Introduction
Migratory birds can be affected by threats occurring on breeding and non-breeding grounds (Newton, Reference Newton2004), and carry-over effects of winter conditions may influence their success or survival in subsequent breeding seasons (Newton, Reference Newton2008; Zwarts et al., Reference Zwarts, Bijlsma, van der Kamp and Wymenga2009). There is thus a growing recognition of the need for a better understanding of the ecology of migratory birds during the non-breeding period (Martin et al., Reference Martin, Chadès, Arcese, Marra, Possingham and Norris2007).
Defining the ranging behaviour, habitat use or environmental variables that determine the distribution of migratory bird species outside the breeding season is essential to define meaningful conservation actions (Martin et al., Reference Martin, Chadès, Arcese, Marra, Possingham and Norris2007). Areas suitable for migrants during non-breeding are sometimes identified based on empirical information (such as local censuses) but can be identified also through modelling (Beresford et al., Reference Beresford, Buchanan, Donald, Butchart, Fishpool and Rondinini2011; Jiguet et al., Reference Jiguet, Barbet-Massin and Chevallier2011).
The pallid harrier Circus macrourus is a medium-sized migratory raptor. Its main breeding populations are in the steppes of Asiatic Russia, Kazakhstan and north-west China, and the majority of birds spend the non-breeding period in sub-Saharan Africa or the Indian subcontinent (del Hoyo et al., Reference del Hoyo, Elliott and Sargatal1994). The pallid harrier is included in Annex I of the European Birds Directive (2009/147/CE), and its habitats throughout its distribution should be protected to ensure its persistence. The species is categorized as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List (BirdLife International, 2013) as a result of population declines. These may be linked to effects during the breeding season but negative effects such as habitat loss and degradation in wintering areas may be equally important (Thiollay, Reference Thiollay2006). Analysis of the pallid harrier's habitat requirements in its African and Indian non-breeding range is considered a priority for conservation (BirdLife International, 2012).
The migratory routes and wintering range of pallid harriers breeding in Kazakhstan and adjacent areas of Russia have been described using satellite telemetry (Terraube et al., Reference Terraube, Mougeot, Cornulier, Verma, Gavrilov and Arroyo2012). Buij et al. (Reference Buij, van der Goes, de Iongh, Gagare, Haccou, Komdeur and de Snoo2012) showed that pallid harriers wintering in northern Cameroon preferentially used rice fields and flooded grasslands, with evidence of sexual differences in habitat use when foraging. However, general knowledge about the ranging behaviour and habitat use of this species during the non-breeding period is lacking and this impedes conservation.
We describe movements by individual harriers during winter, and interannual variation in their winter range. We develop an ecological niche model (based on topographic, habitat and climate variables) to identify suitable wintering areas for pallid harriers, and assess the importance of habitat in determining that niche. Finally, we analyse the importance of existing protected areas for pallid harriers and discuss the implications of our findings for the conservation of pallid harriers globally.
Methods
Tagging and tracking data
Nine adult pallid harriers (four males, five females) were trapped and fitted with solar-powered satellite-received transmitters (PTTs; North Star Science and Technology, King George, USA) during the 2007 and 2008 breeding seasons in the Naurzum and Turgai regions of north-central Kazakhstan (see Terraube et al., Reference Terraube, Mougeot, Cornulier, Verma, Gavrilov and Arroyo2012, for details of capture and tagging).
Birds were tracked using the Argos system of satellites (CLS, Ramonville Saint-Agne, France), which estimates locations of transmitters and calculates an error distribution for each estimate, the location class (LC). We used high-quality locations (LC 3, 2 and 1) for our analyses. Locations with LC 3, 2 and 1 have nominal errors up to 150, 350 and 1,000 m, respectively. Of the nine tagged birds, three stopped transmitting shortly after tagging. Of the remaining six birds, four were tracked for all (one male and one female) or part (one male and one female) of the non-breeding season (hereafter called winter) subsequent to trapping; one female was tracked for two consecutive winters and one for three consecutive winters (Table 1). We use data from the latter two birds to describe interannual variations in wintering areas. A wintering event refers to wintering locations for each bird and wintering season.
Table 1 Data on wintering events of six adult satellite-tracked pallid harriers Circus macrourus, with bird identification number, sex, wintering period, number of wintering locations recorded, size of wintering grounds, and country. Wintering events for which the transmitter stopped working during the wintering season are considered incomplete.
Movements of pallid harriers during winter
During migration, pallid harriers make stopovers that can last up to 15 days (Terraube, Reference Terraube2010). We defined the wintering season (to differentiate from migratory locations) based on when birds settled in an area (i.e. moved < 20 km per day) for > 15 days. We recorded a total of 840 wintering locations from six tracked harriers, of which 64% had a nominal precision of < 350 m (i.e. had LCs of 3 or 2); the number of locations for each wintering event was 11–279 (Table 1). We calculated the home range for each wintering event as the 95% fixed kernel and used the least squares cross-validation procedure to set the smoothing parameter (H), using the Animal Movement extension (Hooge & Eichenlaub, Reference Hooge and Eichenlaub1997) for ArcView v.3.2 (ESRI, Redlands, USA). The size of each kernel polygon was calculated based on a cylindrical equal-area projection of the Earth, using the Projector! extension for ArcView.
Habitat use and ecological niche model
We used the global land cover map GlobCover v. 2.3 (ESA, 2010) to map habitat. GlobCover uses satellite image data from 2009 to map land cover in raster format at 300 m resolution. We rescaled this map by overlaying it with a grid (2.5 arc-min pixel size, i.e. 4.5 × 4.5 km) and assigning a habitat descriptor to each cell, based on the main cover type (mode of pixels) within. This analytical scale matches the nominal error of the satellite locations and has been used in similar studies (Jiguet et al., Reference Jiguet, Barbet-Massin and Chevallier2011; Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a). The habitat associated with each harrier location was that of the cell in which the location occurred. We calculated the proportions of locations in each habitat type for every wintering event and used χ 2 tests to evaluate differences in habitat use between individuals or wintering events.
Given the overall extent of the wintering range (see Results and also Terraube et al., Reference Terraube, Mougeot, Cornulier, Verma, Gavrilov and Arroyo2012) and the small number of tracked birds, it was not possible to study habitat selection by comparing the habitat where harriers were located with habitat at random points, because random locations would probably not fall within areas suitable for harriers. Instead, we modelled the harrier's ecological niche and assessed the importance of habitats in determining that niche, using Maxent, which does not require true-absence data to develop a predictive model (Phillips et al., Reference Phillips, Anderson and Schapire2006; Elith et al., Reference Elith, Phillips, Hastie, Dudik, Chee and Yates2011). The evaluation of distribution models on the basis of tracking data, even when based on a small number of individuals, has been a useful approach for other species (Wisz et al., Reference Wisz, Hijmans, Li, Peterson, Graham and Guisan2008; Monterroso et al., Reference Monterroso, Brito, Ferreras and Alves2009; Gschweng et al., Reference Gschweng, Kalko, Berthold, Fiedler and Fahr2012; Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a). Key assumptions for presence-only models are that sampling is either random or representative throughout the landscape and that detection probability is constant across sites (Yackulic et al., Reference Yackulic, Chandler, Zipkin, Royle, Nichols, Campbell Grant and Veran2012). The latter is clearly met by satellite tracking. In relation to the former, our assumption is that trapped adults represent a random sample of the breeding population and thus of wintering locations of birds from the core breeding distribution area. Sampling bias would also arise if some individuals contributed more than others to the data set. This issue can be addressed by random sampling to homogenize the contributions made by all individuals (Gschweng et al., Reference Gschweng, Kalko, Berthold, Fiedler and Fahr2012; Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a). To do this we randomly selected two locations per month (to accommodate possible variation over time) for each tracked bird during winter; for the two birds with data from two consecutive wintering seasons we pooled data from both wintering events (i.e. only two locations per calendar month were used, irrespective of wintering event). One of the birds, having spent two consecutive winters in Ethiopia, spent its third winter in the Middle East (see Results). Data from this last wintering season were not used for the ecological niche model, which we developed only for the region of Africa bounded by latitude 5–20°N and longitude −19–52°E. Overall, 52 locations contributed to the development of the model (30 of which had a precision of < 350 m), with the number of locations per bird in the range 2–12. We set a random selection of 20% of these occurrence data to test the model.
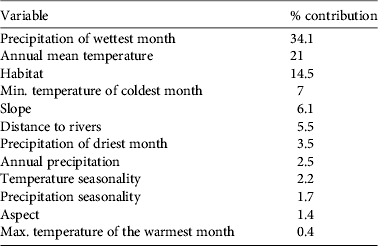
As predictive variables of the ecological niche, we used 12 environmental grid layers at a resolution of 2.5 arc-min (4.5 × 4.5 km) within the above-mentioned region. These included the habitat layer, eight climatic variables, two topographical variables, and distance to rivers (Table 2). The latter was included because exploration of locations with Google Earth (Google Inc., Mountain View, USA) revealed that many locations during the wintering season were close to rivers. Maxent produces a logistic output for every grid cell, ranging between 0 and 1, reflecting relative occupancy probability. Following Limiñana et al. (Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a), we considered cells for which this value was 0.5–0.75 as ‘suitable’ and those for which raw output was > 0.75 as ‘very suitable’. We analysed which habitat categories contributed most to the presence of harriers within the modelled region, taking into account the possible correlations of habitat with other predictive variables (as defined in the Maxent results).
Table 2 Variables used in the ecological niche model.

1 Calculated according to the eight surrounding pixels for every grid cell
2 Pixels with slope < 2° were considered flat (no aspect)
3 Calculated with MiraMon geographical information system (Pons, Reference Pons2008)
Pallid harriers and protected areas
We assessed the extent to which suitable and very suitable areas for the species overlapped with protected areas, based on nationally recognized protected areas listed in the 2010 World Database on Protected Areas (UNEP-WCMC, 2010). When the boundaries of a protected area were not available but its coordinates and extension were indicated, we generated a circular buffer around the given coordinates, the radius of which encompassed the nominal boundaries of the protected area, and used the resulting circular area in our analyses (Soutullo et al., Reference Soutullo, De Castro and Urios2008; Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a).
Results
Wintering areas and home ranges
Tracked harriers wintered within a relatively narrow latitudinal band but showed a wide longitudinal range (Table 1; Fig 1). Four wintered in eastern Africa (Sudan and Ethiopia) and two were tracked to western Africa (Burkina Faso and Niger).

Fig. 1 (a) Ecological niche model results for the pallid harrier Circus macrourus across the Sahel belt in Africa (indicated by the rectangle). Probability of presence in 4.5 × 4.5 km cells is indicated according to a three-category scale (25–50, 50–75 and >75%). (b) Existing protected areas in and around the Sahel belt (UNEP-WCMC, 2010).
Data from the two birds that were tracked for more than one season suggest that winter site fidelity is variable. One bird (42675) spent the first tracked winter in two distinct areas c. 1,000 km apart, spending 1 month c. 250 km north-east of Khartoum (Sudan) and then moving south to an area near the border between Sudan and South Sudan, where it spent c. 3 months. Therefore, the overall home range was large (Table 1) but ranges in each sub-area were much smaller (560 and 1,063 km2 for the first and second areas, respectively). The following winter this bird migrated directly to the southern home range of the previous year, where it spent the whole winter in an area of 663 km2 (Table 1). Another bird (82829) spent the first two tracked winters in a small area in Ethiopia (Table 1) but in its third tracked winter (2010–2011) it settled in Syria, along the Euphrates River (an area along its autumn migratory route during the previous 2 years). It stayed there for 4 months and ranged over a larger area than that used in previous winters in Ethiopia (Table 1). Although a fourth year of wintering was not recorded for this bird because of a cessation of transmissions, we know that it visited and bypassed this Syrian wintering location during migration, after which it travelled into Saudi Arabia and then moved northwards; its last known location was c. 400 km south of the area used the previous winter in Syria (Fig. 2). Individual home ranges of other tracked harriers during the non-breeding season were relatively small (19–448 km2; Table 1).

Fig. 2 Wintering areas of pallid harrier number 82 829. The bird spent two consecutive winters, 2008/2009 and 2009/2010, in Ethiopia (depicted as a star because of the small home range; Table 1). The following winter it remained in Syria (95% fixed kernel in dark grey and 50% fixed kernel in light grey are illustrated). Its autumn migration movements in 2011 were recorded until the satellite transmitter stopped working. (a) Wintering area in 2008/2009 and 2009/2010; (b) wintering area in 2010/2011; (c) movements prior to wintering 2011/2012.
Habitat use
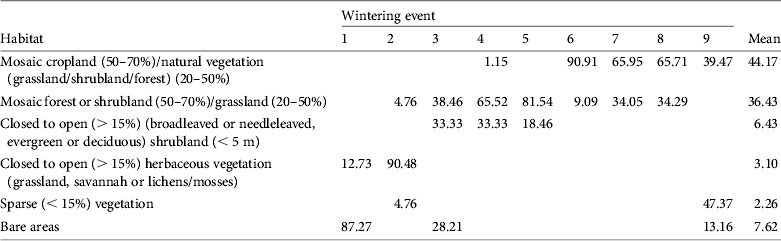
During the wintering season harriers used mostly areas of natural vegetation (mosaics of forest/shrubland and grassland; 36% of locations) or mosaics of cropland and natural vegetation (44% of locations). Other habitats accounted for < 10% of the recorded locations (Table 3). Habitat use differed between individuals (χ 2 40 = 1,928.17, P < 0.001). Some harriers used mainly cropland mosaics (82827 and also 82829 when it wintered in Africa), whereas other birds used different types of natural vegetation (including forest, shrubland or grassland; Table 3). For bird 82829 there were also significant differences in habitat use between wintering events (χ 2 6 = 333.99, P < 0.001); whereas it used mainly mosaics of cropland and natural vegetation in the Sahel, it used mainly sparse vegetation along the Euphrates River in Syria (Table 3). A more detailed inspection of those data, using Google Earth, indicated that the bird may have taken advantage of irrigated croplands along the Euphrates River, which were not identified as such by GlobCover.
Table 3 Percentages of satellite telemetry fixes in the different habitats used by pallid harriers during the wintering season. The numbering of wintering events is the same as in Table 1. Mean values (for all wintering events) of the percentage of fixes in each habitat type are also presented.
Ecological niche model of wintering pallid harriers in Africa
After climatological variables, habitat was one of the main factors that influenced harrier occurrence (Table 4). Maxent results showed that, after controlling for correlations of habitat with other predictive variables, mosaics of forest/shrubland and grassland, mosaics of cropland and forest/shrubland/grassland and closed-to-open herbaceous vegetation (in that order) contributed most to explaining harrier occurrence.
Table 4 Contribution of each environmental variable, in decreasing order, to the ecological niche model for wintering pallid harriers around the Sahel belt.
Suitable areas for this species in the modelled region covered 289,249 km2 and occurred both in the eastern and western parts of the Sahel, whereas very suitable areas covered only 26,752 km2 and were located mainly in eastern Sahel and central Ethiopia/Eritrea (Fig. 1a). The existing network of protected areas in the study region includes 25.4 and 14.1% of the very suitable and suitable areas, respectively. Protected areas that were very suitable for harriers were mainly within the Oromia region of Ethiopia (Fig. 1a); some suitable areas in central Sahel were also within reserves (Fig. 1b). Locations of two of the tracked birds were recorded within protected areas: bird 42674 in northern Burkina Faso (Sahel Reserve; seven of 21 locations recorded) and bird 82829 in Ethiopia (Bale Mountains National Park; 24 of 279 locations recorded).
Discussion
Movements during and between winters
We observed a relatively high fidelity to wintering areas, with the possibility of large interannual variations in the location of wintering areas, in this nomadic long-distance migratory raptor. Although based on a small sample, fidelity to wintering grounds appeared to be higher than fidelity to breeding grounds (distance between locations of subsequent breeding events was 408 ± SD 301 km, n = 3, range 0–834 km; Terraube, Reference Terraube2010). Similar results were obtained for snowy owls Bubo scandiacus, which are also nomadic (although their nomadic movements are shorter than those of the pallid harrier) and faithful to wintering areas (Therrien et al., Reference Therrien, Gauthier and Bety2011). Once settled in their African quarters, pallid harriers move mostly short distances, resulting in smaller home ranges than for the closely related Montagu's harrier Circus pygargus, which also winters in the Sahel (Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a). This may be related to differences in winter diets. The pallid harrier is a small-rodent specialist during breeding (Terraube et al., Reference Terraube, Arroyo, Madders and Mougeot2011) and small mammals and passerines contribute a large proportion of its total biomass consumption in winter (Buij et al., Reference Buij, van der Goes, de Iongh, Gagare, Haccou, Komdeur and de Snoo2012). Hence, if pallid harriers reach an area of high vertebrate prey abundance in winter they may settle and remain there. During winter, Montagu's harriers feed on grasshoppers and locusts (Orthoptera), and individuals may move large distances in search of these prey (Mullié, Reference Mullié, Zwarts, Bijlsma, Van der Kamp and Wymenga2009; Trierweiler & Koks, Reference Trierweiler, Koks, Zwarts, Bijlsma, van der Kamp and Wymenga2009; Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Urios and Reig-Ferrer2012b).
Our results also show the potential for variation from this pattern among and within individual pallid harriers. One of the birds spent two consecutive winters in the same area in Ethiopia and then spent the subsequent winter in an area in Syria located along the pathway used in previous migrations (Terraube et al., Reference Terraube, Mougeot, Cornulier, Verma, Gavrilov and Arroyo2012). Moreover, in the subsequent autumn migration this bird was heading towards Africa (possibly its wintering areas in previous years in Ethiopia) but turned back northwards just before crossing the Red Sea; the transmitter stopped working when the bird was nearing its previous wintering area in Syria (Fig. 2). This shift in the location of the wintering grounds could be associated with a nomadic strategy that allows pallid harriers to exploit unpredictable resources encountered during their dispersion and migration movements. Nomadic species may be particularly efficient in making use of past experience and spatial memory to track and exploit available resources (Bennetts & Kitchens, Reference Bennetts and Kitchens2000). If prey is available, staying in areas visited in previous years may be a better option (in terms of enhancing survival) than attempting to cross harsh areas or ecological barriers to reach traditional wintering grounds (Strandberg et al., Reference Strandberg, Klaassen, Hake and Alerstam2010; Mellone et al., Reference Mellone, Yáñez, Limiñana, Román-Muñoz, Pavón and González2011). Individual variations in migration and wintering behaviour probably depend on resource distribution, as well as experience and condition (e.g. energy stores, breeding status, predation risk, prior knowledge), and even sex (Buij et al., Reference Buij, van der Goes, de Iongh, Gagare, Haccou, Komdeur and de Snoo2012).
Wintering habitats and conservation
During winter, pallid harriers depend more on habitats that include at least some natural vegetation (i.e. grassland, shrubland or open forest) than the closely related Montagu's harrier, which mainly uses cropland during winter (Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a). In addition, and to a greater extent than for Montagu's harriers (Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a), the most suitable areas for wintering pallid harriers had a relatively patchy distribution and were mostly located in the eastern Sahel and Ethiopia. This may be, in part, because areas of natural vegetation (dry grasslands) are more extensive in this region than in the western Sahel (Zwarts et al., Reference Zwarts, Bijlsma, van der Kamp and Wymenga2009). These areas may hold more small mammals, which are important prey for pallid harriers. Small rodents are more abundant in eastern Africa, particularly in the grasslands of the Ethiopian high plateau (Datiko et al., Reference Datiko, Bekele and Belay2007; Workeneh et al., Reference Workeneh, Bekele and Balakrishnan2011), than along the Sahelian belt (Thiollay, Reference Thiollay, Meyburg and Chancellor1989; Simmons, Reference Simmons2000). The association of pallid harriers with habitats other than cropland, and the patchiness of the best wintering areas highlight the vulnerability of this species to the loss of good wintering habitats. The system of grasslands and thorn forests commonly used as foraging and roosting habitat by wintering pallid harriers, according to our results, is under threat in Africa. Habitat quality is declining, probably as a result of the widespread conversion of grassland into cropland, excess harvesting of trees in some areas, overgrazing, and shrub encroachment in less favourable grasslands as a consequence of changes in pastoral activities (particularly the loss of nomadic livestock herding; Western et al., Reference Western, Groom and Worden2009; Zwarts et al., Reference Zwarts, Bijlsma, van der Kamp and Wymenga2009; Donald et al., Reference Donald, Buchanan, Collar, Abebe, Gabremichael and Mwangi2010). Increasing anthropic pressure (through human population growth) is probably a significant cause of loss of areas of natural vegetation in Ethiopia (Meshesha et al., Reference Meshesha, Tsunekawa and Tsubo2012), where most of the highly suitable areas for the species remain. Nomadism may enable pallid harriers to look for alternative areas but if potentially suitable areas are fragmented and far apart this may constitute a cost for the species (Bowling et al., Reference Bowling, Martin and Kitchens2012).
Our results also suggest that the distribution of pallid harriers in Africa during winter is associated with climatic variables. Thus, changes in the general patterns of temperature and rainfall could affect this species’ choice of wintering areas. Changes in rainfall patterns in the Sahel can affect the migration performance and population trends of trans-Saharan migratory birds (Saino et al., Reference Saino, Rubolini, Jonzén, Ergon, Montemaggiori, Stenseth and Spina2007; Newton, Reference Newton2008; Mihoub et al., Reference Mihoub, Gimenez, Pilard and Sarrazin2010) and other prey. For example, orthopteran and passerine abundances in Africa depend on the amount of rainfall in June–September (Morel & Morel, Reference Morel and Morel1978; Zwarts et al., Reference Zwarts, Bijlsma, van der Kamp and Wymenga2009), before the arrival of wintering Palaearctic raptors. Therefore, climate change may act synergistically with land-use changes to negatively affect migratory bird populations (Hein, Reference Hein2006; Hein & de Ridder, Reference Hein and de Ridder2006).
The ecological niche model highlighted the greater importance of eastern compared to western areas in Africa for the pallid harrier. This is in agreement with Thiollay (Reference Thiollay1977, Reference Thiollay, Meyburg and Chancellor1989), who reported increasing abundance along a west-to-east gradient from Senegal to Chad. The model also suggested that the most suitable areas for pallid harriers within the studied region are relatively well represented within the existing network of protected areas, at least when compared with Montagu's harrier and its preferred habitat in the same region (Limiñana et al., Reference Limiñana, Soutullo, Arroyo and Urios2012a). The model highlighted the importance of Bale Mountains National Park and other surrounding protected areas in the Oromia region of Ethiopia. This is consistent with pallid harriers favouring areas of natural vegetation during winter, which are more likely to be represented within protected areas than farmland (Beresford et al., Reference Beresford, Buchanan, Donald, Butchart, Fishpool and Rondinini2011). However, grasslands, which are important for wintering pallid harriers (as shown here), are currently underrepresented within protected areas compared to other natural-vegetation habitats (Lee & Jetz, Reference Lee and Jetz2008; Soutullo et al., Reference Soutullo, De Castro and Urios2008; Buchanan et al., Reference Buchanan, Donald, Fishpool, Arinaitwe, Balman and Mayaux2009), and therefore increasing the area of protected grasslands could benefit the conservation of the species.
Perspectives and limitations
The results presented here should be considered in light of the low number of birds tracked and the fact that some tracked birds contributed few locations to the model. Factors such as the individual variation in wintering areas and ranging behaviour, habitat use, wintering site fidelity, sex, spatial scale and even timing of transmissions may have influenced the results of the ecological niche model. Hence, our results should be regarded as a first step in understanding the needs of this species in winter, and more data are needed to improve precision. Ideally, model predictions should be validated by field observations.
Further research is also needed to identify the most profitable foraging habitats for pallid harriers at local scales, as done by Buij et al. (Reference Buij, van der Goes, de Iongh, Gagare, Haccou, Komdeur and de Snoo2012). Detailed field studies on diet, prey (passerine birds, grasshoppers and small rodents) abundance and foraging success in different habitats (e.g. grassland, cropland, shrubland) and areas (western vs eastern Africa) would be valuable, as would an assessment of the spatial variation in trophic diversity along the longitudinal range of this species’ distribution in winter. Combining this ecological information with estimates of recent changes in land use could result in more effective management of the wintering habitats of harriers in protected areas.
Acknowledgements
We thank Jesus T. Garcia, Bob Stakim, Evgeny and Alexander Bragin, Todd Katzner, and Alexei Timoshenko for help during the fieldwork in Kazakhstan, Ewan Weston for technical support, the late Mike Madders for encouragement and inspiration throughout the project, and Natural Research Ltd for funding. R. Limiñana benefited from a postdoctoral grant (reference 10/12-C) co-funded by ‘Consejería de Educación y Ciencia’ and the European Social Fund. Rob Simmons and an anonymous referee helped improve the article.
Biographical sketches
Ruben Limiñana studies raptor ecology, particularly migration and wintering ecology of migratory raptors. Beatriz Arroyo's research interests include wildlife conservation and ecological conflicts related to human pressure on wildlife. Julien Terraube is particularly interested in population ecology and conservation of threatened predators in ecosystems facing global changes. Michael McGrady has particular interests in demography, dispersal and ranging behaviour of birds of prey, with projects in Europe, Asia, North America, Africa and Central America. François Mougeot has broad interests in ecology, population dynamics and conservation.








