INTRODUCTION
Invasive alien species are the second greatest threat to global biodiversity loss (Sala et al., Reference Sala, Chapin, Gardner, Lauenroth, Mooney, Ramakrishnan, Walker, Steffen, Canadell and Ingram1999). In the case of the marine environment, these invasive species may be escapees following intentional introduction, but are more usually the unintended consequence of global shipping and maritime transport (Carlton, Reference Carlton1987; Williams et al., Reference Williams, Griffiths, Van der Wal and Kelly1988; Carlton & Geller, Reference Carlton and Geller1993; Sax et al., Reference Sax, Stachowicz, Brown, Bruno, Dawson, Gaines, Grosberg, Hastings, Holt, Mayfield, O'Connor and Rice2007; Rodríguez-Labajos et al., Reference Rodríguez-Labajos, Binimelis and Monterroso2009; Briski et al., Reference Briski, Ghabooli, Bailey and MacIsaac2012; Guo et al., Reference Guo, Sax, Qian and Early2012). Although most alien taxa that are introduced into new environments following ballast-water containment or hull-fouling fail to establish viable populations in their new environment (Carlton, Reference Carlton1996), a sufficiently large number do to warrant international programmes of prevention and control.
Although jellyfishes (Cnidaria: Medusozoa) have a number of biological features that allow them to be potentially invasive (Graham & Bayha, Reference Graham, Bayha and Nentwig2007; Bayha & Graham, Reference Bayha, Graham, Pitt and Lucas2014), there are relatively few species (five out of ~201; Bayha & Graham, Reference Bayha, Graham, Pitt and Lucas2014) with proven reports of invasion worldwide, although with many records distributed in different ocean basins (Bayha & Graham, Reference Bayha, Graham, Pitt and Lucas2014). Part of the reason for this must reflect an incomplete understanding of the biology, taxonomy and distribution of most jellyfishes (Dawson, Reference Dawson2005a), many of which have a number of cryptic species (Dawson, Reference Dawson2003; Holland et al., Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004), which was estimated as 7% (Appeltans et al., Reference Appeltans, Ahyong, Anderson, Angel, Artois, Bailly, Bamber, Barber, Bartsch, Berta, Błazewicz-Paszkowycz, Bock, Boxshall, Boyko, Brandão, Bray, Bruce, Cairns, Chan, Cheng, Collins, Cribb, Curini-Galletti, Dahdouh-Guebas, Davie, Dawson, De Clerck, Decock, De Grave, de Voogd, Domning, Emig, Erséus, Eschmeyer, Fauchald, Fautin, Feist, Fransen, Furuya, Garcia-Alvarez, Gerken, Gibson, Gittenberger, Gofas, Gómez-Daglio, Gordon, Guiry, Hernandez, Hoeksema, Hopcroft, Jaume, Kirk, Koedam, Koenemann, Kolb, Kristensen, Kroh, Lambert, Lazarus, Lemaitre, Longshaw, Lowry, MacPherson, Madin, Mah, Mapstone, McLaughlin, Mees, Meland, Messing, Mills, Molodtsova, Mooi, Neuhaus, Ng, Nielsen, Norenburg, Opresko, Osawa, Paulay, Perrin, Pilger, Poore, Pugh, Read, Reimer, Rius, Rocha, Saiz-Salinas, Scarabino, Schierwater, Schmidt-Rhaesa, Schnabel, Schotte, Schuchert, Schwabe, Segers, Self-Sullivan, Shenkar, Siegel, Sterrer, Stöhr, Swalla, Tasker, Thuesen, Timm, Todaro, Turon, Tyler, Uetz, van der Land, Vanhoorne, van Ofwegen, van Soest, Vanaverbeke, Walker-Smith, Walter, Warren, Williams, Wilson and Costello2012). In Brazilian waters (along 9230 km of coast) only one (Phyllorhiza punctata von Lendenfeld, Reference von Lendenfeld1884; Moreira, Reference Moreira1961; Haddad & Nogueira, Reference Haddad and Nogueira2006) of the 22 recorded species of scyphozoans (Morandini et al., Reference Morandini, Ascher, Stampar and Ferreira2005; Lopes et al., Reference Lopes, Coradin, Pombo and Cunha2009) can be considered as exotic to date.
The genus Cassiopea is widely distributed across the globe in shallow tropical waters (Kramp, Reference Kramp1961). Although a total of 10 species are considered valid (Kramp, Reference Kramp1961; Hummelinck, Reference Hummelinck1968; Thiel, Reference Thiel1975), a number of genetically distinct lineages have been identified (Holland et al., Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004). Species of the genus can be abundant in disturbed/eutrophicated environments (Arai, Reference Arai2001). Members of this genus have been considered invasive in the Mediterranean (Galil et al., Reference Galil, Spanier and Ferguson1990; Çevik et al., Reference Çevik, Erkol and Toklu2006; Schembri et al., Reference Schembri, Deidun and Vella2010). Holland et al. (Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004) also mapped the distribution of some populations and attributed the ‘unusual’ pattern observed to maritime transport.
The first report of the genus Cassiopea Péron & Lesueur, Reference Péron and Lesueur1810 in Brazil was published in 2002 (Migotto et al., Reference Migotto, Marques, Morandini and Silveira2002), although a number of sightings and grey-literature accounts pre-date that, but unfortunately without any voucher specimens.
Here we report specimens of Cassiopea from along the Brazilian coast using both morphological and molecular data and we compare our results with published information in order to try and determine their origin. The application of molecular (genetic) data to define and identify populations and species in marine research is now a well-recognized venture (Schander & Willassen, Reference Schander and Willassen2005; Radulovici et al., Reference Radulovici, Archambault and Dufresne2010; De Broyer et al., Reference De Broyer and Danis2011). Together with approaches such as morphology and ecology, this information let us analyse historical aspects such as time of possible invasion based on the divergence of Brazilian jellyfishes compared with the available data in the literature (Holland et al., Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Field sampling
Jellyfish specimens were sampled by hand at a small branch of the Itajuru Channel, a connection of the Araruama Lagoon to the open sea in Cabo Frio county, Rio de Janeiro state (22°52′32″S 42°01′07″W) (Figure 1) during the period November 2008 to October 2012 (weekly intervals from 2008–2009 and every 3 months from 2010–2012). Regular measurements of salinity, dissolved oxygen concentrations and temperature (recorded with an YSI 85 probe) indicate that salinity varied from 0–36, water temperature from 26.6–28.7°C, and dissolved oxygen from 7.01–15.56 µg L−1 in a period of 6 h (from high to low tide).

Fig. 1. Map of Brazil, showing records of Cassiopea Péron & Lesueur, Reference Péron and Lesueur1810 specimens. Squares refer only to polyp records (1–2), triangles refer to medusa photographic records (4–7), star refers to sampling site at Cabo Frio (3), numbers after each symbol refer to date of first sighting in each area: (1) Imbé (29°58′26″S 50°08′18″W; February 2005), Rio Grande do Sul state; (2) São Sebastião (23°49′41″S 45°25′22″W; March 1999), São Paulo state; (3) Cabo Frio (22°52′32″S 42°01′07″W; October 2008), Rio de Janeiro state; (4) Aracruz (19°50′07″S 40°03′28″W; August 2007), Espírito Santo state; (5) Salvador (12°57′26″S 38°31′50″W; February 2012), Bahia state; (6) Macau (5°03′53″S 36°30′18″W; February 2011), Rio Grande do Norte state; (7) Itarema (02°52′48″S 39°54′15″W; June 2012), Ceará state.
Medusae were preserved either in ethanol 95 or 4% formaldehyde solution in seawater. Two hundred freshly collected specimens were examined in the laboratory facilities to measure bell diameter, count number of rhopalia, lappets, mouth arms, define shape of the oral arm appendages and the organization of the canal system (with injection of dye). Morphological comparisons were conducted with descriptions in the literature as well as with specimens of Cassiopea frondosa (Pallas, Reference Pallas1774) and Cassiopea cf. xamachana Bigelow, Reference Bigelow1892 that had been collected in February 2004 at Laguna Golf Club, Varadero (Cuba), and deposited at the Museu Nacional da Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (MNRJ 5837 and 5838, respectively).
Scyphistomae morphologically resembling Cassiopea scyphistomae (Hofmann et al., Reference Hofmann, Neumann and Henne1978; Straehler-Pohl, Reference Straehler-Pohl2009; Heins et al., Reference Heins, Glatzel and Holst2015) were collected at the same place that medusae were found. The scyphistomae were found growing on a variety of substrata, including plastic, wood and rubber shoes as well as on the exotic ascidian Styela plicata (Lesueur, Reference Lesueur1823). Ten scyphistomae (Figure 2) were measured in the laboratory following the parameters proposed by Straehler-Pohl et al. (Reference Straehler-Pohl, Widmer and Morandini2011).

Fig. 2. Cassiopea andromeda (Forskål, Reference Forskål1775) scyphistoma just after collection, note long stalk and planuloid budding at the base of calyx; polyp ~5 mm long.
Voucher specimens of medusae and scyphistomae were deposited at the Museu de Zoologia da Universidade de São Paulo (MZUSP, 1944, 1945).
Molecular protocols
DNA was extracted from the oral arms removed from three specimens of medusae using an Agencourt DNAdvance® kit (#A48708); DNA extraction from scyphistomae was not successful. Partial gene sequences were amplified using PCR, Universal PCR primers for the cytochrome oxidase I gene (COI) were used to amplify ~500 base pairs of this protein coding mitochondrial gene, using the original PCR program (forward LCO1490 and reverse HCO2198 primers; Folmer et al., Reference Folmer, Black, Hoeh, Lutz and Vrijenhoek1994). The PCR products were purified with the Agencourt AMPure® kit (#A63881) and this amplified DNA sequences were prepared to sequencing using the Applied Biosystems BigDye® Terminator v3.1 kit (#4337455), with the same primers and temperature conditions from the PCR's reactions. The sequencing procedure was carried out on a Hitachi ABI PRISM®3100 genetic analyser.
DNA analysis
Sequences were assembled and edited using Geneious™ 5.4.4 (Drummond et al., Reference Drummond, Ashton, Buxton, Cheung, Cooper, Duran, Field, Heled, Kearse, Markowitz, Moir, Stones-Havas, Sturrock, Thierer and Wilson2011), and new sequences were deposited in GenBank (KC464458-KC464459). COI sequences were compared to those of the other Cassiopea specimens available in GenBank (see table 1 in Holland et al., Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004): sequence alignment was made using the MUSCLE plugin in Geneious™ 5.4.4 (default parameters) (Edgar, Reference Edgar2004). Kimura's two-parameter model of base substitution and p-distance was used to calculate genetic distances in MEGA 6.05 software (Tamura et al., Reference Tamura, Peterson, Peterson, Stecher, Nei and Kumar2011). The Maximum Likelihood analysis was conducted via PHyML 3.0.1 beta with a more inclusive model, the general time reversible model with gamma values estimated directly from data (GTR + GAMMA) (Guindon et al., Reference Guindon, Dufayard, Lefort, Anisimova, Hordijk and Gascuel2010). The Maximum Parsimony analysis was conducted via MEGA 5.05 (Tamura et al., Reference Tamura, Peterson, Peterson, Stecher, Nei and Kumar2011): optimal tree was obtained by the search of optimal tree space using the Close-Neighbour-Interchange (CNI) algorithm (see more in Stampar et al., Reference Stampar, Maronna, Vermeij, Silveira and Morandini2012). Support estimation was assessed with two non-parametric methods: bootstrap (500 pseudoreplicates) and SH-aLRT test (Anisimova et al., Reference Anisimova, Gil, Dufayard, Dessimoz and Gascuel2011) in PHyML 3.0.1 beta (Figure 3).
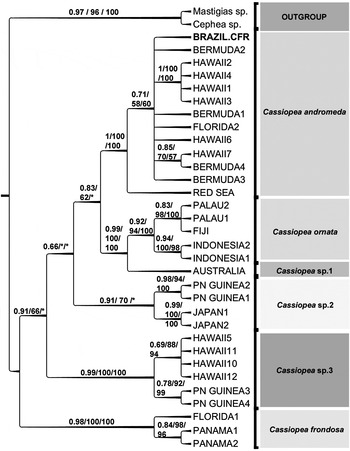
Fig. 3. Left panel – Cladogram representation for maximum likelihood tree (ML) of Cassiopea species with support values on branches (as in figure order: SH-aLRT/maximum parsimony's tree bootstrap result/maximum likelihood bootstrap) * = less than 50; in cases where figure permits, ML bootstrap values are below their respective branch. Right panel: phylogram representation only for same result (ML phylogram).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The morphological and range meristic characters determined from the 200 specimens collected at Cabo Frio are shown in Table 1 in comparison with data from the other presently recognized species in the genus. It should be noted that all inspected specimens were males, suggesting that the population is perhaps maintained through asexual reproduction at the scyphistoma stage. The morphological and meristic data indicate that, with the possible exception of Cassiopea frondosa, it is not possible to distinguish between the different species (see Table 1) using the selected character set because of the high level of overlap between species (see Mayer, Reference Mayer1910; Kramp, Reference Kramp1961; Hummelinck, Reference Hummelinck1968; Thiel, Reference Thiel1975; Holland et al., Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004). The exception, Cassiopea frondosa, can be separated from the other recognized species by the number of rhopalia (12, although some variation is also found) and it is clear that the Brazilian material is not of this species.
Table 1. Comparison of available characters from the literature of the 10 valid/nominal species of the genus Cassiopea Péron & Lesueur, Reference Péron and Lesueur1810 (species list from Mayer, Reference Mayer1910; Kramp, Reference Kramp1961; Gershwin et al., Reference Gershwin, Zeidler and Davie2010). n = several appendages, not specified on the papers. For mouth arms we are considering number of branches, type of branching and general shape, according to the descriptions.

Collected scyphistomae were also measured (N = 10): oral disc diameter 0.65–1.5 mm; total length 2–3.5 mm; stalk length 1.15–2.5 mm; calyx length 0.35–0.5 mm; hypostome length 0.2–0.7 mm; number of tentacles 27–36. These measurements are in accordance with the available data for the genus (Ludwig, Reference Ludwig1969; Straehler-Pohl, Reference Straehler-Pohl2009). The scyphistomae were kept in laboratory conditions, and produced ephyrae (by monodisc strobilation) similar to the young medusae found in the field.
The COI data obtained from the three sequenced specimens were identical. The phylogenetic analysis (Figure 3) including the new Brazilian specimens, and terminals (=sequences) already presented in a previous study (Holland et al., Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004) clustered the Brazilian Cassiopea sequences group with the Cassiopea andromeda samples (from Florida, Bermuda and Hawaii) as defined by Holland et al. (Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004). The molecular distance between the Brazilian material and Florida and Bermuda specimens is 0.54% based on Kimura 2-parameter model and 0.005 on p-distance (3 to 6 nucleotide variation). A comparison of the molecular divergence between the Cassiopea species considered by Holland et al. (Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004) is shown in Table 2, and it reveals that intraspecific variation (from 0.6–10%) is much smaller than interspecific variation (11–26%). It is estimated that the C. andromeda specimens sampled here from Cabo Frio diverged from those in Florida and Bermuda ~500 years ago, which is relatively soon after the ‘discovery’ of Brazil in 1500. In an alternative method (Dawson, Reference Dawson2005b) to estimate the divergence time between species the equation T = d/2λ (where d is the nucleotide distance between populations and the mutation rate λ = 4.87 × 10−6) was applied. Based on this equation the Cabo Frio specimens diverged from Florida and Bermuda ~554 years ago.
Table 2. Estimates of average evolutionary divergence over sequence pairs within and between ‘species’ as defined by Holland et al. (Reference Holland, Dawson, Crow and Hofmann2004). Analyses were conducted using the Kimura 2-parameter model. The rate variation among sites was modelled with a gamma distribution (shape parameter = 1). All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated (total positions in the final dataset: 554). Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA5 (Drummond et al., Reference Drummond, Ashton, Buxton, Cheung, Cooper, Duran, Field, Heled, Kearse, Markowitz, Moir, Stones-Havas, Sturrock, Thierer and Wilson2011). n/c = not possible to estimate evolutionary distances. Figure 3 lists the individuals used in the comparison as well as their location.

Whilst early ships did not have the ballast capacity of modern vessels, and their ballast would invariably have been rocks or other heavy solid material, their hulls would have inevitably been subject to heavy fouling (see more in Carlton & Hodder, Reference Carlton and Hodder1995). An introduction into Brazil via the fouling route is perhaps more likely than by ballast water – although the scyphistomae of Cassiopea can produce a number of planuloids asexually on a daily basis (Hofmann et al., Reference Hofmann, Neumann and Henne1978), which could persist within ballast tanks – because scyphistomae were observed on artificial substrates as well as on another invasive species, Styela plicata (Barros et al., Reference Barros, Rocha and Pie2008). Given that genetic evidence (same haplotypes) indicates that Styela plicata populations off Florida and Brazil are similar (Barros et al., Reference Barros, Rocha and Pie2008), it is possible that populations of both species were introduced into Brazilian waters from Florida.
Cassiopea andromeda clearly has a number of ecological characteristics that predispose it to invasion success, chiefly the ability of its scyphistomae to produce planuloids at a high rate (personal observation). Off Brazil, it is clearly tolerant to quite wide variations in salinity and temperature (salinity 0–36, water temperatures up to ~29°C), and this allows it to be an opportunistic species (Fofonoff et al., Reference Fofonoff, Ruiz, Steves, Cartlon, Ruiz and Carlton2003; Devin & Beisel, Reference Devin and Beisel2007; Zerebecki & Sorte, Reference Zerebecki and Sorte2011). It is known that Cassiopea species can be tolerant to salinity fluctuations (Goldfarb, Reference Goldfarb1914). Several other reports of Cassiopea medusae exist from the coast of Brazil based on photographic records (Figures 1 & 4), as they do for scyphistomae (states of Rio Grande do Sul and São Paulo; Figure 1). Although we do not at this stage have genetic data to confirm their identity to species, it is clear that the genus Cassiopea is finding suitable habitats along the Brazilian coast and that in the future they may be much more common.

Fig. 4. Photographic records of Cassiopea Péron & Lesueur, Reference Péron and Lesueur1810 specimens from Brazilian coast (A–F). (A) Itarema, Ceará state (photo Carlos H.P. Marques & Yara G. Oliveira); (B) Macau, Rio Grande do Norte state (photo Thelma L.P. Dias); (C) Salvador, Bahia state (photo Claudio L.S. Sampaio); (D) Aracruz, Espírito Santo state (photo Oberdan J. Pereira); (E–F) Cassiopea andromeda (Forskål, Reference Forskål1775) from Cabo Frio, Rio de Janeiro state (photos by André C. Morandini and Sergio N. Stampar).
The detection of non-indigenous species in Brazilian waters is important (Rocha et al., Reference Rocha, Vieira, Migotto, Amaral, Ventura, Serejo, Pitombo, Santos, Simone, Tavares, Lopes, Pinheiro and Marques2013), because lists of such species shall serve as elements for conservation policies and priorities. Even as exhaustive biological surveys provide the best methods for detecting alien species, the appearance of unusual taxa in large numbers is often the first evidence of an invasion event. This is the case of the present species, with blooms of C. andromeda (Figure 5) in the Araruama Lagoon since 2008. But not all blooms of unusual species need be similarly interpreted owing to the lack of comprehensive species maps, the scarcity of long-term data on jellyfish blooms (Condon et al., Reference Condon, Graham, Duarte, Pitt, Lucas, Haddock, Sutherland, Robinson, Dawson, Decker, Mills, Purcell, Malej, Mianzan, Uye, Gelcich and Madin2012), and because jellyfish naturally exhibit episodic and seasonal interannual variability (Mills, Reference Mills2001). We are aware that our genetic data only suggest the hypotheses of possible appearance of this species as following an invasive event in the Brazilian shoreline. Furthermore, whilst C. andromeda may have been resident in Brazilian waters for ~500 years, only now are populations (in some areas) blooming. The reasons for this are not yet understood, neither are the impacts on local biological communities, but to date there appear to be no obvious economic or social consequences of the bloom. Regardless, further work on the species in Brazil is now needed to define a broad and complete picture on present and past evolution of the species C. andromeda.

Fig. 5. Medusae of Cassiopea andromeda (Forskål, Reference Forskål1775) at a branch of Itajuru Channel (Cabo Frio, Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil) during December 2008. Note first author as scale (~1.65 m).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are thankful to Solange Brisson and Sara Oliveira for the first observation and alerting us about the occurrence of the animals at Cabo Frio (RJ). Collections were in accordance with Brazilian regulations (SISBIO licence 15031-2 to ACM). We thank Drs Oberdan J. Pereira (UFES), Thelma L.P. Dias (UEPB), Claudio L.S. Sampaio (UFAL) and Helena Matthews-Cascon and Bruno B. Batista (UFC) for recognizing and informing about photographic records in other regions. We also thank Dr Fábio Di Dario (NUPEM, UFRJ) and Mr Enzo C. Morandini for helping in field samples. Different parts of this manuscript were presented as posters at three conferences (II Congresso Brasileiro de Biologia Marinha, III International Jellyfish Blooms Symposium, II World Conference on Marine Biodiversity) and we thank all the audiences for further discussions. We are also indebted to Dr Mark J. Gibbons (UWC, South Africa) for corrections and comments on an earlier version of the text. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for comments and suggestions to improve the text.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
ACM was supported by grants 2010/50174-7, 2011/50242-5 and 2013/50484-4 São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), and by CNPq (301039/2013-5). SNS was supported by grant 2012/01771-9 São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), and by CNPq (481549/2012-9). This is a contribution of NP-BioMar, USP.









