Introduction
Bilateral facial nerve palsy is a rare condition, accounting for less than 2% of all cases of facial palsy. Its incidence is reported to approximately 1 in 5,000,000.Reference Pothiawala and Lateef 1 Unlike unilateral facial nerve palsy, bilateral facial nerve palsy seldom presents secondary to Bell’s palsy. Instead, it often indicates a serious underlying medical condition. Known etiologies include congenital abnormalities, cranial trauma, infection, inflammation, metabolic and autoimmune disorders, stroke, neoplasia, and iatrogenesis.Reference Sim, Choi and Kim 2 , Reference Kilic, Ozdek and Felek 3
In this study, we report the case of a 22-year-old man presenting with bilateral facial nerve palsy, who was later diagnosed with syphilis.
Case Report
A 22-year-old man with no medical history was admitted to the emergency department (ED) of our hospital due to bilateral facial nerve palsy (Figure 1A). For approximately 2 days prior to admission, he was unable to close his eyelids (Figure 1B). At the time of admission, he denied having any sexually transmitted disease and reported no history of unprotected sexual behavior or sexual activity with other men. We collected his history, and the patient denied having a chancre in the previous weeks as well as any history of tick exposure. The values for vital signs at the initial visit were systolic/diastolic blood pressure of 101/56 mm Hg, body temperature of 36.0°C (96.8°F), pulse rate of 61 beats/minute, and respiratory rate of 16 breaths/minute. Physical examination confirmed bilateral facial nerve palsy of the peripheral type (involving an entire side of the face), while examination of other cranial nerves revealed no abnormalities. Facial nerve palsy is diagnosed on the basis of a physical examination of facial expression, and the face should appear symmetric. First, the number of wrinkles apparent on either side of the forehead should be the same. Second, the nasolabial folds should be equal. Third, the corners of the mouth should be at the same height. The central type of facial palsy leads to paralysis of the lower half of one side of the face, whereas the peripheral type is characterized by total facial paralysis, that is, paralysis of both the upper and lower halves of the face on the same side.Reference Campbell 4 Muscle power was normal in all four extremities, sensory examination was unremarkable, and deep tendon reflexes were present. There were no cerebellar signs. No skin or genital abnormality was found during this visit. Laboratory tests revealed a hemoglobin level of 132 g/L (normal range, 116–168 g/L), a white cell count of 11.53×109/L (normal range, 4.5–11×109/L) (78.7% neutrophils), and a C-reactive protein concentration of 15.6 mg/L (normal range, 0.0–5.0 mg/L). Examination of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), obtained by lumbar puncture, revealed no nucleated cells and one red cell. The patient’s glucose level was 3.61 mmol/L (normal range, 2.5–4.2 mmol/L), and protein level was 0.25 g/L (normal range, 0.15–0. 45 g/L). Serum India ink staining and serum antibody tests for Lyme disease, Cryptococcus, and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) yielded negative results. Serum levels of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and thyroid-stimulating hormone were unremarkable. The screening tests for syphilis include the rapid plasma reagin and Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) tests. At the initial presentation, we performed the serologic rapid plasma reagin test, which was non-reactive. Other serologic biochemical and metabolic profiles were normal. The CSF VDRL test and the polymerase chain reaction test for herpes were non-reactive. Because the serologic rapid plasma reagin and CSF VDRL screening tests were non-reactive at the first presentation, we did not perform the serologic Treponema pallidum particle agglutination test at that time. The diagnosis at discharge after this initial visit was bilateral facial nerve palsy of an undetermined cause. We prescribed oral prednisolone for bilateral facial nerve palsy and a neurology outpatient department follow-up.
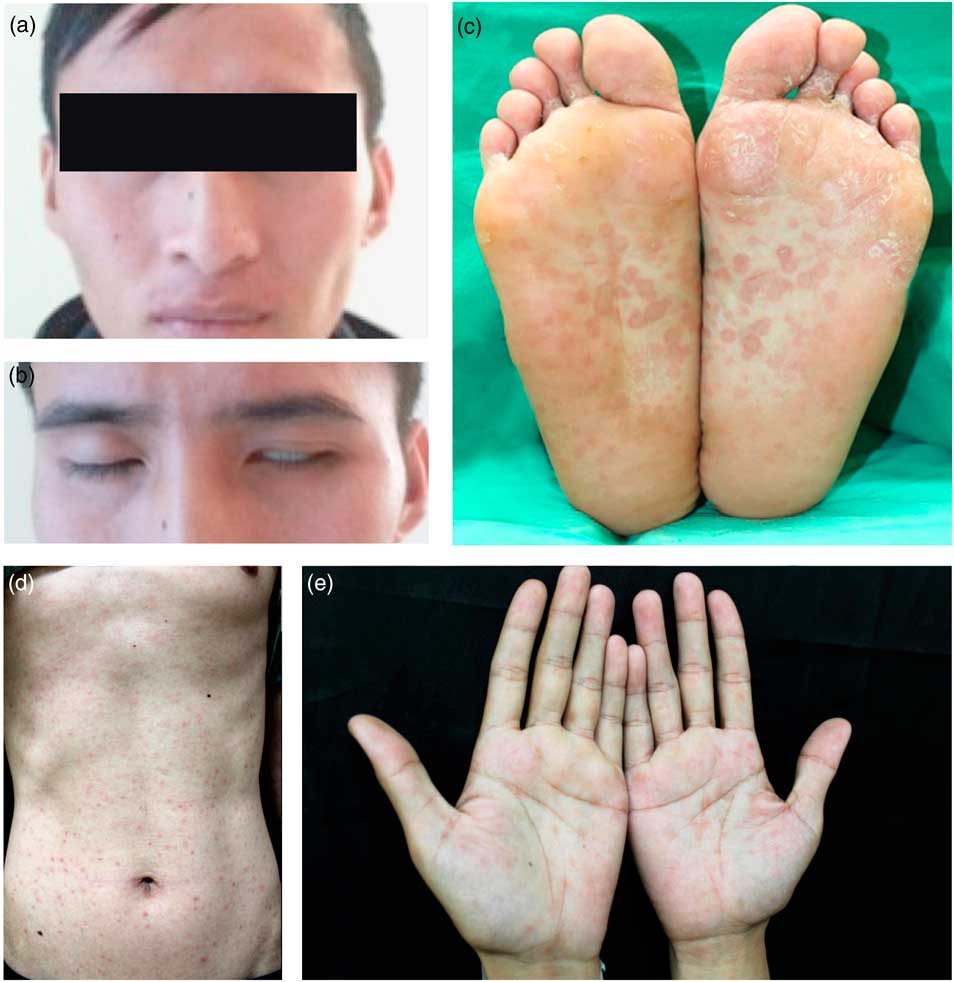
Figure 1 A. A 22-year-old man with bilateral facial paralysis. B. Bilateral facial nerve palsy (peripheral type) was observed, but it was more pronounced on the left side. C-E. Red maculopapular rashes manifested on the trunk, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet.
One week later, a red maculopapular rash appeared on the trunk and on all four extremities of the patient (Figure 1C-E), and he returned to our ED. At that time, the ED doctor consulted a neurologist, who noted that the bilateral facial nerve palsy was partially improved by steroid treatment during the second visit. At this time, the Treponema pallidum particle agglutination test showed a high serum titer (1:1280). A repeat lumbar puncture showed three nucleated cells and three red cells. Glucose and protein levels were normal, and the CSF VDRL test remained non-reactive. However, the rapid plasma reagin serology results were remarkable (1:32). Subsequently, the patient was diagnosed with syphilis. Table 1 summarizes the laboratory data at the first and second presentations, including data for both blood and CSF tests. At the second visit, we attempted to identify the source of the infection. The patient reported two events of unprotected genital sexual exposure with a sex worker approximately 3 and 6 months prior to symptom onset. He denied any unprotected sexual activity prior to these two events.
Table 1 Summary of blood and CSF test results
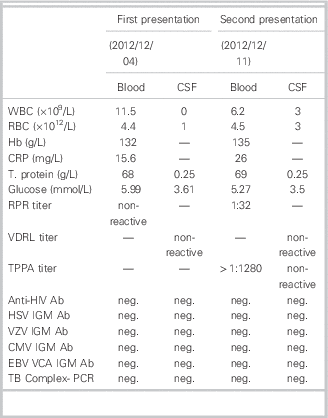
CMV=cytomegalovirus; CRP=C-reactive protein concentration (normal range, 0.0–5.0 mg/L); CSF=cerebrospinal fluid; EBV VCA=Epstein–Barr virus viral-capsid antigen; glucose (normal range, blood: 3.9–6.1 mmol L; CSF /: 2.5–4.2 mmol/L); Hb=hemoglobin level (normal range, 116–168 g/L); HIV=human immunodeficiency virus; HSV=herpes simplex virus; neg.=negative; RBC=red blood cell (normal range, blood: 4.6–6.0×1012/L; CSF: 0–0×1012/L); RPR=rapid plasma reagin; T. protein=total protein level (normal range, blood: 66–87 g/L; CSF: 0.15–0. 45 g/L); TB Complex- PCR=tuberculosis complex-polymerase chain reaction; TPPA=Treponema pallidum particle agglutination; VDRL=Venereal Disease Research Laboratory; VZV=varicella zoster virus; WBC=white blood cell (normal range, blood: 4.5–11×109/L; CSF: 0–0×109/L).
Although magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is not routinely performed in the ED, we had the opportunity to perform brain MRI and nerve conduction velocity testing for this patient after hospitalization, to rule out other organic etiologies such as tumor, other infections, or inflammation. Nerve conduction velocity testing was conducted on all four limbs and revealed no major abnormal findings. Facial stimulation testing showed reduced amplitude of compound motor action potentials, which was more severe on the right side. The blink reflex did not show bilateral latencies of R1, ipsilateral R2, or contralateral R2, indicating bilateral facial neuropathy, which was more severe on the left side. Brain MRI (3.0 T, 3D T1-weighted fast spoiled gradient echo imaging, 1.4-mm slice thickness) was performed in the supine position using gadolinium contrast medium (0.1 mmol/kg, given intravenously) to evaluate the cranial nerves. Contrast enhancement was noted in the facial nerves in the region of the internal auditory canals and temporal bones (Figure 2), suggesting bilateral inflammation or infection. The brain showed normal ventricular size, as well as normal grey/white matter and meningeal signal intensities.
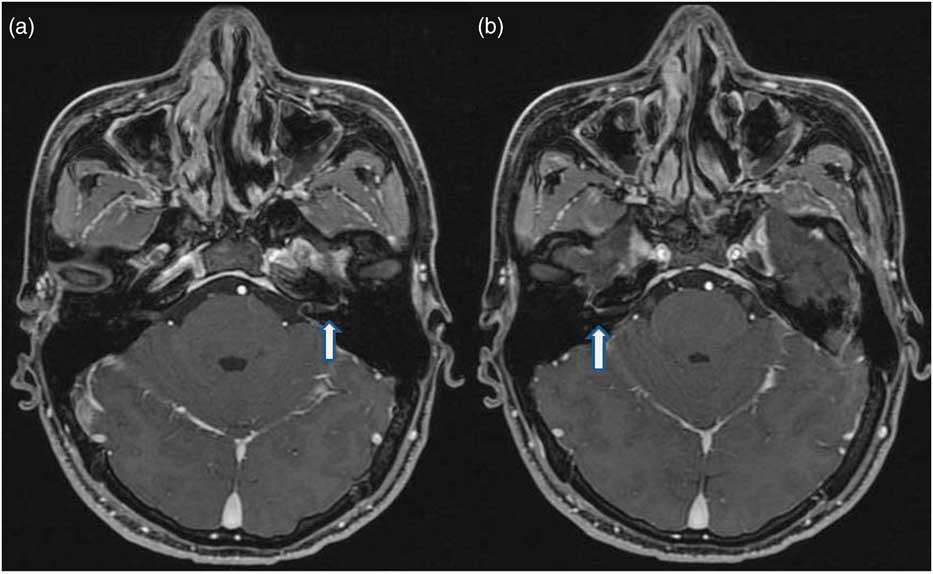
Figure 2 Gadolinium-enhanced MRI showing regular enhancement of the internal auditory canal, labyrinthine, and anterior tympanic portions of the left (A, see arrow) and right facial nerve (B, see arrow).
Intramuscular treatment with benzathine penicillin (2.4 million units) in a single dose was initiated. Within 1 week, facial nerve function and the red maculopapular rashes over the trunk and all four extremities began to improve. Complete recovery was noted at the 3-month follow-up examination.
Discussion
Bilateral facial nerve palsy is an exceedingly rare condition, accounting for less than 2% of all cases of facial palsy. Unlike unilateral facial nerve palsy, which is usually idiopathic, bilateral facial nerve palsy often indicates a serious underlying medical condition, which can include Lyme disease, sarcoidosis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, diabetic (mellitus) neuropathy, and multiple idiopathic cranial neuropathies.Reference Pothiawala and Lateef 1 Here, we report the case of a patient with syphilis who presented with bilateral facial nerve palsy as his initial symptom.
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the spirochete bacterium T. pallidum. With the advent of penicillin treatment and an aggressive public health approach, the annual incidence rate of syphilis in the United States decreased by about 95% between 1943 and 2000.Reference Longo, Fauci and Kasper 5 Between 2000 and 2008, however, the number of cases of syphilis infection in the United States has more than doubled.Reference Longo, Fauci and Kasper 5 These cases especially involve men who engage in homosexual behavior and are co-infected with HIV.Reference Longo, Fauci and Kasper 5 Overall, nearly 12 million new syphilis infections occur each year, with the most affected regions including South America, Southeast Asia, China, and sub-Saharan Africa.Reference Longo, Fauci and Kasper 5 The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending on the stage in which they present. The primary stage involves the appearance of a chancre—a round, painless ulcer or sore on the area of the skin initially exposed to the infection. Left untreated for 2 to 4 weeks, the disease progresses to the secondary stage with the clinical manifestation of a rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.Reference Smith and Anderson 6 Nervous system involvement (neurosyphilis) can occur at any stage of the disease, striking at weeks to years after the initial infection. It is, however, most commonly observed in the final, tertiary stage.Reference Smith and Anderson 6 Although neurosyphilis is often asymptomatic,Reference Smith and Anderson 6 it can sometimes manifest as visual disturbances, hearing loss, and facial palsy.Reference Keane 7
In the case described here, the patient presented with isolated bilateral facial nerve palsy as the initial manifestation of early-stage syphilis. Laboratory examinations, including CSF and serologic tests, yielded normal findings at the initial presentation. It was subsequent to the appearance of a rash on the trunk and all four extremities 1 week after admission that serum rapid plasma reagin and Treponema pallidum particle agglutination titers were remarkable (1:32 and 1:1280, respectively). Notably, CSF VDRL remained non-reactive. The patient denied any history of unprotected sexual behavior until the diagnosis was made. Other cases of facial nerve palsy associated with syphilis have been reported in the literature. In 1929, Strauss reviewed 37 cases of syphilis with bilateral facial nerve palsy, of which 23 were in the early stage of syphilis, 6 were in the late stage, and 8 were in an undetermined stage.Reference Strauss 8 A review article by Keane found that 2 of 43 cases of bilateral facial nerve palsy were induced by syphilis infection.Reference Keane 7 A potential differential diagnosis of bilateral facial nerve palsy could be syphilitic meningitis, which was reported by Merritt et al. to be the most common etiology involving cranial nerves, especially the facial and auditory nerves.Reference Merritt, Adams and Soloman 9 In an analysis of 34 patients, unilateral facial nerve involvement was noted in 16 cases, whereas bilateral palsy was observed in 2 cases.Reference Merritt, Adams and Soloman 9 However, based on the clinical symptoms and CSF findings, syphilitic meningitis was less likely in the current case.
On the basis of the skin rashes over the trunk and extremities as well as the laboratory data showing that CSF VDRL was non-reactive, we deduced that the syphilis infection was in the secondary stage before penicillin G treatment was initiated. Had the skin rashes not appeared, physicians could have easily misdiagnosed the cause underlying the bilateral facial nerve palsy. Because a detailed history and serum syphilis tests were necessary to provide early diagnostic clues, we recommend that syphilis infection be considered in the differential diagnosis of bilateral facial nerve palsy. The diagnosis of syphilis is based on both non-treponemal and treponemal serologic tests. Non-treponemal tests are often screening tests and include the rapid plasma reagin and VDRL tests. Treponemal tests are used for confirmation after a reactive non-treponemal test and include the Treponema pallidum particle agglutination and Treponema pallidum hemagglutination assays (TPHA). The sensitivity and specificity of serologic tests for syphilis are listed in Table 2. The positive predictive value or negative predictive value of syphilis tests depends on disease prevalence in the population tested.Reference Seña, White and Sparling 10 The positive predictive value of syphilis tests can reach 90% as syphilis prevalence or clinical suspicion increases in the population tested.Reference Seña, White and Sparling 10 As noted in Table 2, the sensitivity of the serologic rapid plasma reagin test at the primary syphilis stage is only 74%–87% (well below 100%). For our case, the serologic rapid plasma reagin test was non-reactive at the first presentation, causing us to miss the diagnosis of syphilis at this time.
Table 2 Sensitivity and specificity of serologic tests for syphilis

NA=not available; RPR=rapid plasma reagin; TPHA=Treponema pallidum hemagglutination assay; TPPA=Treponema pallidum particle agglutination; VDRL=Venereal Disease Research Laboratory.
(Adapted from Seña AC, White BL, Sparling PF. Novel Treponema pallidum serologic tests: a paradigm shift in syphilis screening for the 21st century. Clin Infect Dis 2010;51(6):700-8.)
Take-Home Clinical Message Pertinent To Emergency Physicians
Despite the negative initial screening test, it was considered important to record the patient’s sexual history and follow up on his condition. Because of the only moderate sensitivity of the rapid plasma reagin test, we believe syphilis should be included in the differential diagnosis for bilateral facial nerve palsy, and patients should be closely followed even when the initial screening test is negative. We believe this to be especially true for bilateral facial nerve palsy in young people, or in populations with high risk of sexual exposure. Emergency physicians should be aware of syphilis as a rare but possible etiology of bilateral facial nerve palsy. Syphilis might be making a comeback in young men with a sexual history, especially in men with homosexual exposure and HIV. Failure to recognize the facial signs of syphilis could result in inappropriate management, which could, in turn, affect the clinical outcome. For young adults presenting to the ED with bilateral facial nerve palsy, a thorough history of sexual exposure and serum rapid plasma reagin and Treponema pallidum particle agglutination is warranted. More thorough assessments, including additional laboratory and radiological tests, may also be necessary. Furthermore, if a patient with an initial presentation of bilateral facial nerve palsy and a negative syphilis screen reports a history of exposure to sex workers in places with a higher incidence of syphilis, the use of empiric penicillin may be warranted.
Competing interests: None declared.






