsford2006). Understanding these processes is therefore crucial for spatially explicit management strategies such as Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) (Palumbi, Reference Palumbi2003). Population genetic studies of crustacean species have revealed that while some species appear to be almost panmictic over large geographic areas (Domingues et al., Reference Domingues, Creer, Taylor, Queiroga and Carvalho2010; Pampoulie et al., Reference Pampoulie, Skirnisdottir, Hauksdottir, Olafsson, Eiriksson, Chosson, Hreggvidsson, Gunnarsson and Hjorleifsdottir2011), others display extensive population structure (Babbucci et al., Reference Babbucci, Buccoli, Cau, Cannas, Goni, Diaz, Marcato, Zane and Paternello2010; Jorde et al., Reference Jorde, Sovik, Westgaard, Albretsen, Andre, Hvingel, Johansen, Sandvik, Kingsley and Jorstad2015). Failure to identify discrete population units and/or mismatch between geopolitical and biological stocks may compromise fishery sustainability (Waples et al., Reference Waples, Punt and Cope2008; Reiss et al., Reference Reiss, Hoarau, Dickey-Collas and Wolff2009). Species-specific genetic assessments over multiple spatial scales are therefore necessary for the optimization of spatial conservation/management strategies (Almany et al., Reference Almany, Connolly, Heath, Hogan, Jones, McCook, Mills, Pressey and Williamson2009).
Genetic studies of crustaceans have typically focused on taxa with sedentary adults (Jorde et al., Reference Jorde, Sovik, Westgaard, Albretsen, Andre, Hvingel, Johansen, Sandvik, Kingsley and Jorstad2015). In this context the brown crab, Cancer pagurus (L.), occurring continuously in shallow shelf waters of the NE Atlantic from the Lofoten Islands (Norway) to Morocco (Bennett, Reference Bennett1995) and supporting one of the most important commercial European fisheries, represents an interesting candidate for investigation as both larval and adult stages have substantial dispersal potential. Adults are described as benthic and mobile, but there are pronounced dispersal differences between the sexes. Males are largely resident, making short random movements within small territories, while females migrate significantly longer distances, and more frequently, than males (Edwards, Reference Edwards1979; Bennett & Brown, Reference Bennett and Brown1983; Latrouite & Le Foll, Reference Latrouite and Le Foll1989; Ungfors et al., Reference Ungfors, Hallback and Nilsson2007). In the English Channel, female migrations of up to 200 nautical miles have been reported with some crabs achieving a mean speed of 1.07–1.62 nautical miles per day (Pawson, Reference Pawson1995). The pelagic larval stage lasts for approximately three months (Eaton et al., Reference Eaton, Brown, Addison, Milligan and Fernand2003; Weiss et al., Reference Weiss, Thatje, Heilmayer, Anger, Brey and Keller2009; Hunter et al., Reference Hunter, Eaton, Stewart, Lawler and Smith2013) and while little is known about the ecology of juveniles they are rarely caught in offshore waters, suggesting that adult crabs only move to deeper water as they grow and reach maturity. Tagging studies have revealed that adult female migrations are consistently against prevailing currents (Ungfors et al., Reference Ungfors, Hallback and Nilsson2007; Hunter et al., Reference Hunter, Eaton, Stewart, Lawler and Smith2013). As the larvae are poor swimmers likely to passively drift while entrained in currents, it has been suggested that contranatent female migrations are a spawning behaviour aimed at facilitating return to areas of maternal origin. Even in the absence of additional extrinsic factors, the seemingly opposing dispersal of females and larvae is expected to limit ‘life-time dispersal’ and may thus influence spatial patterns of recruitment and structuring of reproductive populations.
Previous genetic studies of brown crab are consistent with connectivity over large geographic areas. Ungfors et al. (Reference Ungfors, McKeown, Shaw and Andre2009), using microsatellite markers, reported no significant genetic differentiation among samples spanning 1300 km of waterway distance within the Norwegian Sea, Skagerrak and Kattegat. In a more geographically extensive study, using the same microsatellite loci, McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) described evidence of broad scale connectivity throughout the Celtic Sea, English Channel, North Sea and Scandinavian waters. Against this background of gene flow a number of samples exhibited ‘chaotic genetic patchiness’ (sensu Hedgecock, Reference Hedgecock and Beaumont1994) which was interpreted as being driven by a combination of spatio-temporal variation in recruitment and larval retention associated with coastline features, specifically bays and inshore areas. While such processes may be irrelevant over longer (i.e. evolutionary) timescales they may significantly impact stocks on timescales of interest to fishery stakeholders and may both decrease resilience of local stocks to fishing and increase unpredictability in recovery (Kuparinen et al., Reference Kuparinen, Keith and Hutchings2014). They also highlighted how even in the absence of population isolation, crab management may need to be tailored at local levels to physical and biological drivers of such recruitment variability.
The Irish Sea supports a socioeconomically important fishery exploited by Irish and British fishers. The region also contains the UK's first Marine Conservation Zone (MCZ) located at Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel off the North Devon coast. The Irish Sea has been poorly represented in population genetic studies of brown crab to date. To address this knowledge gap, a primary objective of this research was to assess population genetic structuring within the Irish Sea and interpret such patterns in the context of connectivity and spatial recruitment patterns. The inclusion of samples from within the Lundy No-Take Zone (NTZ) also permitted analysis of the functioning of the MPA. As the Lundy NTZ is located in what might be considered a retentive environment, the urgency of such information is highlighted by the findings of McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) which suggested that such habitats may be associated with elevated recruitment stochasticity. In addition, Watson et al. (Reference Watson, McKeown, Coscia, Wootton and Ironside2016) found signatures of elevated recruitment variability within the Lundy NTZ for European lobster (Homarus gammarus). A second objective was to investigate the connectivity of the Irish Sea with other regions. This was obtained by integrating the data from McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) for loci common to both studies. The outcomes of this study provide useful information on (i) the spatial scale that should be considered for management of the brown crab resource and (ii) by comparison with a previous lobster study, the functioning and effectiveness of the Lundy NTZ for crustacean species with different life histories.
Materials and methods
Sample collection, DNA isolation and microsatellite genotyping
Haemolymph was collected from a total of 514 crabs at 13 locations within the Irish Sea (Table 1, Figure 1A). Sampling locations were along the coasts of Wales (West Anglesey (AW), Menai Straits (NW), Aberystwyth (CB), Oxwich (OX), Mumbles (M) and the Gower (SW)) and the Republic of Ireland (Howth (ND), Dun Laoghaire (SD), Carne (WEX) and Dunmore East (WF)). Samples were also collected at Lundy Island in the Bristol Channel (Lundy NTZ (LNTZ), outside the NTZ in May (LIA) and in June (LIB)). Haemolymph was collected from commercially caught individuals, hence above the 130 mm Minimum Landing Size (MLS) for the Irish Sea region (SEAFISH 2009), except for NW, OX and M where juveniles were sampled. DNA was extracted using either the QIAGEN DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, CA-USA) or the CHELEX 100 (Bio-Rad, CA-USA) protocol (Walsh et al., Reference Walsh, Metzger and Higuchi1991). Individuals were then genotyped at 11 species-specific microsatellite loci developed by McKeown & Shaw (Reference McKeown and Shaw2008a) which were amplified in a single multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCRs were carried out using a QIAGEN Multiplex PCR Kit (QIAGEN, CA-USA) in a final volume of 15 µl, containing 7.5 µl of Multiplex Kit Buffer and 1 µl of genomic DNA. Primer volumes varied: 0.35 µl Cpag-4C1; 0.3 µl Cpag-1B9, Cpag-3A2, Cpag-3D7, Cpag-4 and Cpag-5D8; 0.25 µl Cpag-38; 0.2 µl Cpag-1C8, Cpag-6C4B and Cpag-15; and 0.1 µl Cpag-2A5B. The PCR cycle involved an initial denaturation step at 95°C for 15 min, followed by 34 cycles of 45 s at 94°C, 45 s at 55°C and 45 s at 72°C, and a final extension step at 72°C for 45 min. PCR amplicons were separated using an ABI 3730 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems) and genotyped using GeneMapper 4.0 (Applied Biosystems).
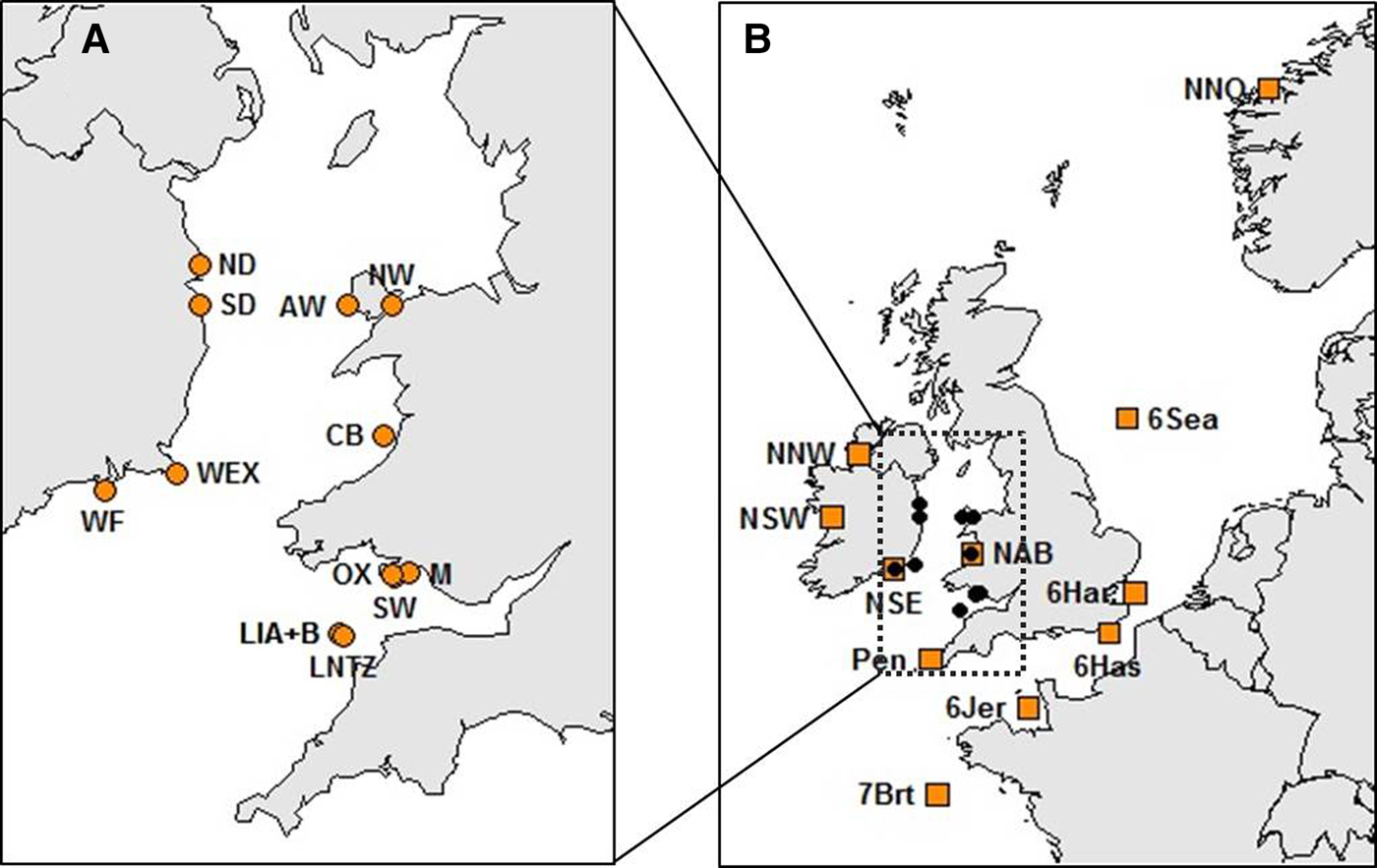
Fig. 1. Brown crab sample sites (see Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1 for details). (A) Irish Sea and Bristol Channel samples analysed for 11 microsatellite loci as part of new genotyping from this study. (B) Samples spanning the NE Atlantic for which data for 8 loci were obtained from McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) (amber boxes) overlaid upon the Irish Sea/Bristol temporal replicates (black dots).
Table 1. Brown crab sample information, including sample code, geographic coordinates, sampling time and sample size
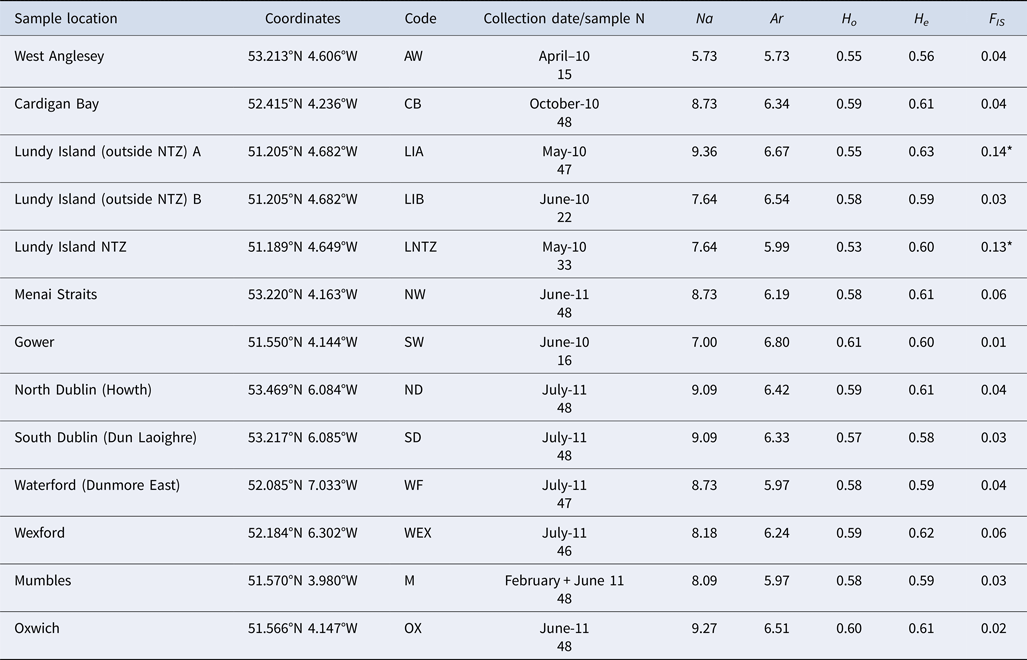
Multilocus (mean) genetic variability measures: Na (allele number); Ar (allele richness); H O (observed heterozygosity); H E (expected heterozygosity); F IS (standardized genetic variance within samples. * denotes significant deviations from HWE expectations.
To assess regional patterns comparative analysis of the Irish sea samples with samples from a wider geographic range across the NE Atlantic (Supplementary Table 1; Figure 1B), specifically the Celtic Sea, English Channel and North Sea including Scandinavian waters (McKeown et al., Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017), was performed using genotypic data for the 8 loci common to both studies (Cpag-5D8, Cpag-4, Cpag-6C4B, Cpag-3A2, Cpag-1B9, Cpag-3D7, Cpag-2A5B and Cpag-15). To ensure compatibility of genotypes between studies a subset of individuals from McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) was re-genotyped using the protocols used for this study.
Statistical analysis
Genetic variation within samples was characterized using number of alleles (N A), allelic richness (A R; El Mousadik & Petit, Reference El Mousadik and Petit1996), observed heterozygosity (H O) and expected heterozygosity (H E) (Nei, Reference Nei1978), all calculated using GENALEX 6.2 (Peakall & Smouse, Reference Peakall and Smouse2006). Genotype frequency conformance to Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) expectations and genotypic linkage equilibrium between pairs of loci were tested using exact tests (10,000 batches, 5000 iterations) in GENEPOP 3.3 (Raymond & Rousset, Reference Raymond and Rousset1995). Deviations from HWE were measured using F IS, calculated according to Weir & Cockerham (Reference Weir and Cockerham1984) and tested for significance by 10,000 permutations in FSTAT 2.9.3 (Goudet, Reference Goudet1995).
Genetic differentiation between and among samples was assessed using pairwise and global (i) F ST values with significance assessed by 10,000 permutations and (ii) exact tests of allele frequency homogeneity, all performed in ARLEQUIN 3.5 (Excoffier et al., Reference Excoffier and Lischer2010). The simulation method implemented in POWSIM (Ryman & Palm, Reference Ryman and Palm2006) was used to estimate the sample size-dependent Type I and Type II error probabilities of exact tests. The assumption of neutrality of the microsatellite loci was assessed using the FDIST outlier test implemented in LOSITAN (Antao et al., Reference Antao, Lopes, Lopes, Beja-Pereira and Luikart2008). F ST matrices were visualized using principal coordinate analysis in GENALEX. Mantel tests, implemented in GENALEX were used to test for correlation between pairwise F ST and geographic distances between sample sites (i.e. isolation by distance (IBD)). Geographic distances were calculated as the shortest sea distances between approximate centres of sampling locations. Hierarchical analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA; Excoffier et al., Reference Excoffier, Smouse and Quattro1992) was performed in ARLEQUIN to partition genetic variance among groups of samples (F CT) and among samples within groups (F SC) with significance levels of F CT and F SC tested using 1000 permutations. Genetic structure was also investigated without a priori sample information included using the Bayesian clustering analysis implemented in the program STRUCTURE (Pritchard et al., Reference Pritchard, Stephens and Donnelly2000). Following recommendations by Hubisz et al. (Reference Hubisz, Falush, Stephens and Pritchard2009) analyses were replicated for both the original ‘no locprior’ and new ‘with locprior’ models. Each run consisted of a burn-in of 106 steps followed by 5 × 106 steps. Randomization procedures in FSTAT were used to detect significant differences in heterozygosity, A R, F IS, F ST and relatedness among user defined groups of samples following 10,000 permutations.
Results
Genetic diversity among Irish Sea crab
The total number of alleles range from 5 to 30 (average 12.8). Levels of genetic variability were very similar among samples (Table 1). All loci were polymorphic in each sample with the exception of Cpag1C8 (7 alleles overall) which exhibited no variation in 5 samples (AW, CB, LIB, LNTZ, M). No significant linkage disequilibrium was detected between any locus pair in tests performed for each sample or globally across all samples. HWE tests for each locus/sample comparison reported 20 cases of deviations, in all cases due to heterozygote deficits. Locus Cpag-4 exhibited significant heterozygote deficits for 6 (CB, LIA, LNTZ, NW, WF, WEX) out of 13 samples, no other locus exhibited more than 3 deviations from HWE. No sample exhibited significant heterozygote deficits at more than 2 loci except LIA (5) and WEX (3).
Among the Irish Sea samples global tests of differentiation were not significant (F ST = 0.001; P = 0.15; Exact P = 0.7). No locus exhibited any signal of non-neutral evolution, i.e. no significant outliers identified (Supplementary Figure 1). Pairwise F ST values were very low with only 4 out of 78 tests significant (Table 2), while all pairwise exact tests were not significant. Simulation analysis indicated that exact tests based on comparisons between the average sample sizes had a probability of 0.98 of detecting differentiation at a level of F ST = 0.01 and a Type I error rate of 0.05. There was no significant IBD effect (r = 0.005; Mantel P = 0.48) and Bayesian clustering analysis unanimously supported a model of K = 1 (P > 0.99; ~0 for all other K values tested).
Table 2. Pairwise F ST estimates between all samples
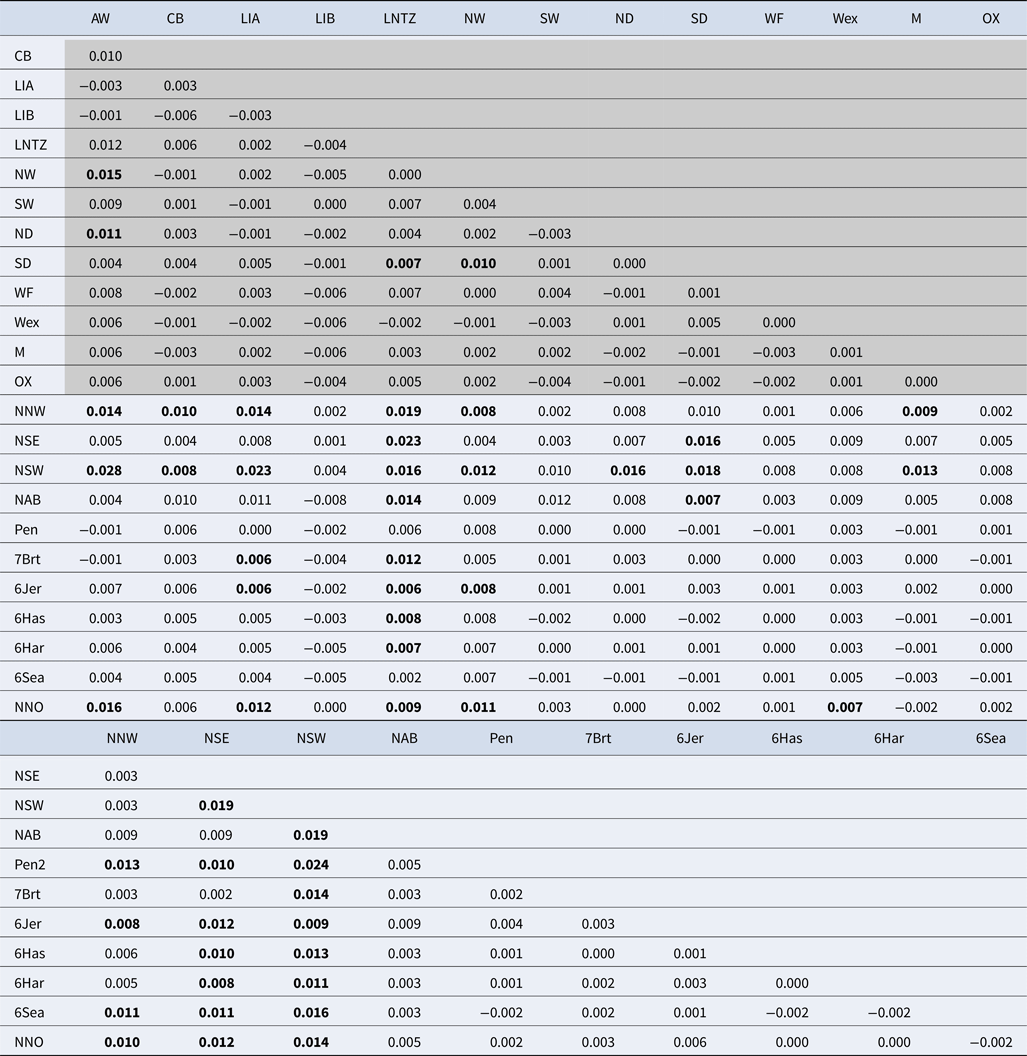
Values within shaded area are estimated from 11 microsatellite loci while values in clear area are estimated from 8 microsatellite loci. See Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1 for sample codes. F ST values identified as statistically significant following 10,000 permutations are in bold.
Genetic diversity across the NE Atlantic
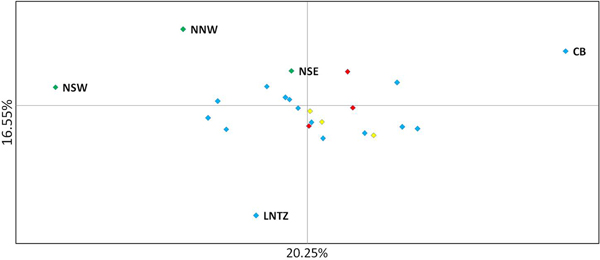
Upon integrated analysis of the Irish Sea samples and the selected samples from McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) for the 8 loci common to both studies, global F ST remained numerically small but was statistically significant (F ST = 0.003; P < 0.001). The corresponding global exact test was not significant (P = 0.7). All pairwise exact tests were also not significant and Bayesian clustering analysis also failed to detect structuring (P = 1 for K = 1). Inspection of pairwise F ST values indicated that while the majority of pairwise comparisons within and between regions were not significant certain samples were associated with a large number of significant F ST values. Among these were the three Irish samples from McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) (west coast: NNW and NSW; south-east coast: NSE) while the Lundy NTZ sample exhibited significant F ST values in comparisons with a number of samples collected from outside the Irish Sea (Table 2 and Figure 2). The differentiation of these samples could be described as patchy in that comparisons between geographically close samples often reported larger F ST than comparisons with more distant samples. There was no significant isolation by distance effect (r = 0.155; Mantel P = 0.15) and AMOVA revealed more differentiation within regions (F SC = 0.001; P = 0.013) than between regions (F CT = 0.0004; P = 0.13) (three regions used in AMOVA: 1 – Irish/Celtic Seas, 2 – English Channel, 3 – North Sea). There was no difference in global estimates of genetic differentiation when samples were partitioned according to sex (e.g. global F ST males/females = 0.001/0.003; two-tailed test P = 0.325). All loci conformed to neutral expectations (Supplementary Figure 2) and levels of intrasample genetic variability were comparable across all samples (Supplementary Table 2).
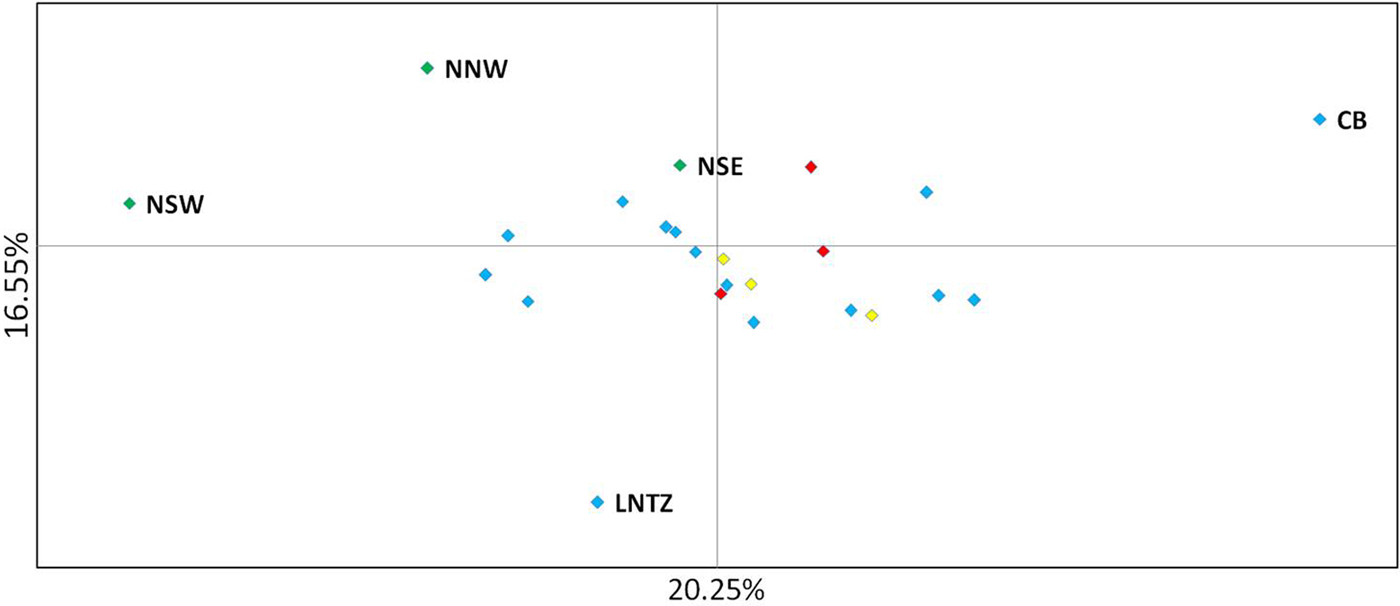
Fig. 2. Principal coordinate analysis of multi-locus pairwise F ST based on 8 microsatellite loci. Irish differentiated samples are labelled as are the Lundy NTZ and Cardigan Bay sample. Remaining samples are colour coded as to location (blue – Irish Sea/Bristol Channel; red – English Channel; yellow – North Sea).
Discussion
The investigation of demographic patterns over multiple spatial scales is vital for the optimization of spatially explicit conservation strategies at both local and regional levels. In this study microsatellite markers were used to investigate population processes within the Irish Sea, including comparisons between the Lundy NTZ and surrounding unprotected areas at 11 loci. Regional patterns were then assessed by integrative analysis of data from McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) for a subset of 8 loci common to both studies. Consistent with expectations of larval and adult mixing we found no evidence for genetic structuring among samples within the Irish Sea/Bristol Channel, including the Lundy NTZ. On a wider geographic scale the lack of spatial structure was also consistent with high levels of genetic connectivity among the Irish/Celtic Seas, English Channel and North Sea. A number of samples, including the Lundy NTZ exhibited patchy genetic differentiation, that has previously been described for the species and attributed to spatio/temporal recruitment heterogeneity occurring against a background of high gene flow (McKeown et al., Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017). The study also shows that brown crabs retain high levels of genetic variation among samples despite being heavily exploited with no difference in levels of variation for the Lundy NTZ and surrounding ‘fished’ areas.
Global and pairwise tests of genetic differentiation among Irish Sea samples were mostly non-significant. For many marine species estimates of genetic structure may be compromised by adult dispersal resulting in mechanical mixing of differentiated populations (Nielsen et al., Reference Nielsen, Nielsen, Meldrup and Hansen2004). STRUCTURE analysis, which can distinguish admixed population units failed to find any evidence of population differentiation, though resolution of such analyses may be limited when differentiation among groups is subtle (Latch et al., Reference Latch, Dharmarajan, Glaubitz and Rhodes2006). Brown crab males and females exhibit markedly different migration patterns with females undertaking long migrations while males are regarded as being largely resident (Edwards, Reference Edwards1979; Bennett and Brown, Reference Bennett and Brown1983; Latrouite & Le Foll, Reference Latrouite and Le Foll1989; Ungfors et al., Reference Ungfors, Hallback and Nilsson2007). Similar to results from McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) analysis of sex partitioned samples revealed no significant differentiation among males that could indicate an underlying structure that is being obscured by adult female migration. Genetic analyses of early life history stages (e.g. juvenile recruits) have in some taxa revealed structuring/cohesion not detectable in older life history stages due to ontogenetic mixing (e.g. Christie et al., Reference Christie, Tissot, Albins, Beets, Jia, Ortiz, Thompson and Hixon2010). A number of the Irish Sea samples analysed here were comprised exclusively of juveniles which must be considered unlikely to have undertaken any extensive migrations. However, these samples also exhibited no signals of genetic differentiation. Such genetic homogeneity is readily consistent with results from other studies. Biophysical modelling of larval dispersal for a number of species has predicted that the hydrography of the region would facilitate larval dispersal between Irish and British coasts (Coscia et al., Reference Coscia, Robins, Porter, Malham and Ironside2013; Gormley et al., Reference Gormley, Mackenzie, Robins, Coscia, Cassidy, James, Hull, Piertney, Sanderson and Porter2015). In a study employing near identical sample collection sites to this one, Watson et al. (Reference Watson, McKeown, Coscia, Wootton and Ironside2016) found no genetic structure across the Irish and Celtic Sea in the European lobster (Homarus gammarus), a species for which dispersal is restricted to the larval stage unlike crab where postlarval dispersal is reported. Watson et al. (Reference Watson, McKeown, Coscia, Wootton and Ironside2016) also reported no differences between the Lundy NTZ and other Irish Sea/Bristol Channel samples. The lack of population genetic structure indicates high levels of gene flow within and between the Irish Sea and Bristol Channel.
At the regional level, the majority of pairwise comparisons between the Irish Sea/Bristol Channel and samples from the English Channel and North Sea were largely non-significant. Corresponding AMOVA among-region indices of variation were not significant and there was no isolation by distance effect. A lack of genetic differentiation between Irish Sea and surrounding waters has been reported for a number of marine species such as plaice Pleuronectes platessa (Was et al., Reference Was, Gosling and Hoarau2010), flounder Platichthys flesus (Hemmer-Hansen et al., Reference Hemmer-Hansen, Nielsen, Gronkjaer and Loeschcke2007) and gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata (Coscia et al., Reference Coscia, Vogiatzi, Kotoulas, Tsigenopoulos and Mariani2012). Overall, the results here, along with the brown crab population genetic studies by McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) and Ungfors et al. (Reference Ungfors, McKeown, Shaw and Andre2009) support high gene flow among the Irish Sea, Celtic Sea, English Channel and North Sea (including the Kattegat and Skagerrak). Weak, or lack of, genetic structuring along the European Atlantic coast has also been reported for a number of invertebrate species with high larval dispersal potential, such as the green crab Carcinus maenas (Domingues et al., Reference Domingues, Creer, Taylor, Queiroga and Carvalho2010), sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Duran et al., Reference Duran, Palacin, Becerro, Turon and Giribet2004), European lobster H. gammarus (Triantafyllidis et al., Reference Triantafyllidis, Apostolidis, Katsares, Kelly, Mercer, Hughes, Jorstad, Tsolou, Hynes and Triantafyllidis2005), spider crab Maja brachydactyla (Sotelo et al., Reference Sotelo, Moran, Fernandez and Posada2008) and velvet swimming crab Necora puber (Sotelo et al., Reference Sotelo, Posada and Moran2009). Some recent population genetic studies of lobster (Ellis et al., Reference Ellis, Hodgson, Daniels, Collins and Griffiths2017) and great scallop (Pecten maximus) (Morvezen et al., Reference Morvezen, Charrier, Boudry, Chauvaud, Breton, Strand and Laroche2016) have revealed signs of restricted gene flow between Scandinavian and other Atlantic populations linked to oceanographic retention of larvae. However, in the case of brown crab, even if larval dispersal is restricted gene flow may be facilitated by postlarval dispersal. Such postlarval dispersal has been implicated as maintaining recurrent gene flow across the Flamborough frontal system in the North Sea which has been highlighted as a predicted physical barrier to dispersal of brown crab larvae between areas north and south of the front (Eaton et al., Reference Eaton, Brown, Addison, Milligan and Fernand2003).
In the study by McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) spanning the NE Atlantic, despite geographically extensive gene flow, specific samples exhibited significant differentiation from a number of other samples but this differentiation was spatially and temporally ‘patchy’ in the sense that differentiation could be greater between temporal replicates from a given site and/or a geographically nearby site than between more distant samples. This fitted with the commonly reported pattern of chaotic genetic patchiness (CGP) (Johnson & Black, Reference Johnson and Black1982) and, as is often the case, was interpreted as being due to reproductive skews (sweepstakes recruitment) and/or larval cohesion generating genetic differences despite gene flow. The three Irish samples common to both studies (NNW, NSW, NSE) exhibited CGP in both the original study (McKeown et al., Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) and in comparisons with the new Irish Sea/Bristol Channel data reported here. Within the combined 8 loci data set the Lundy NTZ yielded a number of significant test results in comparisons between samples from the English Channel and North Sea, however this differentiation could also be described as patchy as the Lundy NTZ was not differentiated from most Irish Sea samples that were themselves largely homogeneous with the Channel and North Sea samples. McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) suggested larval retention along complex coastlines as a driver of the CGP and as the Lundy NTZ is located at the mouth of the Bristol Channel similar seascape drivers could be involved. Although no patchiness was observed for the Lundy control samples a significant heterozygote deficit was observed for Lundy control sample A. Such deficits among samples of mixed cohorts may stem from recruitment skews within, and thus differentiation among, cohorts (Harvey et al., Reference Harvey, McKeown, Rastrick, Bertolini, Foggo, Graham, Hall-Spencer, Milazzo, Shaw, Small and Moore2016). Watson et al. (Reference Watson, McKeown, Coscia, Wootton and Ironside2016) reported genetic signals compatible with sweepstakes recruitment among European lobster samples in the Lundy NTZ and suggested that this may be linked to increased variances in reproductive success due to the presence of larger lobsters compared with surrounding fished areas. McKeown et al. (Reference McKeown, Hauser and Shaw2017) similarly suggested that the greater fecundity of crabs in the English Channel and Celtic Sea compared with the North Sea, where no patchiness was detected, may increase the chance of sweepstakes recruitment in those regions. In keeping with this theme Palero et al. (Reference Palero, Abello, MacPherson, Beaumont and Pascual2011) posit that for the lobster Palinurus elephas, the biased exploitation of large individuals led to a reduction in the number of large females and a consequent reduction in variance in reproductive success. While a confirmation of the processes driving the patchy genetic structure will require cohort specific analysis (Christie et al., Reference Christie, Tissot, Albins, Beets, Jia, Ortiz, Thompson and Hixon2010) the signals of altered recruitment dynamics for two crustacean species (brown crab and lobster) within the Lundy NTZ warrant further investigation.
McKeown & Shaw (Reference McKeown and Shaw2008b) suggested that the combination of female genetic monogamy placing a limit on the number of males that can successfully breed, alongside the selective harvesting of females may contribute to fishery driven genetic erosion. However, levels of genetic variability were consistently high across all samples and similar to values reported for other NE Atlantic decapods (e.g. Sotelo et al., Reference Sotelo, Moran, Fernandez and Posada2008, Reference Sotelo, Posada and Moran2009; Domingues et al., Reference Domingues, Creer, Taylor, Queiroga and Carvalho2010). In a study of two MPAs in the western Mediterranean by Perez-Ruzafa et al. (Reference Perez-Ruzafa, Gonzalez-Wanguemert, Lenfant, Marcos and Garcia-Charton2006) higher values of total and standardized allelic richness were observed in protected populations of Diplodus sargus sargus than in unprotected ones. Here similar levels of variability were reported for the Lundy NTZ and other samples. Calo et al. (Reference Calo, Munoz, Perez-Ruzafa, Vergara-Chen and Garcia-Charton2016) also reported similar levels of genetic diversity for protected and unprotected areas in the saddled sea bream (Oblada melanura). While we do not have samples from before the commencement of commercial harvesting or during the initial stages of exploitation when loss of diversity may be most pronounced (Ryman et al., Reference Ryman, Utter and Laikre1995) and thus cannot rule out the possibility that some genetic variation has been lost due to fishing, the results indicate that high levels of genetic variation are maintained within the species which is fundamental for maintaining sustainable yields and adaptability of populations (Kenchington et al., Reference Kenchington, Heino and Nielsen2003). As for many other marine species that maintain high levels of genetic variation despite high levels of exploitation, genetic loss may be being buffered by factors such as gene flow, overlapping generations and high mutation rates (Kennington et al., Reference Kennington, Cadee, Berry, Groth, Johnson and Melville-Smith2013).
In conclusion, our analyses support the view that brown crabs within the Irish Sea and surrounding sampled areas are derived from a single genetically panmictic population and suggest that if current spawning stock sizes and management practises are maintained genetic drift is not strong enough to reduce neutral genetic diversity. The high connectivity throughout the studied area has implications for the distribution of future MPAs (Larson & Julian, Reference Larson and Julian1999) and emphasizes the need for international cooperation in the management of the resource. This is a timely consideration in light of the potential for mismatch between biological and geopolitical stock boundaries in the Irish Sea after Brexit. A key aspect of such management should be the application of genomic approaches which may detect population isolation and adaptation patterns beyond the resolution of this study (King et al., Reference King, McKeown, Smale and Moore2017) and that can be used to disentangle the drivers of genetic patchiness in this species.
Supplementary material
The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315418000632
Acknowledgements
The Irish Sea data collection was performed as part of SUSFISH, a 3 year project funded by the European Union Regional Development Fund (ERDF) under the Ireland Wales Programme 2007–2013 (INTERREG4A, Project No. 042) while the concatenated data analysis was performed as part of the EU BLUEFISH project.