Published online by Cambridge University Press: 28 September 2018
A number of recent studies have demonstrated the existence of so-called large- and very-large-scale motions (LSM, VLSM) that occur in the logarithmic region of inertia-dominated wall-bounded turbulent flows. These regions exhibit significant streamwise coherence, and have been shown to modulate the amplitude and frequency of small-scale inner-layer fluctuations in smooth-wall turbulent boundary layers. In contrast, the extent to which analogous modulation occurs in inertia-dominated flows subjected to convective thermal stratification (low Richardson number) and Coriolis forcing (low Rossby number), has not been considered. And yet, these parameter values encompass a wide range of important environmental flows. In this article, we present evidence of amplitude modulation (AM) phenomena in the unstably stratified (i.e. convective) atmospheric boundary layer, and link changes in AM to changes in the topology of coherent structures with increasing instability. We perform a suite of large eddy simulations spanning weakly (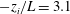 $-z_{i}/L=3.1$) to highly convective (
$-z_{i}/L=3.1$) to highly convective (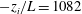 $-z_{i}/L=1082$) conditions (where
$-z_{i}/L=1082$) conditions (where 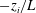 $-z_{i}/L$ is the bulk stability parameter formed from the boundary-layer depth
$-z_{i}/L$ is the bulk stability parameter formed from the boundary-layer depth 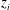 $z_{i}$ and the Obukhov length
$z_{i}$ and the Obukhov length 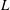 $L$) to investigate how AM is affected by buoyancy. Results demonstrate that as unstable stratification increases, the inclination angle of surface layer structures (as determined from the two-point correlation of streamwise velocity) increases from
$L$) to investigate how AM is affected by buoyancy. Results demonstrate that as unstable stratification increases, the inclination angle of surface layer structures (as determined from the two-point correlation of streamwise velocity) increases from 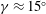 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}\approx 15^{\circ }$ for weakly convective conditions to nearly vertical for highly convective conditions. As
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D6FE}\approx 15^{\circ }$ for weakly convective conditions to nearly vertical for highly convective conditions. As 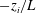 $-z_{i}/L$ increases, LSMs in the streamwise velocity field transition from long, linear updrafts (or horizontal convective rolls) to open cellular patterns, analogous to turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection. These changes in the instantaneous velocity field are accompanied by a shift in the outer peak in the streamwise and vertical velocity spectra to smaller dimensionless wavelengths until the energy is concentrated at a single peak. The decoupling procedure proposed by Mathis et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 628, 2009a, pp. 311–337) is used to investigate the extent to which amplitude modulation of small-scale turbulence occurs due to large-scale streamwise and vertical velocity fluctuations. As the spatial attributes of flow structures change from streamwise to vertically dominated, modulation by the large-scale streamwise velocity decreases monotonically. However, the modulating influence of the large-scale vertical velocity remains significant across the stability range considered. We report, finally, that amplitude modulation correlations are insensitive to the computational mesh resolution for flows forced by shear, buoyancy and Coriolis accelerations.
$-z_{i}/L$ increases, LSMs in the streamwise velocity field transition from long, linear updrafts (or horizontal convective rolls) to open cellular patterns, analogous to turbulent Rayleigh–Bénard convection. These changes in the instantaneous velocity field are accompanied by a shift in the outer peak in the streamwise and vertical velocity spectra to smaller dimensionless wavelengths until the energy is concentrated at a single peak. The decoupling procedure proposed by Mathis et al. (J. Fluid Mech., vol. 628, 2009a, pp. 311–337) is used to investigate the extent to which amplitude modulation of small-scale turbulence occurs due to large-scale streamwise and vertical velocity fluctuations. As the spatial attributes of flow structures change from streamwise to vertically dominated, modulation by the large-scale streamwise velocity decreases monotonically. However, the modulating influence of the large-scale vertical velocity remains significant across the stability range considered. We report, finally, that amplitude modulation correlations are insensitive to the computational mesh resolution for flows forced by shear, buoyancy and Coriolis accelerations.