INTRODUCTION
A great expansion of meta-science is under way. There has been a proliferation of studies that investigate patterns behind millions of scholarly publications.Footnote 1 Digital applications spring up en masse that allow users to investigate networks of co-citation patternsFootnote 2, browse through scholars’ academic profilesFootnote 3, or automatically obtain lists of ‘trending’ papers from one's favorite research domain based on the attention they receive in news outlets and social media.Footnote 4 Such tools open up the system of science to render it more inclusive towards authors, readers, citizen scientists and other beneficiaries.Footnote 5 They allow for a precise and voluminous research discovery, they stimulate scholarly collaborations across the globeFootnote 6, they lower the risk of ‘research waste’, they illuminate systemic trends and inequitiesFootnote 7, and they generate enhanced chances for truth-seeking inspiration and serendipity. And all this dynamic adheres to a community-led and inclusive philosophy without charging any fees. The backbone of this impressive development form initiatives that offer freely accessible, interoperable, machine-readable and transparent scientific metadata.
The gist of these open metadata can be accessed through a single platform called CrossRef. The data are structured thus that they are not only readable by human eyes, but also by machines. A programmed script could loop through and fetch the metadata of millions of papers in little time. The key to each item or publication is offered by a persistent identifier (PID), the so-called digital object identifier (DOI). And with this DOI, one can access various datasets other than CrossRef so as to obtain advanced article-level information: a given paper's outbound references and inbound citations, the licenses behind a work, the multiple open access versions (such as pre-prints) that are available for a publication, or a live-updated list of wider events that indicate a scholarly article's societal impact, such as whether it was cited in Wikipedia or mentioned in global news outlets. Most of these datasets follow FAIR principles, that is, they are ‘findable’, ‘accessible’, ‘interoperable’ and ‘reusable’, and completely free and open.Footnote 8 Scientific units other than articles have likewise been ennobled by PIDs and FAIR datasets (such as with ORCID for authors, or with ROR for research organizations).Footnote 9 Linking these identifiers with DOIs, the combination of various data sources generates ever more, granular and advanced overviews of the scientific landscape at large.
And these linked open data are the reason why so many new tools and scientometrics analyses have sprung up in the recent years. The dominance of costly, commercial, restricted databases (like Web of Science) now faces serious rivalry. Open metadata have truly revolutionised meta-science. Almost no field of research has remained untouched by this development.
The stress of the last sentence is on ‘almost’ – for there is one academic domain that has been notably absent from this meta-scientific revolution: the field of law. Adjacent fields such as political science or sociology have been imbued with advanced and comprehensive meta-scientific studies.Footnote 10 Only law remains in a blind spot.
The reason for the omission of legal studies lies in the anomaly of law reviews. Law reviews differ from the dominating model of scientific journals in many ways. They are student-edited (rather than editorial boards boasting reputable researchers), non-refereed (rather than undergoing peer reviews), allow for multiple submissions at once (rather than claiming exclusive submissions), use a distinct technical infrastructure (mostly Scholastica for submissions rather than ManuscriptCentral or similar tools), are self-published (rather than that they belong to the typical oligopoly of the scholarly publishers), exhibit cartelistic citation patternsFootnote 11, and so on.Footnote 12 But the focus of this paper is a further, crucial difference: Law reviews generally do not deposit scholarly metadata at CrossRef (see Table 1).Footnote 13 They do not assign DOIs to papers. And it is because of this that legal scholarship has remained isolated from grand meta-scientific endeavours.Footnote 14
Table 1: The composition of the category ‘Law’ in Web of Science's Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) 2020 with regards to their metadata-depositing behaviour at CrossRef.

This is indeed an anomaly compared to other social scientific disciplines (cf. Figure 1). In other research domains, almost all the journals that are indexed in the respective categories of Web of Science's Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) deposit metadata at CrossRef. In communication studies, for instance, 97.9% of the journals have open metadata in this sense (as of late 2021). In the field of law, that rate is a mere 61.1%, with much of the non-open share being accounted for by law reviews.

Figure 1: The share of journals that deposit metadata at CrossRef by discipline, as of late 2021. The selection of the seven disciplines from the Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) is based on the one followed by the Observatory of International Research, or OOIR, at https://ooir.org.
There are only two law reviews indexed in the SSCI that currently deposit metadata at CrossRef. One is the University of Pittsburgh Law Review which began doing so back in 2003, possibly because of its integration in the broader open access framework of the University of Pittsburgh library's digital publishing program. The other one is the Michigan Law Review that only initiated the depositing of metadata in 2018.Footnote 15
But would it not be possible to find substitutes for CrossRef-deposited metadata about scholarly articles? At least for some meta-scientific analyses and tools, one could perhaps resort to another way of data extraction. If one simply wished to generate an information retrieval script that listed the latest papers (accompanied by information about author names, publication dates and abstracts) published in a select group of important law reviewsFootnote 16, might there not be equivalent data sources available for free? Manual data-collection would certainly be too laborious to undertake for an extended period. An automated process of webscraping would likewise face difficulties since every law review's website exhibits a different layout, each of which requires a new code for the webscraping script. Given the lack of a metadata deposit, the only other option would be to draw from automatically updated Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feeds. RSS feeds are widely used across the internet, structured in a machine-readable way as they are formatted in the so-called Extensible Markup Language (XML), and they allow for the harbouring of metadata based on labelled fields and values.Footnote 17 For a given publication, for instance, an RSS feed can contain a ‘title’-field which lists the article's title, a ‘creator’-field which enumerates the authors, a ‘pubDate’-field which points to the date of publication, and so on. Does it not mean that, even in the absence of CrossRef-deposited open metadata, a script could automatically access the law reviews’ RSS feeds regularly (say, once an hour or once a day), fetch their data and store them for further information processing (e.g., by showing a ‘latest papers’-list on a website or on a Twitter bot account), or even conduct further meta-scientific analyses (e.g., on the co-author networks)?
It is in light of such observations that one might identify a knowledge gap. RSS feeds have hardly ever been sounded out as a source of scientific metadata – apart from a few tentative reflections in the early 2000sFootnote 18 well before the broader consolidation of CrossRef (which was founded in 1999). This is an interesting omission; after all, RSS are ubiquitous, popular within the academic communityFootnote 19, structured and thus machine-readable, freely accessible and might contain standardised metadata about scholarly articles.Footnote 20 It is possible that RSS feeds could indeed serve as equivalent data sources for some scientometrics purposes in case a journal does not deposit metadata at CrossRef. This intuitive assumption, however, requires a more systematic in-depth exploration which this paper seeks to offer.
Note that for the present paper, commercial databases such as Web of Science or Scopus or HeinOnline or WestLaw or Lexis Nexis would not offer suitable equivalents. While those databases do allow for large-scale analyses of law reviews and their, say, citation patterns or author namesFootnote 21, they are not equivalent to open metadata due to their untransparent algorithms and general inaccessibility (unless one is affiliated with an institution that subscribes to these databases): CrossRef ‘serves a similar function to Westlaw's KeyCite, Lexis's Shepard's, and HeinOnline's ScholarCheck but with some remarkable improvements […CrossRef's] citation network is more open; a reader does not need to subscribe to a proprietary database to see the citations to and from the article’.Footnote 22
This paper proceeds to answer whether is it possible to use RSS feeds as a substitute to CrossRef-deposited open metadata, and what kind of meta-scientific uses can be extracted from the law reviews’ RSS feeds. It does so by surveying the data structure of their RSS feeds regarding their utility for a fictitious meta-scientific use case – a ‘latest papers’-tool or an alerting service that notifies users about the newest papers, alongside an author database that documents differences in productivity in terms of publication numbers, and which additionally shows inter-journal citation patterns. After outlining the methodical approach, the paper reports that most of the law reviews’ RSS feeds are unusable even for simple meta-scientific endeavours; only a basic ‘latest papers’-tool would be possible to achieve with the RSS feeds, and even here it is just a subset of just 21 law reviews (from a population of 51 law reviews) that can be captured in this manner. The paper closes with discussions on the general recent decline of law reviews, and calls for them to adopt DOIs and deposit open metadata so as to rescue their broader scholarly visibility and impact.
METHODS
Are the RSS feeds of the law reviews usable for a simple meta-scientific purpose like a ‘latest papers’-tool that additionally shows the number of publications by author as well as the number of mutual citations among the law reviews? To answer this question, it was first necessary to access the web presence to each student-edited, non-peer reviewed law review as indexed in Web of Science's Social Science Citation Index (SSCI). A common way to identify the existence of an RSS feed is to view the source code behind a given website – usually done in the web browser by opening the right-click-menu and choosing the ‘Source View’ option – and to search for the string ‘RSS’ to appear. The web addresses to the RSS feeds for each law review were collected manually in September 2021.
While the SSCI indexes 51 law reviews, two of them deposit metadata at CrossRef which is why their RSS feeds would not be analyzed as a substitute for CrossRef metadata. The starting sample thus consists of 49 law reviews. However, as 13 of them do not offer any RSS feeds, the sample is down to 36 law reviews. A further look showed that of the 36 remaining law reviews, there were 15 whose RSS feeds were either empty, outdated, or only pertained to the law reviews’ informal web blog or general news announcements (such as call for papers), and not to full-fledged articles. They were thus not useful for fetching article-level data about the scholarly articles in the law reviews.
The study therefore remained with a mere 21 RSS feeds from a population of 49 law reviews, meaning that only less than a half (42.8%) of the law reviews could potentially offer RSS feeds as a potential alternative to open scholarly metadata.
These 21 RSS feeds were then accessed in October 2021, and their data structure were analyzed regarding their utility for the fictitious but basic meta-scientific purpose. A database that regularly stores the newest articles published in all SSCI-indexed law reviews would list the title of each paper, the date of publication, the author(s), a summary, and a link to the article alongside the publication source (the law review). The database should also keep record of the authors’ publication counts as it seeks to document the most productive authors in a given time period. And finally, it wishes to quantify inter-law-review linkages as operationalised by the number of references, so as to convey which law reviews are ‘closer’ to other law reviews in terms of mutual citations.
In brief, the data needed for such a project from each law review are:
• Titles of the publications
• Dates of the publications
• Link to the publications
• Authors of the publications (in the form of persistent identifiers like ORCID and/or names)
• Summaries (abstracts) of the publications
• References of the publications (which should identify the cited sources)
RESULTS
As stated above, only less than half of the law reviews even offered a basic, functional RSS feed. If one wished to generate a database of all the latest articles in every SSCI-indexed law review, then this would be impossible to achieve. This section thus rather answers the modified question whether it would be possible to create a database storing the latest articles in at least those 21 SSCI-indexed law reviews that do exhibit useful RSS feeds.
The answer, in brief, is: yes, it would be possible to show the latest papers of these law reviews based on their RSS feeds, alongside links, summaries and publication dates. However, it would not be possible to generate an author database of sufficient data quality (due to the lack of PIDs and the lack of data availability), and it would be completely impossible to convey data about inter-law review citation patterns (because the article-level references that are contained in the RSS feeds cannot be reliably extracted).
To get into greater details, the 21 RSS feeds allowed one to fetch the title of each article (usually in the <title>-tag), a link to the article (usually in the <link>-and/or <guid>-tag), the publication date of the article (in the <pubDate>-tag) and a short summary or at least the starting paragraphs of the article (usually in the <description>, sometimes in a <content>-tag). One could thus imagine a website that automatically updates itself by linking to the newest articles sorted by publication date in the 21 law reviews, with textual snippets shown for each listed document.
Other than, the availability of other data across the sample was rather scarce. For instance, author-level data are difficult to fetch. While all RSS feeds contained a <creator>-tag, they were most often harboured by the username of the website administrator from the respective law review, and not by the actual authors of the texts. Only in 3 cases were the <creator>-tags correctly attributed to the article authors – and even in such cases was it only possible to see the name of the first author when there was a multiple authorship (where everyone after the first author was summarised as ‘et al.’). Needless to say, these tags only showed the author names and not other identifiers like ORCID. As a consequence, multiple spellings of a person's name could not be attributed to a specific person unambiguously (such as when a person publishes once as ‘Anton J. Reiß’, then as ‘Anton Reiß’, another time as ‘Anton J. Reiss’, and yet another time as ‘ANTON JOHANNES REISS’), or a same name carried by multiple people could not be disambiguated (such as multiple authors carrying the names ‘Jane Doe’ or ‘Li Wang’). A few further RSS feeds contained full texts of the articles where the author names were visible – however, it is logically impossible to extract author names (with so-called regular expressions, or regex) unambiguously in a text that harbours HTML tags.Footnote 23
The same impossibility to extract specific components of a HTML file with the help of regex also pertains to the citation data. There were 6 RSS feeds that contained the full texts of articles, including the HTML codes that design the layout of the article in the browser, but also with the visibility of the articles’ footnotes or endnotes that usually comprised the references cited by the articles. Since the endnotes were highly structured in HTML <a>-nodes, one could imagine to scrape them with regex; but again, a precise extraction of the references (e.g., cited author names, cited publication source medium title, cited year etc.) would encounter insurmountable difficulties when HTML tags are present. In addition, the usance that law reviews’ endnotes tend to be relatively verbose likewise compounds the difficulty. In brief, it is not possible to reliably extract the article-level references from these RSS feeds.
Table 2: Result of the analysis of law reviews’ RSS feeds.

Abbreviations: SSCI = Social Science Citation Index (from the Web of Science); RSS = Really Simple Syndication; PIDs = persistent identifiers.
There are further difficulties with regards to the RSS feeds when compared with CrossRef metadata. First, RSS feeds typically only date back to the 10 or 20 most recent articles. It is therefore impossible to obtain standardised data about older papers. Second, they often mix article types, confounding full-fledged scholarly articles with blog posts, calls for papers, submission guidelines and other announcements. Not always is there a possibility to distinguish these types in a clean and automatic way (such as through <category>-tags in the RSS feeds). Third, despite some homologous elements, the RSS feeds still lack sufficient harmonization – sometimes, for instance, the <description>-tag contained the full texts of the articles, but sometimes they only showed a snippet or summary of the articles. In another example, the <creator>-tag sometimes showed the (first) author names, but most often it only listed the username of the website's internal content management system. Fourth, none of the RSS feeds were based on PIDs, so that linking the extracted data with other data sources (such as Wikidata or ORCID) would not be possible. And fifth, metadata other than the basic one sought for are fully lacking – such as licenses, volume and issue numbers, and so on.
To sum up the finding, out of a sample of 49 SSCI-index and non-CrossRef-depositing law reviews, 28 did not offer any or at least no functional, article-level RSS feeds. The other 21 may show utility for staying up-to-date about the latest law review articles in an unstructured manner. One would know about the title of each article, the publication date, the link to the article, and a summary of the article was likewise present.
However, other than that, the RSS feeds are not useful for further meta-scientific purpose. One cannot collect data about authors and their numbers of publications with sufficient data quality (there are only 3 law reviews whose RSS feeds convey author names, and even then they only list the first author in case of multiple authors), and it is completely impossible to reliably extract reference patterns from the law reviews (there are only 6 RSS feeds that contain the references, but they are embedded in HTML tags such that they cannot be reliably extracted with a common text-mining method utilizing regular expressions).
DISCUSSION
This paper departed from the observation that most student-run law reviews do not deposit scholarly metadata in an openly accessible manner. A consequence of this omission is that meta-scientific analyses regarding legal research are difficult to conduct. While scientometrics investigations have already illuminated publication patterns across all kinds of scientific areas, law has remained ostensibly absent from this movement. This paper thus asked whether there are substitutes – with RSS feeds serving as a possible candidate due to their ubiquity and their structured composition. However, the analysis that covered the 51 law reviews that are indexed in Web of Science's SSCI showed that RSS feeds do not serve as equivalents to the scientific metadata platform CrossRef. RSS feeds hardly offer any reliable data for meta-scientific purposes; they lack standardization, they lack granularity, they omit important data. Of three possible projects that were eyed by this paper (and that are commonly done within the field of scientometrics) – a website listing the latest papers across all law reviews, a co-author network, and a calculation of mutual citations across various law reviews – none could be realised with the help of RSS feeds. A miniature version of the first project could have been realised with a subset of just 21 law reviews, which would be the most that could be achieved with RSS feeds as a source of scholarly metadata. The finding implies that scholarly metadata as drawn from RSS feeds are unusable for basic meta-scientific tools (at least with regards to law reviews).
This paper thus adds a further knowledge to a survey of the quality of scholarly metadata: RSS feeds are by far not equivalent to open scholarly metadata harboured behind PIDs. If law reviews keep the status quo, it will remain immensely difficult to collect data about law reviews in a large-scale manner. Their outputs will thus remain in a blind spot of meta-scientific analyses. The whole research discipline of law will suffer from a lack of information about itself – such as in terms of co-author networks, gendered or regional biases, the changing nature of citations, and so on.
While the finding seemed straightforward, there are still a few limitations to be kept into account. For instance, the sample of the investigation only contained the 51 law reviews that are indexed in Web of Science's SSCI as of 2020. It thus left out the huge number of law reviews that are not indexed in SSCI – while the total number is unknown, a prominent list knows of at least 696 student-edited law reviews in its most recent edition.Footnote 24 In addition, the investigation remained limited to the field of law and the particular journal species of law reviews; but it is not impossible to assume that other disciplines’ and other journals’ RSS feeds may contain some useful information that are not captured by the metadata deposited at CrossRef. For instance, before the Initiative for Open Abstracts (I4OA) started its activities in 2020, more than 90% of scholarly abstracts were hidden inaccessibly in CrossRef.Footnote 25 One could investigate whether there are cases where RSS feeds contain abstracts while CrossRef does not, which would allow one at least not to discard RSS feeds fully for meta-scientific purposes. This paper's empirical investigation, at least, found summaries of articles in 100% of all functional RSS feeds, which might at least point to one useful aspect of this data source.
One could ask a more fundamental question: How relevant are law reviews expected to be in the coming years and decades? To what extent the law reviews’ omission would really hurt legal meta-science. For over time, law reviews have been in a numerical decline at least in the primary data source for scientometrics analyses, namely in Web of Science. While law reviews constituted half of Web of Science's SSCI category of law in 1997, their share went down to less than a third by 2021 (see Figure 2). One cannot rule out that the lack of open metadata might further decrease the law reviews’ visibility, especially for researchers in adjacent fields. For instance, the Observatory of International Research (OOIR) regularly tweets out the ‘trending’ papers based on Altmetric Attention Scores (which in turn is based on DOIs) in a given social scientific discipline to thousands of followers from the broader social scientific community. For the field of law, the top trending papers are always from metadata-depositing journals; student-edited law reviews are never visible, by definition, because they lack the DOI and the accompanying metadata which would enable machines to fetch their altmetric scores.
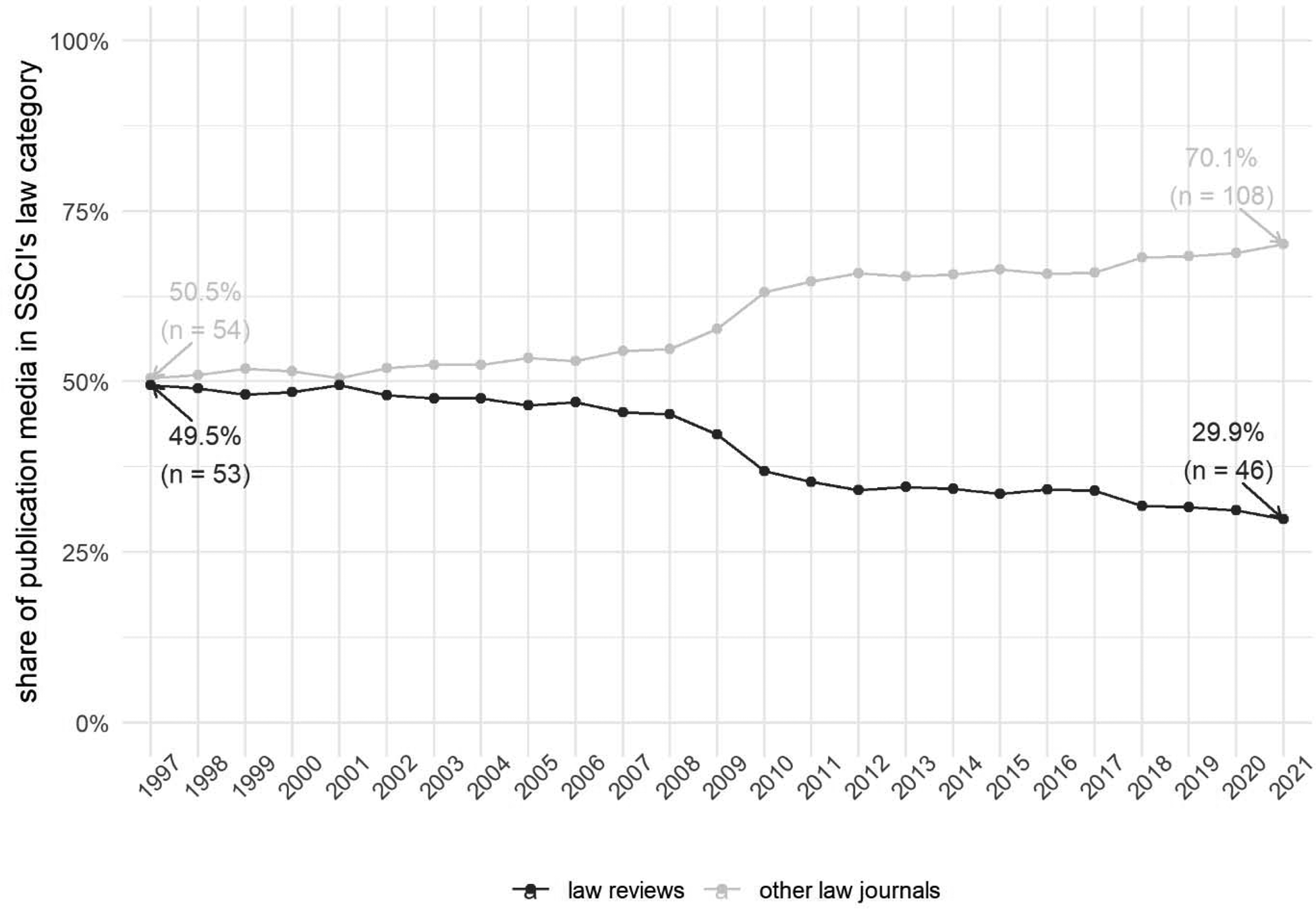
Figure 2: Changes in the share and number of non-peer-reviewed, student-edited law reviews as opposed to other (peer-reviewed) law journals within the Web of Science's Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) category of Law, 1997-2021.
The lack of visibility and impact may also be illustrated with the law reviews’ relative stagnation in their median journal's impact factor, a metric that calculates the average number of citations a journal receives to its documents, as opposed to other law journals (see Figure 3). While law reviews still fare better than peer-reviewed law journals, the difference has been diminishing rapidly in the past decade.
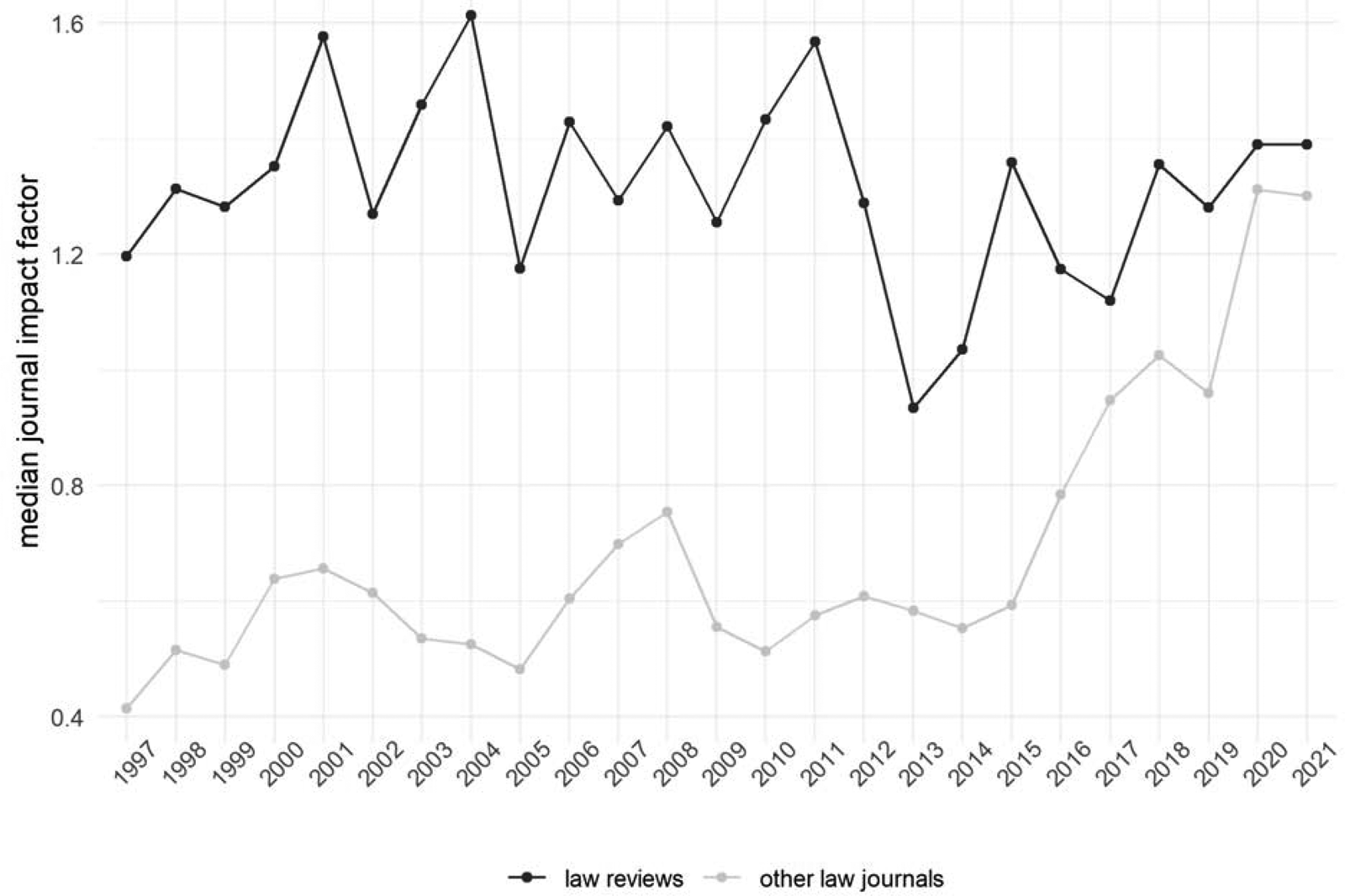
Figure 3: Changes in the median impact factor of non-peer-reviewed, student-edited law reviews as opposed to other (peer-reviewed) law journals within the Web of Science's Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) category of Law, 1997-2021.
Whatever the implication of this paper's findings – the most obvious one would be a call for law reviews to adopt DOIs and to start depositing metadata in an openly accessible way.Footnote 26 Almost 15 years ago, one could have pointed ‘to the need to develop effective data cleansing procedures for RSS feeds’Footnote 27, but perhaps RSS feeds might be too obsolete to be revived in the face of superior alternatives. Otherwise, one cannot rule out that law reviews will further decline in their broader scholarly and societal visibility and impact.Footnote 28







