Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 October 2023
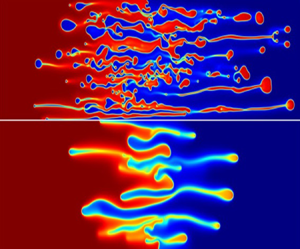
The coupled effects of thermodynamic and hydrodynamic instabilities are studied during viscous fingering (VF). We introduced a modified Cahn–Hilliard phase-field model in conjunction with the Korteweg force in the classical VF model and derived consistent governing equations. The free energy of the partially miscible system is described using a modified Flory–Huggins model, which allows us to investigate the temporal evolution of spatial inhomogeneities. The mass flux in the Cahn–Hilliard equations is modified according to modern diffusion theory. The governing equations have been solved through an in-house model implementation using the COMSOL multiphysics software. We successfully demonstrated the transition from the finger-like structures to the droplet formation during spinodal decomposition as demonstrated experimentally in the literature. Our results are also in agreement with earlier numerical results obtained using a classical Landau type mixing energy. We further systematically studied the effects of the Margules parameter (interaction parameter) and the gradient parameter, which is associated to the thermodynamic length scale and capillary number on the VF. Aysmmetric features of the binary mixture are also investigated showing a stronger thermodynamic effect on the system with increasing phase separation and, hence, droplet formation.