Introduction
On July 23, 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO; Geneva, Switzerland) declared the monkeypox 2022 outbreak the seventh-ever Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). Monkeypox 2022 is a viral illness whose transmission rate and clinical features have shifted, enabling it to produce an unprecedented, rapidly expanding outbreak in non-endemic regions world-wide. Reference Zumla, Valdoleiros and Haider1 Sustained human-to-human and community transmission are well-documented. 2 Phylogenetic data indicate that the monkeypox virus in the 2022 outbreak has acquired significant mutations, 3 which may account for its increased human-to-human transmission and altered clinical features. Human monkeypox has likely been circulating as a cross-continent, cryptic human transmission for some time; Reference Happi, Adetifa and Mbala4 however, the first 2022 case outside of Africa was confirmed in the United Kingdom on May 7th in an individual with a history of travel to Nigeria. 5 Case numbers precipitously increased in subsequent days, and epidemiological data revealed that many cases were not associated with travel to endemic regions.
As of July 25, 2022, confirmed cases rose to 17,156 in at least 69 non-endemic countries. Reference Mathieu, Dattani and Ritchie6 Patients in the 2022 outbreak frequently present with non-classical signs and symptoms. While monkeypox may not be as easily transmissible as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the escalating outbreak is a public health emergency and can lead to reverse zoonosis with the creation of new endemic areas, recurrent outbreaks, and negative effects on health care staffing. In addition, if containment measures are not immediately implemented, there is a high risk of the virus swiftly moving into vulnerable populations, such as children, pregnant women, the elderly, and the immunocompromised, leading to higher morbidity and mortality. As of July 2022, limited testing capacity and vaccine supply contribute to this concern.
This research report provides a concise summary of current knowledge about monkeypox and a novel Identify-Isolate-Inform (3I) Tool (Figure 1) for use by Emergency Medical Services (EMS) medical directors, policymakers, educators, and frontline EMS professionals who may encounter a suspected or confirmed case. The Appendix (available online only) contains a fillable version of the 3I Tool that can be customized with local contact information.
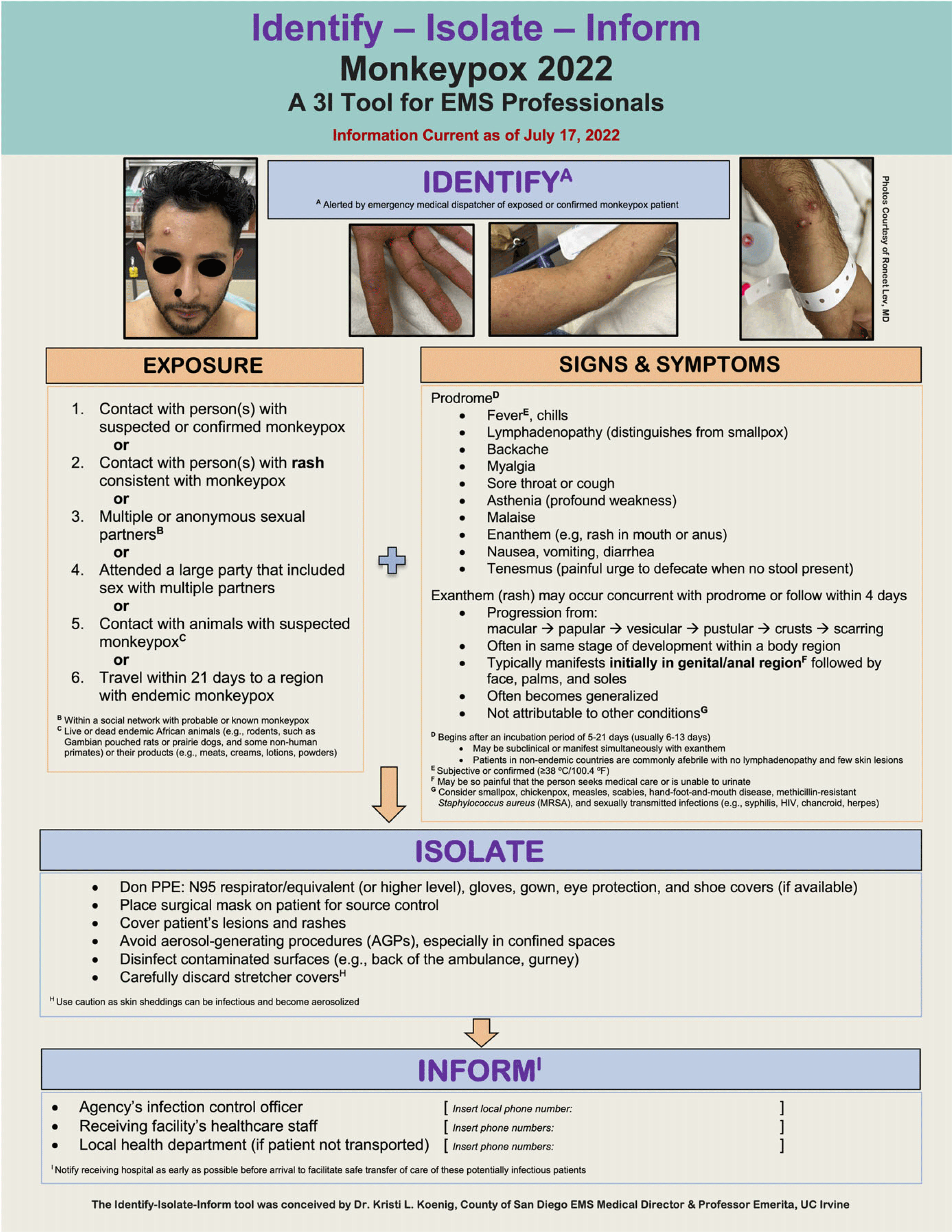
Figure 1. Monkeypox 2022 Identify-Isolate-Inform (3I) Tool for EMS Professionals.
Abbreviations: 3I, Identify-Isolate-Inform; EMS, Emergency Medical Services; PPE, personal protective equipment.
Background
Historical Monkeypox Clinical Presentation
Classically, monkeypox patients present with signs and symptoms resembling smallpox, a disease declared “globally eradicated” by the WHO in 1980. 7 The incubation period ranges from five to 21 days (typically between six to 13 days). The first signs and symptoms are constitutional and called a prodrome because they manifest before the rash. These include influenza-like illness (fever, chills, sore throat, cough, malaise, asthenia, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting); Reference Reynolds, Yorita and Kuehnert8 lymphadenopathy (a distinguishing feature from smallpox); and enanthem, often in the mouth and anus. Prodromal signs and symptoms typically precede the exanthem (rash) by one to four days. While the route of infection can influence clinical manifestations, Reference Reynolds, Yorita and Kuehnert8 initial skin lesions in human Reference Ogoina, Iroezindu and James9 and non-human primates Reference Patrono, Pléh and Samuni10 often present in the anogenital region and then appear on the face, palms, and soles before spreading centrifugally. Skin lesions progress through macular, papular, vesicular (blister), and pustular stages, followed by scabbing and healing. In addition, lesions present in the same stage of development in a given body region. Long-term sequelae of monkeypox infection can include disfiguring scars Reference Beer and Rao11 and permanent blindness resulting from corneal lesions. Reference Hughes, McCollum and Pukuta12
2022 Monkeypox Clinical Presentation
Unlike the classical monkeypox presentation, cases from the 2022 outbreak may not begin with a prodrome, skin lesions tend to be subdued, and lesions in a given body region may be at various stages of development. Furthermore, the constitutional symptoms can manifest simultaneously with the rash and enanthem. Moreover, lymphadenopathy and lesions on the palms and soles are less common. Hence, these features may have limited utility for differentiating monkeypox from other diseases. Monkeypox can appear similar to numerous more common diseases. The differential diagnosis of monkeypox is broad (Figure 2); thus, prehospital clinicians should have a low threshold for implementing monkeypox precautions.

Figure 2. Selected Agents in the Differential Diagnosis of Monkeypox.
Managing exposed persons in the 2022 outbreak can be challenging as the presentation may be subtle. Prehospital clinicians should consider monkeypox as a potential diagnosis in patients with risk factors for exposure because it can be infectious during a subclinical prodromal phase or before rash onset. Reducing monkeypox transmission helps avoid additional global stresses on the health care system. Strategies for reducing transmission include physical distancing, symptom monitoring, and standard hygienic practices. These approaches may obviate the need for quarantine of exposed health care workers, thereby contributing to preserving health care system capacity. Reference Koenig, Marty and Beÿ13
Patients seeking care may exhibit only prodromal symptoms or be unaware of their infectious skin lesions. The differential diagnosis varies based on vaccination status, prior exposure, virus clade, and disease stage. Monkeypox can resemble various dermatological conditions and sexually transmitted infections (STIs; Figure 3). Reference Koenig, Beÿ and Marty14 Distinguishing between monkeypox and other more common diseases in the prehospital setting can be challenging. Detecting alternate infections, especially other STIs, does not exclude the possibility of monkeypox. Hospitalization for monkeypox is rare and usually results from the need to treat secondary infections or manage intractable pain emanating from lesions.

Figure 3. Selected Pathogens (Agents) in Monkeypox Differential Diagnosis.
Monkeypox virus is predominantly spread through close contact with infected skin lesions and can also be transmitted via bodily fluids and large droplets. Aerosolization of the virus (eg, from intubation, other medical procedures, or shaking contaminated bedsheets) can result in transmission to health care workers and others. Persons with confirmed monkeypox can mitigate transmission risk by covering infectious lesions, wearing a mask, and isolating themselves during the contagious period. Once lesions have healed, which can take two to four weeks or longer, they cease to be a source of infection.
Report
Prehospital workers may be the first health care professionals to encounter suspected or confirmed monkeypox patients. Clinicians must learn to recognize the risk factors and presentations and consider monkeypox as a possible diagnosis. They should also take special precautions to prevent disease transmission and ensure the effective transfer of care at the receiving facility. More comprehensive data on the history, background, presentation, and management of monkeypox 2022 and the 3I concept are available. Reference Koenig, Beÿ and Marty14
Identify-Isolate-Inform (3I) Tool
The 3I framework was conceived in 2014 during the 2013-2016 Ebola virus outbreak when several Ebola cases presented at hospitals in the United States. The framework is designed to give clinicians high-level, actionable guidance for properly managing infectious diseases and has been applied to at least ten other conditions. Reference Koenig15–Reference Koenig, Beÿ and McDonald23 Figure 1 presents a prehospital adaptation of the Monkeypox 3I Tool Reference Koenig, Beÿ and Marty14 with specific considerations for EMS professionals.
Identify
Work is on-going to ascertain whether suspected or confirmed monkeypox patients can be identified at the emergency medical dispatch level. While travel history remains important in determining disease exposure risk, documented community spread in non-endemic regions has limited its usefulness. After emergency medical dispatchers identify a person with suspected or confirmed monkeypox, EMS professionals are advised to implement appropriate infection prevention measures before patient contact. These are similar to those applied during the COVID-19 pandemic and may include:
-
Requesting the patient to mask and come to the door of the residence, bringing medications, if possible (allowing first responders to remain outside);
-
If first responders must go inside to evaluate a patient, first send in a scout paramedic wearing full personal protective equipment (PPE);
-
Apply a surgical mask to the patient for source control (if tolerated); and
-
Avoid aerosol-generating procedures (AGPs).
If monkeypox is suspected, prehospital professionals should determine the patient’s likelihood of having the disease based on signs and symptoms and exposure risk. Cases in the 2022 outbreak are less likely to present with classical clinical indicators (Figure 4). Exposure risks independent of travel history include contact with persons or animal reservoirs suspected or confirmed to have monkeypox and contact with infected surfaces or other formites.

Figure 4. Classical Versus Monkeypox 2022 Presentations.
Isolate
Prehospital clinicians should don appropriate PPE throughout first contact, transport, care transfer, and during disinfection of the transport vehicle. Proper PPE includes an N95 respirator/equivalent (or higher), gloves, gown, eye protection, 24 and shoe covers, if available. Notably, PPE used during the COVID-19 pandemic is sufficient to protect prehospital professionals from monkeypox. Source-control measures, including placing a surgical mask on the patient and covering exposed lesions, can lessen the risk of transmission in enclosed spaces (eg, the back of an ambulance). Similarly, avoid AGPs whenever possible because of the increased exposure risk and potential for infectious monkeypox virus aerosols to linger for extended periods in enclosed spaces. Reference Verreault, Killeen, Redmann and Roy25
Inform
It is imperative that transporting crews relay the patient’s suspected or confirmed monkeypox status to the receiving facility early to allow time for the hospital to prepare and minimize risks of infection spread and delays in the transfer of care. Local or state protocols may require prehospital clinicians to report communicable infectious diseases to their agency’s infection-control officer or health authority, especially for patients not transported to a hospital. Follow required protocols when reporting communicable diseases and health care worker exposures.
Discussion
This research report discusses considerations for the management of suspected or confirmed monkeypox 2022 in the prehospital setting. As of July 11, 2022, a literature search of the PubMed (National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Institutes of Health; Bethesda, Maryland USA); MEDLINE (US National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health; Bethesda, Maryland USA); CINAHL (EBSCO Information Services; Ipswich, Massachusetts USA); and Scopus (Elsevier; Amsterdam, Netherlands) databases did not identify any published articles specifically addressing EMS considerations for monkeypox. Given the rapidly evolving nature of the 2022 outbreak, only limited data are available describing the clinical presentation, management, epidemiology, and long-term outcomes. Furthermore, the diagnosis cannot be confirmed in the prehospital setting. Despite this, applying the Monkeypox 3I Tool for EMS Professionals (Figure 1) can increase opportunities to detect presumptive monkeypox and reduce the risk of disease transmission.
As demonstrated by the COVID-19 pandemic, prehospital clinicians play a critical role in the management of public health emergencies. Throughout the pandemic, prehospital professionals have assisted with out-of-hospital treatments, vaccination campaigns, and patient transport, among other activities. Although monkeypox 2022 is unlikely to cause a global pandemic on the scale of COVID-19, it is nevertheless a major international public health threat. Prehospital clinicians can apply their unique training and role as the interface between at-risk patient populations and health care to mitigate the further spread of monkeypox 2022.
Conclusion
Monkeypox 2022 represents a rapidly escalating outbreak with extensive and sustained global human-to-human and community transmission. Cases in the 2022 outbreak differ from classical clinical presentations as described in endemic regions of Central and West Africa and during the 2003 zoonotic monkeypox outbreak in the United States. Reference Reynolds, Yorita and Kuehnert8 Importantly, before this outbreak, monkeypox was very rare; thus, most health care workers have never encountered the disease. Expansion of cases to non-endemic regions creates a risk of reverse zoonosis and the creation of new endemic zones across the globe.
Prehospital clinicians play a key role in infectious disease mitigation, as demonstrated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The science on the monkeypox 2022 outbreak continues to evolve. It is imperative that clinicians, particularly those in the prehospital setting who may encounter suspected or confirmed cases, immediately identify and isolate such patients to protect themselves and other health care workers from exposure and inform the relevant health authorities to help mitigate the spread of this re-emerging infectious disease.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare none.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Materials
To view supplementary material for this article, please visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S1049023X22001121







