Introduction
Early chemical insecticides were derived either from plants (botanicals) or from inorganic compounds. For example, indigenous peoples have extracted rotenone from the roots of tropical and subtropical plants of the family Fabaceae for centuries and used the compound to catch fish. More recently, since about the 1930s, rotenone has been used in fisheries management to eradicate undesirable fish species, and in agriculture to control insect pests of fruit, vegetable and forage crops, as well as to kill fleas (Siphonaptera), ticks (Acari: Ixodidae, Argasidae), and mites (Acari) on pets and livestock (McClay Reference McClay2000; Anonymous 2007). Nicotine, a botanical insecticide extracted from tobacco, Nicotiana Linnaeus (Solonaceae), was used as a plant spray in parts of Europe as early as 1690 and was in general use by the mid 19th century (Schmeltz Reference Schmeltz1971). Likewise, the botanical insecticide pyrethrum, sold as a powder made from ground Chrysanthemum Linnaeus (Asteraceae) flowers, was used in the home to control body lice and crawling insects starting in about the mid 19th century (Glynne-Jones Reference Glynne-Jones2001).
Inorganic insecticides (contact insecticides containing metals or sulphur) have a much longer history of use than botanical compounds. By the 9th century AD the Chinese were using arsenic-containing compounds to control garden insects (Fishell Reference Fishel2013), and Homer described the use of sulphur as a fumigant in his epic poem The Odyssey written in the 8th century BCE. In 1893, lead arsenate was developed by the United States of America Federal Bureau of Entomology for control of gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar (Linnaeus) (Lepidoptera: Erebidae), in Massachusetts, United States of America (Metcalf and Flint Reference Metcalf and Flint1939; Spear Reference Spear2005). Because of its efficacy and other desirable properties (e.g., persistence), lead arsenate was rapidly adopted for use in agriculture worldwide, in particular to control codling moth, Cydia pomonella Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), in apple, Malus domestica Borkhausen (Rosaceae) orchards (Peryea Reference Peryea1998).
The first aerial applications of an insecticide to control forest insect pests were conducted in Canada from 1927 to 1930 (Nigam Reference Nigam1975). Altogether, more than 85 000 kg of calcium arsenate dust were applied to 3278 ha of forest in Nova Scotia, Ontario, Québec, and British Columbia, Canada in attempts to control infestations of spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Clemens (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), and hemlock looper, Lambdina fiscellaria Guenée (Lepidoptera: Geometridae). Dosage rates varied from 11–45 kg/ha (dosage rates and reports of area sprayed in most source documents were reported in imperial measures, we have converted these to metric). Application methods were similar to those used to protect agricultural crops in the southern United States of America (i.e., crop dusting). The trials produced indifferent results against spruce budworm, but were more encouraging against hemlock looper (Nigam Reference Nigam1975). For various reasons, including high cost, concerns about safety and limitations of available equipment, forest spray trials were terminated after 1930 and did not resume for another 13 years (Randall Reference Randall1975).
The development of synthetic organic insecticides began in the 1940s with the development of the organochlorine insecticide dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). During the latter stages of World War II large quantities of DDT were used for control of mosquitos (Diptera: Culicidae), and other insect disease vectors. After the war the use of DDT as an aerially applied insecticide for the control of forest insect pests, particularly spruce budworm and other defoliators, marked the beginning of an era that saw significant research and development of various insecticides for use in the forest insect pest management. The result was that over the past 90 years experimental trials and operational chemical control have been conducted against many insect pests in Canada. While outcomes have varied, in many cases chemical control has proven to be a viable management option for many insect pests.
In this review we focus on research and control operations on the most significant forest pests (e.g., spruce budworm), with examples from other important pest systems, or from programmes that represent significant advancements in the field of chemical control. Details on specific programmes or work against a specific pest can be found in Prebble (Reference Prebble1975a), Armstrong and Ives (Reference Armstrong and Ives1995), and the reports of the Interdepartmental Committee on Forest Spraying Operations (1958–1972), the Annual Forest Pest Control Forum (1974–1995), and the Forest Pest Management Forum (1996–2014) (these reports are available online at http://cfs.nrcan.gc.ca/publications).
Chemical control of the spruce budworm larvae
The first aerial spray trials of DDT to control spruce budworm were conducted in Algonquin Park, Ontario, Canada in 1944–1945 (Sippell and Howse Reference Sippell and Howse1975). Various dosages were tried from 0.5 to 5.0 kg DDT/ha, but control was limited. Nevertheless, the province of Ontario conducted operational spray programmes using DDT against spruce budworm in northwestern Ontario in 1945 and 1946, as well as additional spray trials (Sippell and Howse Reference Sippell and Howse1975). Results varied, but in general good control was obtained at dosage rates in excess of 1 kg/ha.
Following these trials, there was a short hiatus in budworm spraying until 1952. During this period, spruce budworm populations were building to epidemic levels in eastern Canada (Blais Reference Blais1983). Previous outbreaks of the spruce budworm were tolerated in New Brunswick and Québec, because the lumber and pulp and paper industries were still relatively small, and they could draw on untapped reserves of wood to feed their mills. However, by the 1950s losses to spruce budworm were no longer acceptable. Inventories were fully exploited and a need for spruce budworm control was recognised (Kettela Reference Kettela1975b). The first control operation in New Brunswick took place in 1952, when about 81 000 ha of the approximately 486 000 ha budworm infestation were sprayed with DDT at 1 kg/ha (Miller and Kettela Reference Miller and Kettela1975). In the same year, ~3200 ha were treated in Québec with DDT at the same dosage rate (Blais et al. Reference Blais, Benoit and Martineau1975). Since then, spruce budworm control operations using chemical insecticides have occurred somewhere in Canada every year (except for 1959), employing a wide variety of products (Fig. 1). The scale of the spray operations has varied considerably through time and across jurisdictions with large control programmes occurring in New Brunswick and Québec in the 1970s and 1980s, and only much more modest programmes in western Canada since the mid-1990s (Fig. 2).
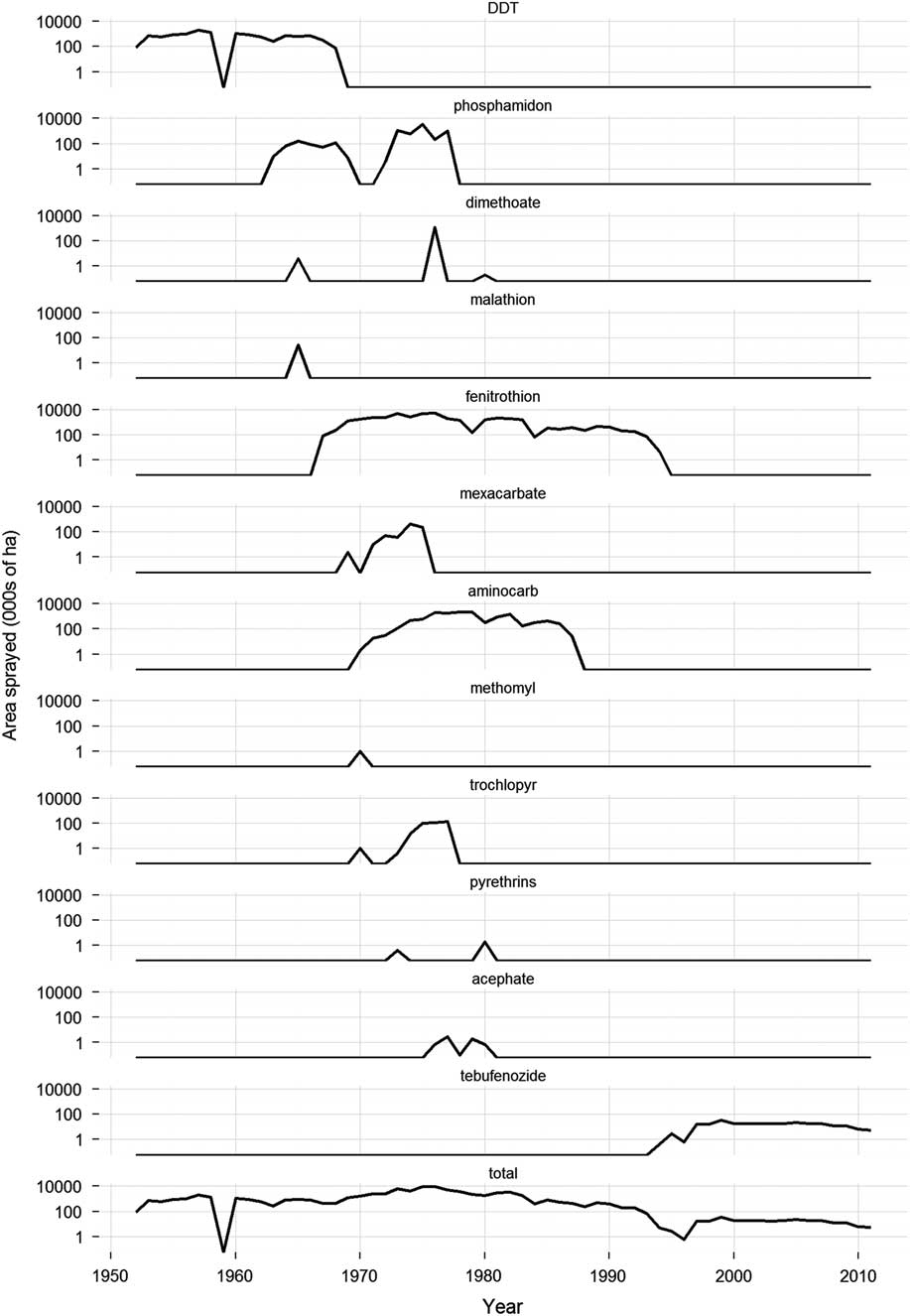
Fig. 1 Change over time in insecticides used in Canada for the control of spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Clemens (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), 1950–2011. Only products applied on an operational or semi-operational basis are included. Sources: Prebble (Reference Prebble1975b), The National Forestry Database (2012), reports of the Interdepartmental Committee on Forest Spraying Operations (1958–1972), the Annual Forest Pest Control Forum (1974–1995), and the Forest Pest Management Forum (1996–2013) (these reports are available online at http://cfs.nrcan.gc.ca/publications). Notes: 1) Pyrethrins includes permethrin applications. Pyrethrins are restricted to Christmas tree plantations, seed orchards, and high valued woodland areas, by ground application only. 2) Trochlopyr is restricted to balsam fir, Abies balsamea (Linneaus) Miller (Pinaceae), and spruce, Picea Dietrich (Pinaceae), in woodlots, rights-of-way, Christmas tree plantations, and municipal parks. 3) totals may sum to more than the total area sprayed in any one year, because multiple insecticides were frequently applied in combination over the same area.
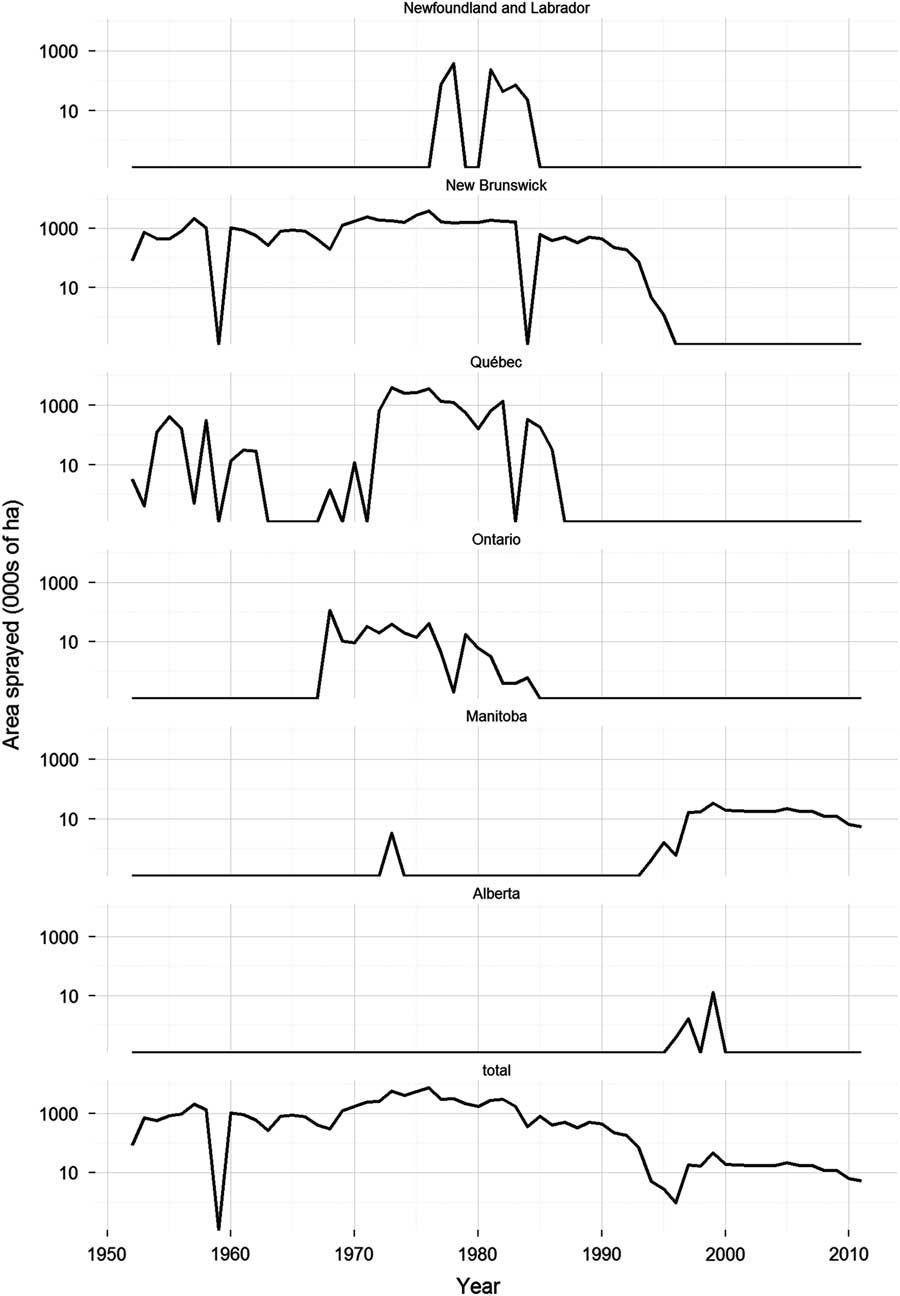
Fig. 2 Temporal trends in area sprayed in six Canadian provinces on an operational or semi-operational basis with chemical insecticides to control spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Clemens (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Data sources as in Figure 1.
From the beginning of the spray programme, split applications were conducted on a portion of the treated forest. As the name suggests, in a split application the total amount of insecticide applied per unit area is split between two or more applications in order to target different stages of spruce budworm. The first application of insecticide is made at the peak occurrence of third and fourth instars when the insect is maximally exposed on the foliage. This is the same timing of application as in a single application approach. The second application is made at the peak occurrence of fourth and fifth instars (Shea and Nigam Reference Shea and Nigam1984). Successful split applications provide superior foliage protection than a single application (Shea and Nigam Reference Shea and Nigam1984), but are more costly and can be difficult to execute. For example, in a large operation there may not be enough time or aircraft to treat the entire area twice, or the second application can be cancelled due to poor weather. The result is that the reduced dosage of the first application may not provide the same level of control as would be achieved using a single application.
DDT was the preferred control option for spruce budworm through all of the 1950s and most of the 1960s (Fig. 1), a period during which more than 6.6 metric tonnes of DDT was applied to Canadian forests (Nigam Reference Nigam1975). DDT was efficacious against spruce budworm, relatively inexpensive, readily available, and easy to apply using the technology available at the time. However, by the mid-1950s some of the negative aspects of DDT spraying began to be recognised.
In New Brunswick, where portions of the northwestern Miramichi watershed were treated with DDT in 1954 and 1956, substantial mortality of young Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar Linneaus (Salmoniformes: Salmonidae), and stream insects was reported and linked to the spray operation (Kerswill Reference Kerswill1957). Following this and a number of subsequent similar incidents (Kerswill Reference Kerswill1967; Kerswill and Edwards Reference Kerswill and Edwards1967), steps were taken to try to reduce the impact of DDT spraying on aquatic organisms: the dosage rate of DDT was reduced from 0.6 to 0.3 kg/ha and the guidelines were strengthened to avoid directly over-spraying aquatic systems (Miller and Kettela Reference Miller and Kettela1975).
In 1963, the organophosphate insecticide phosphamidon was introduced into the New Brunswick spraying operation, when ~8900 ha of forest were sprayed along several salmon rivers (Macdonald Reference Macdonald1963). Phosphamidon is much less toxic to fish than DDT (Johnson and Finley Reference Johnson and Finley1980) and its use along streams was expected to reduce the hazard to the Atlantic salmon fishery (Macdonald Reference Macdonald1963). The practice of spraying phosphamidon for budworm control along important Atlantic salmon streams was maintained until 1967. However, DDT continued to make up the bulk of the New Brunswick spray programme because of its cost advantage over phosphamidon (about CAD$1.23/ha for DDT versus CAD$3.70/ha for phosphamidon in 1963, or CAD$9/ha versus $28/ha in 2015 dollars. Source: personal communication by B.W. Flieger to the 1963 Meeting of the Interdepartmental Committee on Forest Spraying Operations, 29 October 1963, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada).
Phosphamidon was not without its own problems. From the outset concerns were expressed that, based on its toxicological profile and some preliminary field tests, phosphamidon might be hazardous to birds (Fowle Reference Fowle1965; Pearce Reference Pearce1968). Nevertheless, phosphamidon spraying continued well into the 1970s, when the evidence that phosphamidon was killing large numbers of birds (Pearce et al. Reference Pearce, Peakall and Erskine1976) could no longer be ignored and its use was terminated (Fig. 1).
Environmental concerns associated with the spraying of DDT and phosphamidon, and an observation that spruce budworm might be developing resistance to DDT (Randall Reference Randall1965), stimulated the search for new insecticides. Starting in the mid-1960s, the Department of Fisheries and Forestry Chemical Control Research Institute began an aggressive research programme to identify new control agents for spruce budworm and other forest insect pests (e.g., Randall and Nigam Reference Randall and Nigam1967; Nigam Reference Nigam1968), a programme that continued through the 1980s at the newly formed Forest Pest Management Institute of the Canadian Forest ServiceFootnote 1 (Helson and Nigam Reference Helson and Nigam1995). The process to screen candidate insecticides involved up to five steps (Nigam Reference Nigam1975; Helson and Nigam Reference Helson and Nigam1995): (1) determination of contact toxicity, as measured by mortality rates of test insects sprayed in a modified Potter’s tower (Nigam Reference Nigam1975: 10, fig. 1); (2) determination of residual toxicity, as measured by mortality rates of test insects on potted trees that had been sprayed and exposed to outside weathering for varying periods up to 10 days; (3) application on individual trees under field conditions by equipment that simulates aerial application; (4) ground application by mist blower to small plots; and (5) experimental aerial application to blocks of infested forest.
Between 1966 and 1988, more than 100 new insecticides and insecticide formulations were screened in the laboratory for potential use against the spruce budworm (Helson and Nigam Reference Helson and Nigam1995). About one quarter of these were evaluated in small-scale field trials for either efficacy or potential environmental impacts (Table 1). Based on the positive results of a small-scale field trial in 1965 (Fettes and Randall Reference Fettes and Randall1965), the organophosphate insecticide fenitrothion was tested semi-operationally for spruce budworm control in New Brunswick in 1967. Further large-scale experiments were conducted in 1968 to optimise the dosage rate, application rate and spray timing. Fenitrothion had replaced DDT for spruce budworm control in New Brunswick and would remain so for the next 25 years (Fig. 3). In addition fenitrothion was first applied operationally in Québec in 1970 and was used until 1986, the last year chemical insecticide spraying was allowed in the province and it was used operationally – but on a much smaller scale - in Ontario from 1968 to 1976 (Fig. 3).
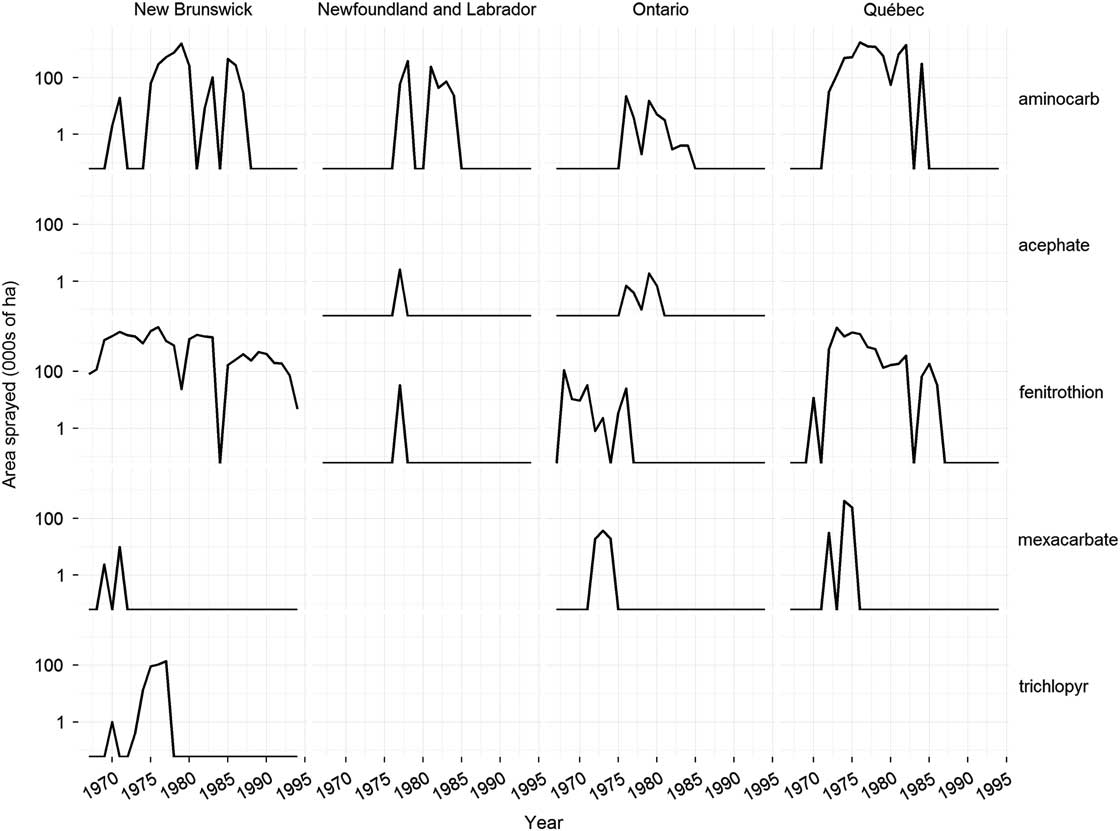
Fig. 3 Change over time in major insecticides used to control spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Clemens (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), in eastern Canada. Data sources as in Figure 1.
Table 1 Studies on the efficacy and impacts of insecticides intended for use against spruce budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana Clemens (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae).
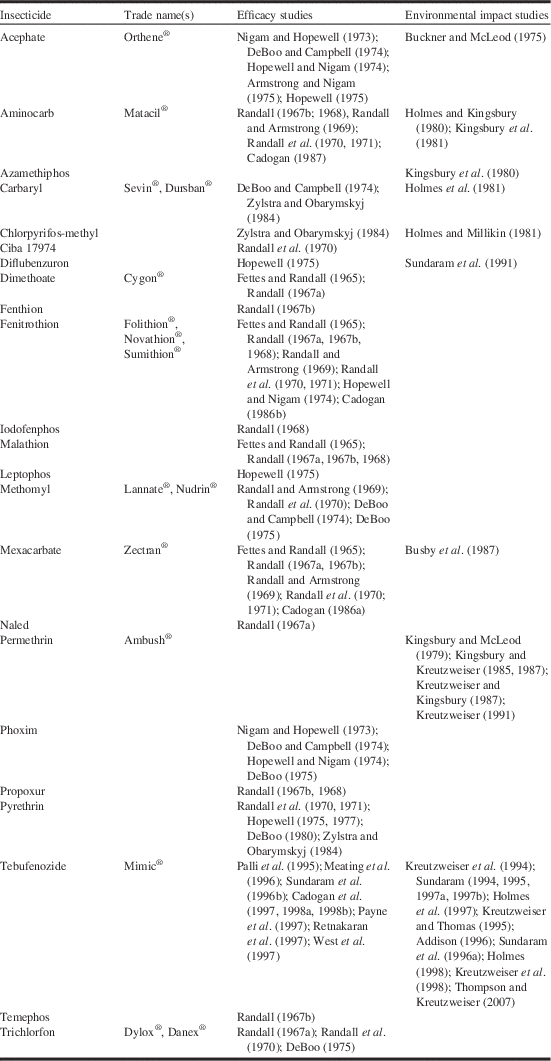
Following successful field trials in 1969 and 1970 (Kettela Reference Kettela1969; Armstrong Reference Armstrong1970), the carbamate insecticides aminocarb and mexacarbate (Table 1) were field tested semi-operationally in New Brunswick in 1971 (Fig. 3). Although the results were poor compared to fenitrothion (Kettela Reference Kettela1971), even larger trials were conducted in Québec in 1972 (Fig. 3). Aminocarb was used operationally in Newfoundland, New Brunswick, Québec, and Ontario between 1973 and 1987 (Fig. 3), second only to fenitrothion in total area sprayed (~40 million ha for fenitrothion and ~13.5 million ha for aminocarb). Although aminocarb was very effective against spruce budworm and generally had fewer environmental impacts than fenitrothion, its registrant (Bayer Inc.) decided in 1987 that it would no longer manufacture the product unless major quantities were ordered well ahead of time. This does not appear to have occurred as aminocarb was discontinued in 1989 and its registration expired in 2000.
Mexacarbate was used operationally in Québec and Ontario from 1972 to 1975 (Fig. 3), but the product was never registered. In the mid-1980s, the producer (Union Carbide Corporation) showed considerable interest in registering a new formulation of the product, and a number of laboratory and field investigations were conducted by Canadian Forestry Service (now Natural Resources Canada Canadian Forest Service) researchers to generate the necessary registration data (e.g., Sundaram and Nott Reference Sundaram and Nott1985; Sundaram et al. Reference Sundaram, Feng, Boyonoski and Manniste-Squire1985, Reference Sundaram, Nott, Holmes and Boyonoski1986, Reference Sundaram, Boyonoski and Feng1987; Holmes Reference Holmes1986; Cadogan Reference Cadogan1986a; Busby et al. Reference Busby, Holmes, Pearce and Fleming1987). In 1986, Union Carbide Corporation divested itself of a number of businesses, including its agricultural products business. The new owner of mexacarbate, May & Baker Ltd (now part of Bayer Agrochemicals) was not interested in pursuing the product’s registration. One possible reason was that the forest protection market was too small and unpredictable to justify the capital investment into a chemical that had few or no other uses, similar to the reasons given by Bayer for not offering aminocarb after 1987.
Several other insecticides had some degree of operational use through the 1970s. Acephate was applied to relatively small areas in Ontario and Newfoundland from 1976 to 1980 (Fig. 3). It failed to gain wider acceptance, because of formulation problems, high cost relative to the alternatives available (fenitrothion and aminocarb) and concerns about its effects on birds (e.g., Richmond et al. Reference Richmond, Henny, Floyd, Mannan, Finch and DeWeese1979; Zinkl et al. Reference Zinkl, Henny and Shea1979). In 1976, dimethoate was applied to >1 million ha of spruce budworm-infested forest in Québec in split applications with fenitrothion and aminocarb (Fig. 1). The fenitrothion/dimethoate splits provided adequate foliage protection, but the aminocarb/dimethoate splits did not (Paquet and Desaulniers Reference Paquet and Desaulniers1977). Because it is relatively nontoxic to honey bee, Apis mellifera Linnaeus (Hymenoptera: Apidae), (Reynolds et al. Reference Reynolds, Stern, Fukuto and Peterson1960), trichlorfon was applied operationally for spruce budworm control in New Brunswick in stands near blueberry, Vaccinium angustifolium Aiton (Ericaceae), production areas from 1974 to 1977.
In small-scale and large-scale field trials, the synthetic pyrethroid insecticide permethrin proved to be very efficacious in controlling spruce budworm (DeBoo Reference DeBoo1980; Zylstra and Obarymskyj Reference Zylstra and Obarymskyj1984). Unfortunately, permethrin proved to be so highly toxic to fish and aquatic invertebrates (Kingsbury and Kreutzweiser Reference Kingsbury and Kreutzweiser1987; Kreutzweiser and Kingsbury Reference Kreutzweiser and Kingsbury1987; Kreutzweiser and Sibley Reference Kreutzweiser and Sibley1991; Sibley et al. Reference Sibley, Kaushik and Kreutzweiser1991) that it could not be registered for aerial application, due to the unacceptable risk of spray products drifting into aquatic systems. In Canada, permethrin is currently registered for spruce budworm control by ground application only in Christmas tree plantations, high-value stands used for seed production, and other high-value woodland areas that are extensively managed (Anonymous 1992). Its use is further restricted to areas that are more than 100 m away from productive fishery waters or waterfowl habitats (Anonymous 1992).
After 1987, fenitrothion was the only registered chemical insecticide available for spruce budworm control (Green Reference Green1988), but its environmental impacts were still questioned (e.g., Plowright et al. Reference Plowright, Pendrel and McLaren1978; Plowright and Rodd Reference Plowright and Rodd1980; Busby et al. Reference Busby, Pearce and Garrity1981, Reference Busby, Pearce, Garrity and Reynolds1983, Reference Busby, White and Pearce1990; Fairchild and Eidt Reference Fairchild and Eidt1993; Ernst et al. Reference Ernst, Wade, Hennigar and Julien1994). In March 1989, Environment Canada published a comprehensive literature review of the environmental effects of fenitrothion use in forestry (Ernst et al. Reference Ernst, Pearce and Pollock1989) and concluded that:
…the use of fenitrothion under current use patterns and conditions in forest spraying is causing, or has the potential to cause, considerable adverse environmental impact, specifically with respect to ecological processes associated with pollinating insects, song birds and aquatic organisms.
This conclusion resulted in the recommendation that an early re-evaluation of the registered forestry uses of fenitrothion be undertaken. In response, and after consultation with affected parties and interested agencies, the Plant Industry Directorate of Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada announced a “Special Review of Fenitrothion” in October 1990. As part of the review process, information on the environmental hazards of fenitrothion was reviewed by a technical review team composed of members from Environment Canada, The Canadian Wildlife Service, Natural Resources Canada, and the Department of Fisheries and Oceans (Pauli et al. Reference Pauli, Holmes, Sebastien and Rawn1993). Summaries of the risk and value assessments, and a list of potential regulatory options, were released for public consultation in April 1993 (Anonymous 1993). In April 1995, a regulatory decision was announced that stated that the registration for broad-scale application of fenitrothion for control of spruce budworm and hemlock looper would not be extended beyond 1998 (Anonymous 1995). The decision to phase out the use of fenitrothion over a four-year period was intended to accommodate the short-term economic need for fenitrothion, and allow sufficient time for the alternative products (e.g., tebufenozide) to be developed and other existing products, e.g., Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner (Bacillaceae) (B.t.), to be improved. In practice, provincial governments and the forest protection industry had already started to phase-out their use of fenitrothion and the product was never applied beyond 1994 (Fig. 1).
The development and registration of tebufenozide, an insect moulting hormone analogue, marked a significant departure from the organophosphate and carbamate insecticides that dominated spruce budworm spraying operations through the 1970s and 1980s. Organophosphates and carbamates are neurotoxins, sharing a common mode of action (i.e., cholinesterase inhibition) in arthropods, fish, birds, and mammals. Tebufenozide acts on a different biochemical pathway specific to insects by mimicking the action of the insect moulting hormone ecdysone (Retnakaran et al. Reference Retnakaran, Krell, Feng and Arif2003). The specificity of tebufenozide to insects, especially among the Lepidoptera (Smagghe and Degheele Reference Smagghe and Degheele1994; Sundaram et al. Reference Sundaram, Palli, Krell, Sohi and Retnakaran1999; Retnakaran et al. Reference Retnakaran, Gelbic, Sundaram, Tomkins, Ladd and Primavera2001), made the compound an environmentally attractive alternative to traditional chemical insecticides.
Before its registration, extensive laboratory and field testing was done to determine the efficacy of tebufenozide against spruce budworm and its potential to cause harm to the environment (Table 1). These studies found that tebufenozide was highly effective and that the risk of harm to non-target organisms was minimal at the environmental concentrations expected under operational conditions. The result was that tebufenozide was granted temporary registration for control of forest and woodland pests, including spruce budworm, in 1996, and full registration in 2006. Tebufenozide was the only product used operationally against spruce budworm in Manitoba from 1997 to 2011. It was also used operationally in Alberta in 1999 (Fig. 2), along with B.t.
Ono (Reference Ono2002) reported that forest stands sprayed with tebufenozide in Alberta in 1999 were still free of visible defoliation in 2001, although the same was not true of stands that had been sprayed with B.t. This “carry-over effect” was also reported in Manitoba (Cadogan et al. Reference Cadogan, Scharbach, Krause and Knowles2002). In some cases spruce budworm populations declined to almost incipient levels a year after plots were sprayed with tebufenozide, even though budworm control in the year of application was unsatisfactory. Based on the results of laboratory experiments, Cadogan et al. (Reference Cadogan, Scharbach, Krause and Knowles2002) speculated that tebufenozide residues on egg-laying surfaces could inhibit oviposition by spruce budworm moths, and that tebufenozide residues present at the time of egg hatch might be toxic to first instars. However, a field trial of tebufenozide in Manitoba in 2000 found no effects on egg density or egg hatch nor any effects on egg hatch (Régnière et al. Reference Régnière, Cadogan and Retnakaran2005) and a laboratory study found that the consumption of tebufenozide by budworm larvae delayed ovarian maturation in females, reduced sperm production in males, and affected some behaviours associated with sex pheromone communication but there were no effects on fecundity or mating success (Dallaire et al. Reference Dallaire, Labrecque, Marcotte, Bauce and Delisle2004). These two studies suggest little support for carry-over effects of tebufenozide.
Doucet et al. (Reference Doucet, Frisco, Cusson, Bauce, Palli and Tomkins2007) demonstrated contact toxicity of spruce budworm to tebufenozide. However, in that study a laboratory assay was used where tebufenozide was dissolved in acetone and used to impregnate filter paper. Thus, it was likely that the toxicity that was observed was due to uptake through the cuticle, and not by ingestion as would be expected to occur in the field. Lack of tebufenozide toxicity to first and second instars is supported by field observations showing that aerial application of tebufenozide targeted at first instars did not affect population densities in the year following treatment (Régnière et al. Reference Régnière, Cadogan and Retnakaran2005). Thus, at best, the evidence for carry-over effects from tebufenozide in the year after treatment are equivocal, and not supported by the available data as no study has yet to demonstrate toxicity of tebufenozide in early instars, or mortality due to spray residuals either by contact toxicity or from feeding on treated foliage.
Chemical control of spruce budworm moths
All of the spruce budworm chemical control work described in the proceeding section was aimed at reducing spruce budworm damage (e.g., defoliation, tree mortality) by suppressing larval populations. Traditionally suppressing larvae is perceived as the most efficient means of pest control in forest systems. However, in the 1970s in New Brunswick, there was research on an alternative method of influencing the course of budworm infestations by spraying moths. In theory, if enough moths could be killed before egg-laying, egg deposition in sprayed areas would be reduced, leading to fewer larvae the next year.
Between 1972 and 1977, several large-scale spray trials were conducted, the largest being an ~809 000 ha phosphamidon treatment in 1974, to determine the efficacy of various insecticides (phosphamidon, but also fenitrothion, acephate, aminocarb, carbaryl, and pyrethrum), as well as dosage rates and optimal spray timing (Miller et al. Reference Miller, Varty, Thomas, Greenbank and Kettela1980). Although initial results were promising, including a 40–50% reduction in egg density (Kettela Reference Kettela1975a), the strategy was eventually abandoned for various reasons, including: (1) inconsistent population suppression, due to immigration of females into sprayed areas; (2) the requirement for multiple applications (up to five in a year) to deal with moth immigration and continual emergence; and (3) environmental concerns associated with the use of phosphamidon (see Varty and Titus Reference Varty and Titus1974 and the preceding section).
Chemical control of other defoliating insects
Many of the insecticides and systems primarily developed for spruce budworm control were adapted and used to control other forest insect defoliators. Starting around the same time that the original DDT trials were conducted against spruce budworm in Ontario, spray trials against various looper (Lepidoptera: Geometridae) species were conducted in British Columbia (see previous sections). In 1946, DDT was applied at the rate of 1.1 kg/ha to ~5058 ha to control an outbreak of western hemlock looper (Lejeune Reference Lejeune1975d). Two years later, DDT was used at the same rate on ~4700 ha against western false hemlock looper, Nepytia freemani Munroe (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), (Lejeune Reference Lejeune1975c). Successful control operations were conducted using DDT against mixed populations of hemlock looper and greenstriped forest looper, Melanolophia imitata Walker (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), in Stanley Park, Vancouver in 1958 and 1959 (Turnquist Reference Turnquist1991). Two large operational spray programmes were conducted against saddlebacked looper, Ectropis crepuscularia Denis and Schiffermüller (Lepidoptera: Geometridae), in 1960 (~730 ha) and 1961 (~4000 ha) using DDT at 0.6 kg/ha (Lejeune Reference Lejeune1975a) Other attempts to chemically control looper populations in British Columbia occurred in 1964, when ~650 ha were treated semi-operationally with phosphamidon at 0.9 kg/ha against greenstriped forest looper (Kinghorn and Richmond Reference Kinghorn and Richmond1965), and 20 ha were treated experimentally with phosphamidon against hemlock looper (Turnquist Reference Turnquist1991), and in 1975 when 60 ha were treated with acephate against western false hemlock looper (DeBoo and Taylor Reference DeBoo and Taylor1995). The results of many of these trials were equivocal, because the insect populations were already in decline due to disease. In general, outbreaks of many species of looper tend to develop and decline very rapidly, with tree mortality sometimes occurring before the infestation is even detected. This feature of looper outbreaks means that chemical controls are often not needed because the population has already declined by the time it becomes apparent that an infestation even existed. There are however, some exceptions to this pattern, the hemlock looper in eastern Canada being the most obvious.
In eastern Canada, outbreaks of hemlock looper occur at regular intervals predominantly on balsam fir, Abies balsamea (Linneaus) Miller (Pinaceae). Individual infestations tend to build up quickly, defoliation and mortality of trees occurs over a year or two, and then populations decline abruptly. However, an outbreak, spread across a number of stands, can last for five or six years (Prebble Reference Prebble1975b). An unprecedented, severe outbreak of hemlock looper in Newfoundland in the 1960s threatened the wood supply of the expanding pulp and paper industry, leading to chemical control operations in 1968 (~174 000 ha) and 1969 (~832 000 ha) (Otvos and Warren Reference Otvos and Warren1975). Fenitrothion was applied over most of the area, but phosphamidon was used near major waterways. Dosage rates varied from 140 to 280 mL/ha depending on the development stage of the insect, and the insecticide was usually applied in split applications. The results of the spray programme were considered to be very successful, protecting ~9.9×106 m3 of wood and hastening the collapse of the outbreak (Otvos and Warren Reference Otvos and Warren1975).
A second hemlock looper control operation was required in Newfoundland in the 1980s. Between 1985 and 1988, fenitrothion was applied to ~484 000 ha of infested forest (Crummey Reference Crummey1986, Reference Crummey1987, Reference Crummey1988, Reference Crummey1989) with a smaller area also treated with B.t.. Fenitrothion was applied at 210–280 g/ha, depending on stage of insect development, in split applications where possible. Results were variable, depending on spray conditions and larval populations, but in general the objectives of reduced larval populations and foliage protection were achieved. Fenitrothion was also used against hemlock looper in New Brunswick, but at a much smaller scale; ~17 800 ha were treated in 1990 (Hartling and Carter Reference Hartling and Carter1991) and ~6900 ha in 1993 (Forest Protection Limited 1994). However, as discussed earlier, the broad-scale use of fenitrothion in forest insect control operations was phased out by 1999, leaving B.t. as the only available option against hemlock looper.
A small-scale field test in 1995 demonstrated that tebufenozide could be an alternative to B.t. for hemlock looper control (West et al. Reference West, Thompson, Sundaram, Sundaram, Retnakaran and Mickle1997). Tebufenozide persists on foliage for six weeks or more (Sundaram et al. Reference Sundaram, Sundaram and Sloane1996b), therefore it was thought that a single application could be made around the time eggs are hatching. This application would remain active throughout the period when the larvae were feeding. Controlling hemlock looper is important, because the larvae are wasteful feeders (they do not consume the entire needle), and the early instars can cause considerable damage before conventional sprays are applied. An operational trial on 1433 ha was conducted in 2001 to test the efficacy of tebufenozide applied at a dosage rate of 70 g/ha under Newfoundland conditions (Crummey Reference Crummey2002; D. Lavigne, Forest and Agrifoods Agency, Corner Brook, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada, personal communication). Sufficiently good results were obtained such that the insecticide was applied operationally in Reference Ono2002, 2003, and 2007 to a total of 43 667 ha from hemlock looper (Crummey Reference Crummey2003, Reference Crummey2004; D. Lavigne, personal communication).
Two other budworm species have been the object of chemical control operations in Canada. In 1957, ~61 100 ha of forest in British Columbia, severely defoliated by western blackheaded budworm, Acleris gloverana (Walsingham) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), were sprayed with DDT at a dosage rate of 1 kg/ha, and another 2020 ha were sprayed at 0.6 kg/ha (Lejeune Reference Lejeune1975b). A lower dose of DDT (0.28 kg/ha) was applied to ~12 700 ha in 1960 (Lejeune Reference Lejeune1975b). Finally, in 1973, ~11 700 ha were treated with a split application of fenitrothion at 210 g/ha (Carrow Reference Carrow1974). All three outbreaks collapsed naturally, either due to weather or disease.
Chemical control operations were conducted against jack pine budworm, Choristoneura pinus Freeman (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), in Manitoba, Ontario, and Québec. The first experimental trials in Manitoba in 1967 involved DDT, fenitrothion and aminocarb applied to a total of 640 ha (DeBoo and Hildahl Reference DeBoo and Hildahl1967). The infestation collapsed in 1968, but the spray applications prevented extensive top-kill of trees, the most common result of repeated defoliation during a jack pine budworm outbreak (Prebble Reference Prebble1975c). In Ontario, 4940 ha of jack pine infested forest was treated in 1968 and 1969 with fenitrothion at rates of either 280 mL/ha or 420 mL/ha in a single application, or 280 mL/ha in a split application (Sippell and Howse Reference Sippell and Howse1975). In 1972, an additional 730 ha were treated with mexacarbate at a dosage rate of 84 mL/ha. Fenitrothion results were generally good, but there was little evidence of foliage protection in the mexacarbate-treated blocks (Sippell and Howse Reference Sippell and Howse1975). Fenitrothion was used to treat jack pine budworm infestations in Québec in 1970 and 1972 with satisfactory results (Martineau Reference Martineau1975).
Chemical control of bark and wood boring insects
Wood-boring and bark-boring insects are not amenable to chemical control, at least at large operational scales, because the most damaging life stages of these insects are protected under the bark and most of the tree bole can be infested. While some of the better contact insecticides such as carbaryl can cause high mortality of bark beetles when manually sprayed on tree boles (reviewed by Hastings et al. Reference Hastings, Holsten, Shea and Werner2001), generally the application of chemicals over the entire infested bole is too labour-intensive for large-scale operational programmes.
An exception to this situation was the use of the herbicide, monosodium methanearsonate (MSMA), in direct control operations to reduce populations and limit the spread of mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponserosae Hopkins (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), and spruce beetle, D. rufipennis (Kirby). For mountain pine beetle, the procedure involved luring beetles into pheromone-baited trees that were treated with MSMA by injecting the chemical into a shallow axe frill around the base (Dyer and Hall Reference Dyer and Hall1979; McMullen et al. Reference McMullen, Safranyik and Linton1986). For spruce beetle the procedure was similar, except trees were injected with MSMA then felled two weeks later and then colonised naturally by the insect (Hodgkinson Reference Hodgkinson1985). The translocated MSMA kills the trap tree and the beetle larvae under the bark. As the beetles are dead, the trap tree does not have to be burned on site or removed, but simply allowed to decompose. MSMA treatment was favoured in British Columbia, because it was effective, relatively inexpensive and easy to apply in remote areas (British Columbia Ministry of Forests 1995; Morrissey et al. Reference Morrissey, Dods and Elliott2008). From 1995 to 2004, ~5080 kg of MSMA was applied to almost 500 000 trees in British Columbia for mountain pine beetle control (Morrissey et al. Reference Morrissey, Albert, Dods, Cullen, Lai and Elliott2007). However, due to the scale of the operation, concerns soon arose about the possible effects of arsenic residues on wildlife, in particular woodpeckers and other forest birds (Morrissey et al. Reference Morrissey, Albert, Dods, Cullen, Lai and Elliott2007, Reference Morrissey, Dods and Elliott2008). The British Columbia government’s permit to use MSMA expired in 2005, and the registration for Glowon® MSMA, the commercial product used in mountain pine beetle control, expired in 2008.
Insecticides are no longer used against bark beetles in operational forest management programmes. However, chemical control of elm bark beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) is commonly done in some Canadian cities for the control of Dutch elm disease, a fungal infection of elm, Ulmus Linnaeus (Ulmaceae). Currently, chlorpyrifos, permethrin, and carbaryl are registered for control of elm bark beetles for application by basal spraying. Of these three, chlorpyrifos is the most effective against elm bark beetle (Oghiakhe and Holliday Reference Oghiakhe and Holliday2011). Booth and Johnson (Reference Booth and Johnson2009) also reported good efficacy of acephate delivered by stem injection against red elm bark beetle, Magdalis armicollis Pierce (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), in elm.
Wood-boring species, especially longhorned beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) and ambrosia beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), in Canada typically cause most of their damage to log inventories in mill yards. Many of the same inorganic pesticides tested against bark beetles (e.g., Lindane) were applied against woodborers in mill yards (Shore and McLean Reference Shore and McLean1995). Chemical controls can kill larvae under the bark and others confer protection to piled conifer logs from attack when the logs are sprayed before the beetles disperse (Lejune and Richmond Reference Lejeune and Richmond1975). The spraying of log decks is effective at protecting exposed surfaces, but beetles can colonise logs further down in the deck that did not receive the benefit of the spray. As well, the use of chemicals requires costly procedures in the mills to protect workers. Consequently, chemicals have not been employed operationally in mill yards since the 1970s (Shore and MacLean Reference Shore and McLean1995). Woodborer management has been better achieved using water application on log decks, semiochemicals, and cultural controls (i.e., better management of inventory to process logs before beetle flight periods) than was achieved using chemical controls.
New chemicals
A botanical insecticide extracted from the seed kernels of the neem tree, Azadirachta indica Jussieu (Meliaceae), has received considerable attention over the last 20 years as a tactic for use against various forest insect pests. A number of products, all containing the compounds azadirachtin A and azadirachtin B as the putative active ingredients have been examined. Some formulations have been designed for conventional broadcast application against defoliators, while others have been developed for use as systemic insecticides administered using stem injections to target woodborers and defoliators (Naumann et al. Reference Naumann, Rankin and Isman1994; Lyons et al. Reference Lyons, Helson, Jones, McFarlane and Scarr1996; Wanner et al. Reference Wanner, Helson and Kostyk1997; Helson et al. Reference Helson, de Groot, McFarlane, Zylstra and Scarr1998, Reference Helson, Lyons and Wanner2001; Duthie-Holt et al. Reference Duthie-Holt, Borden and Rankin1999; Naumann and Rankin Reference Naumann and Rankin1999; Poland et al. Reference Poland, Haack, Petrice, Miller and Bauer2006; McKenzie et al. Reference McKenzie, Helson, Thompson, Otis, McFarlane and Buscarini2010; Booth and Goettel Reference Booth and Goettel2012). Azadirachtins have several properties that make them attractive for forestry use: (1) they can be applied as either a foliar spray or systemically by injection (Helson Reference Helson2001); (2) they have multiple modes of action (antifeedant, growth regulating, and reproductive impairment) (Naumann et al. Reference Naumann, Rankin and Isman1994); (3) they exhibit low toxicity to mammals and birds (Schmutterer Reference Schmutterer1990); (4) they pose little risk to most nontarget invertebrates, including beneficial insects (Thompson and Kreutzweiser Reference Thompson and Kreutzweiser2007; Kreutzweiser et al. Reference Kreutzweiser, Thompson, Grimalt, Chartrand, Good and Scarr2011); and (5) they have low to moderate persistence in water, soil, and foliage (Thompson and Kreutzweiser Reference Thompson and Kreutzweiser2007). However, azadirachtins are highly toxic to zooplankton (specifically adult copepods) so mitigation is required to avoid deposition of sprayed materials in water bodies (Kreutzweiser et al. Reference Kreutzweiser, Back, Sutton, Thompson and Scarr2002, Reference Kreutzweiser, Back, Sutton, Pangle and Thompson2004a, Reference Kreutzweiser, Sutton, Back, Pangle and Thompson2004b).
In 2000, a commercial formulation of azadirachtin (Neemix 4.5®) was granted temporary registration for use in aerial applications. The next year small operational control programmes (totalling ~4100 ha) were carried out against balsam fir sawfly, Neodiprion abietis Harris (Hymenoptera: Diprionidae), in Newfoundland and again in 2002 (Crummey Reference Crummey2002, Reference Crummey2003), but the product’s registration lapsed at the end of 2002. Neemix 4.5® was also applied experimentally in 1999 in Ontario against pine false webworm, Acantholyda erythrocephala Linnaeus (Hymenoptera: Pamphiliidae), and in Newfoundland using ground-based equipment against yellowheaded spruce sawfly, Pikonema alaskensis Rohwer (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae) (Thurston Reference Thurston2000). Results against pine false webworm were positive, with a significant reduction in defoliation at the end of the season. Results against yellowhead spruce sawfly were more equivocal, the application was made late and as a result there was no difference in defoliation in the spray blocks compared to controls. However, larvae in the spray blocks were less vigorous.
An experimental ultra-low aerial application of Fortune Aza (3% azadirachtins) at a rate of 50 g/ha was conducted in southern Ontario to assess deposition in red pine, Pinus resinosa Alton (Pinaceae), plantations and efficacy against pine false webworm (Lyons et al. Reference Lyons, Helson, Thompson, Jones, McFarlane and Robinson2003; Thompson et al. Reference Thompson, Mickle, Lyons, Helson, Robinson and Chartrand2003). That study demonstrated foliar deposits well in excess of levels that cause 91% mortality in laboratory bioassays against pine false webworm, as well as significant reductions in insect abundance and defoliation compared to untreated controls. These results suggested that ultra-low-volume aerial applications of azadirachtin-based insecticides could be effective as part of an integrated pest management programme for the pest.
An injectable formulation of azadirachtin (TreeAzin®) was developed by Natural Resources Canada Canadian Forest Service for use against emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). The formulation exhibits rapid uptake and translocation of the formulation in both green ash, Fraxinus pennsylvanica Marshall (Oleaceae), and white ash, Fraxinus americana Linnaeus, trees (Grimalt et al. Reference Grimalt, Thompson, Chartrand, McFarlane, Helson and Lyons2011) and significant inhibition of larval development as well as reduction of adult emergence (McKenzie et al. Reference McKenzie, Helson, Thompson, Otis, McFarlane and Buscarini2010). Subsequent studies demonstrated that azadirachtin residues in the foliage of treated ash can inhibit the fecundity of emerald ash borer adults when leaves are consumed during maturation feeding. This mode of action provides a dual mechanism that targets both larval and adult life stages of emerald ash borer (D. Thompson, Great Lakes Forestry Centre, Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada, personal communication).
Following several years of research and use under emergency registration, TreeAzin® was registered in 2012 for emerald ash borer and several other insect pests including gypsy moth, jack pine budworm, pine false webworm, and spruce budworm as well as tent caterpillars, Malacasoma Hübner (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae); arborvitae leafminers, Argyresthia Hübner (Lepidoptera: Argyresthidae); and birch leafminer, Fenusa pumila Leach (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae). TreeAzin® is owned by Natural Resources Canada Canadian Forest Service and licensed to BioForest Technologies Inc. (Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, Canada) for worldwide distribution. Ongoing research suggests parallel potential for use of TreeAzin® against red elm bark beetle (Booth and Goettel Reference Booth and Goettel2012) and Asian longhorned beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) (Beltrán et al. Reference Beltrán, Ibáñez, Gracia-Lor, Sancho, Hernández and Thompson2014). Similar to its effect on emerald ash borer, Treeazin® also inhibits growth in Asian longhorned beetle larvae and causes reduced fecundity of maturation feeding adults (D. Thompson, personal communication).
Spinosyns are natural insecticides produced via fermentation culture of the actinomycete Saccharopolyspora Lacey and Goodfellow (Pseudonocardiaceae). These compounds show activity against a number of forest pests, including: gypsy moth, pine false webworm, spruce budworm, yellow headed spruce sawfly, leaf beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae), conifer sawflies (Hymenopera: Diprionidae), and eastern tent caterpillar, Malacasoma americanum Fabricus (Lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae). Spinosyns dissipate rapidly when applied under typical forest use patterns in Acadian and Great Lakes-St. Lawrence forest regions (i.e., mixed conifer and deciduous forests) and have minimal toxicity to mammals and low toxicity to beneficial insects (Thompson et al. Reference Thompson, Harris, Buscarini and Chartrand2002a, Reference Thompson, Harris, Lanteigne, Buscarini and Chartrand2002b; Holmes and Kettela Reference Holmes and Kettela2006; Kettela et al. Reference Kettela, Stewart, Pest and Holmes2006; Thompson and Kreutzweiser Reference Thompson and Kreutzweiser2007). Spinosyns are currently registered in Canada for use against agricultural crops, ornamentals, and against turf insects but have not been registered for aerial application in forests.
Imidacloprid is another systemic insecticide that has been shown to be effective at controlling wood-boring insects (Poland et al. Reference Poland, Haack, Petrice, Miller and Bauer2006). Imidacloprid is a chloro-neonicotinyl insecticide (neonicotinoid) that blocks the nicotinergic neuronal pathway in insects (Elbert et al. Reference Elbert, Becker, Hartwig and Erdelen1991). Two imidacloprid based products, Confidor® 200SL and IMA-jet®, are registered in Canada for use by stem injection against a variety of insect pests, including emerald ash borer, Asian longhorned beetle, and brown spruce longhorn beetle (Tetropium fuscum Fabricius; Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). However, recent studies have shown that imidacloprid applications, by stem injection, soil injection, or soil drench, pose a significant risk to natural decomposition processes, as a result of lethal and sublethal effects on decomposer organisms that feed on imidacloprid-contaminated leaves (Kreutzweiser et al. Reference Kreutzweiser, Good, Chartrand, Scarr and Thompson2007, Reference Kreutzweiser, Good, Chartrand, Scarr, Holmes and Thompson2008a, Reference Kreutzweiser, Good, Chartrand, Scarr and Thompson2008b, Reference Kreutzweiser, Good, Chartrand, Scarr and Thompson2008c, Reference Kreutzweiser, Thompson and Scarr2009). Neonicotinoids have also been identified as posing a risk to bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) resulting in a moratorium against its use by the European Commission (European Food Safety Authority 2013; Rondeau et al. Reference Rondeau, Sanchez-Bayo, Tennekes, Decourtye, Ramirez-Romero and Desneux2014). The risks of neonicotinoids to ecosystems have also been the subject of a recent major review (Van der Sluijs et al. Reference van der Sluijs, Amaral-Rogers, Belzunces, Bijleveld van Lexmond, Bonmatin and Chagnon2015).
Development of insecticide delivery technology
Aircraft and aerial application technology
As insecticides changed over the years, the technology involved in aerially applying insecticides to forests also changed. The original “crop dusting” method of the 1920s gave way to hydraulic boom-and-nozzle systems for applying liquid formulations of insecticides to large operational spray blocks (Fig. 4).
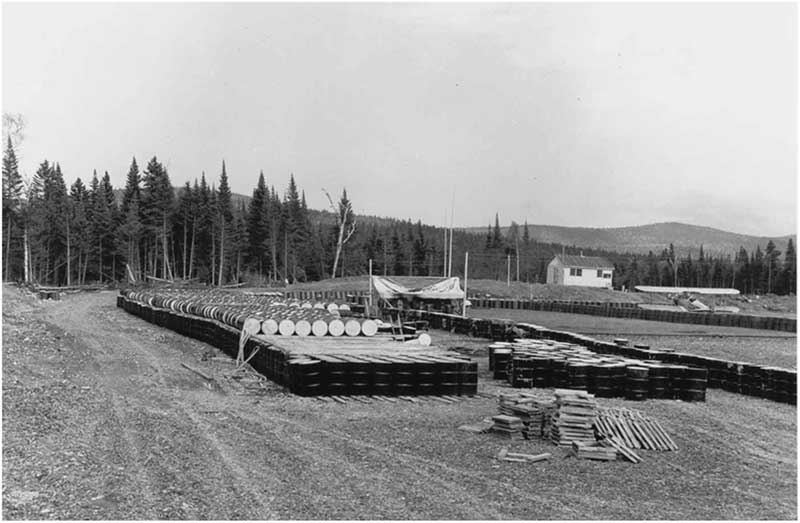

Fig. 4 Spray plane and drums of formulated dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) at a spray base in New Brunswick during the 1952 spruce budworm programme. Photograph credit: Natural Resources Canada, Canadian Forest Service.
In New Brunswick in the 1950s and most of the 1960s, DDT and phosphamidon were diluted in a carrier (e.g., water, fuel oil) and applied at rates of 4.7 L/ha. In 1968 in New Brunswick, the application rate was reduced to 1.9 L/ha with good results (Kettela Reference Kettela1968) such that the application rate was further reduced to 1.4 L/ha in 1969. The advantages of the lower application rates included: (1) increased efficacy, as a result of better coverage of the target area with a finer droplet spectrum; (2) increased aircraft payload, allowing larger blocks to be sprayed with less ferry time; and (3) reduced cost of materials (i.e., carrier, aviation fuel).
In 1975, Forest Protection Limited (Lincoln, New Brunswick, Canada) purchased 22 World War II-era Grumman TBM Avenger single-engine aircraft, fitted with boom and nozzle spray emission systems, that became the workhorses of the New Brunswick spray programme until the 1990s (Kettela Reference Kettela1995). The same basic spray system with low volume application rates was employed in Québec to treat large operational spray blocks, although using large, multi-engine aircraft (Blais et al. Reference Blais, Benoit and Martineau1975; Dorais et al. Reference Dorais, Auger and Pelletier1995).
Starting in the mid-1960s, researchers at the Chemical Control Research Institute investigated the concept of ultra-low-volume spraying using rotary atomisers (Randall Reference Randall1975). Rotary atomisers produce very small and relatively uniform distributions of droplets (20–100 μm diameter) at low or ultra low application rates (Cadogan Reference Cadogan1995) and can also be used on smaller, slower flying aircraft, because the droplet spectrum is determined by the speed of the rotors rather than the speed of the aircraft (McLeod et al. Reference McLeod, Lucarotti, Hennigar, McLean, Holloway and Cormier2012). Ultra-low-volume spraying using aircraft equipped with Micronair rotary atomisers (Micron Group, Bromyard, Herefodshire, United Kingdom) was first conducted operationally in Ontario in 1972.
Small aircraft (e.g., Stearman bi-planes, Grumman Ag Cats) were introduced into control programmes in the mid-1970s in New Brunswick, and in the early 1980s in Québec, to treat small blocks that could not be treated using larger aircraft (Dorais et al. Reference Dorais, Auger and Pelletier1995; Kettela Reference Kettela1995). Spray trials in New Brunswick in 1984 and 1986 demonstrated the efficacy of fenitrothion and aminocarb applied at ultra-low-volume rates (0.4 L/ha), leading to the registration of this use pattern for small aircraft (Kettela Reference Kettela1995).
Navigational control
Considerable progress has also been made in the navigational control of spray aircraft operation. Historically, spray programmes relied on pilot skill to navigate small aircraft around spray blocks using balloons, tree flags, and readily identifiable topographic features (Dixon and Irving Reference Dixon and Irving1985; Juneau Reference Juneau1989). This often resulted in problems, such as overspraying, missed swaths, and spray deposits outside of block boundaries, ultimately leading to inconsistent control, wasted spray product, and unintended environmental impacts.
In 1961, Forest Protection Limited developed an aerial flagging system for guiding its larger, faster (280 km/hour), less maneuverable TBM aircraft (Dixon and Irving Reference Dixon and Irving1985). In this system, a spray team of two or three TBMs was guided by two light “pointer” aircraft (e.g., Cessna 172s). Each pointer aircraft carried a pilot and a navigator or “pointer” trained in low-level visual navigation and equipped with topographic maps marked with block boundaries and spray lines. The pointer aircraft would lead the spray team along the intended spray line, and signal “booms on” and “booms off” at the block boundaries (i.e., when and where to start and stop spraying insecticide). The system worked well but was costly to operate both in terms of aircraft and staff.
In Québec, where large, multi-engine aircraft were used to spray at heights of 100 m above the forest canopy (compared to 15–30 m for the TBM), an inertial navigation system was used to guide spray aircraft (Dorais et al. Reference Dorais, Auger and Pelletier1995). The system was capable of guiding the spray aircraft to the spray block, locating the starting points of the spray lines, maintaining track along parallel spray lines, indicating “boom on” and “boom off”, and returning the aircraft to base (Randall Reference Randall1975).
Today’s modern spray aircraft are equipped with global positioning system aerial navigation systems, radar altimeters, automatic flow control systems, automatic boom control systems, and data logging capability (e.g., AccuairTM McLeod et al. Reference McLeod, Lucarotti, Hennigar, McLean, Holloway and Cormier2012). The navigation system provides exact positioning and guidance over the spray block, and provides pilots with in-flight feedback on their performance. Global positioning system and spray application data can be imported into a pesticide application information system and reviewed by pest managers to evaluate the spray programme and correct spray application problems (Pines Reference Pines2010; McLeod et al. Reference McLeod, Lucarotti, Hennigar, McLean, Holloway and Cormier2012).
Public policy
In Canada the regulation of pesticides and the monitoring of forest management programmes are responsibilities shared by the federal and provincial governments. The various roles and responsibilities of the two levels of government have changed over time as detailed by Prebble et al. (Reference Prebble, Prentice and Fettes1975) and Kingsbury (Reference Kingsbury1995). Some of the legal and public policy implications of this structure were reviewed 30 years ago (Castilli and Vigod Reference Castilli and Vigod1987). After a long and extensive consultation process the province of Ontario produced a series of guidelines for forest management (Ontario Environmental Assessment Board 1994). The current version of this document (Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources 2003, 2007) includes specifications for how decisions are to be made about the use of insecticides in Ontario’s forests. Other provinces have similar guidelines. Kingsbury (Reference Kingsbury1995) discussed the evolution of the public policy landscape around forestry and the use of insecticides in the 1970s and 1980s. Part of this evolution was driven in response to increasing public attention to the environmental effects caused by pesticides, which was a result of Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring (Carson Reference Carson1962). One effect of this change was an increase in research into the environmental effects of pesticides, including non-target impacts (e.g., Table 1). Other work has examined the public’s willingness to pay for insect control in forests (MacDonald et al. Reference MacDonald, McKenney and Nealis1997), general attitudes among the public on forest pest control (Chang et al. Reference Chang, Lantz and MacLean2009) and the economic costs and potential benefits of forest pest control (e.g., Slaney et al. Reference Slaney, Lantz and MacLean2009, Reference Slaney, Lantz and MacLean2010). There does not appear to have been any recent assessments of the public policy implications of forest pest management using modern chemical controls and modern tactics (e.g., B.t., tebufenozide, or azadirachtins) or the use of chemical controls in the urban forest; or the use of chemical controls against invasive species. There also do not appear to have been any review of the legal or public policy implications of legislation and legal proceedings around insecticide use in forests since that of Castilli and Vigod (Reference Castilli and Vigod1987).
Conclusions
Chemical insecticides will likely always have a place in forest pest management. However, present trends suggest the routine application of chemicals to control defoliating insects across large swaths of Canadian forest is almost certainly a thing of the past (e.g., Figs. 1–3). Previous experience with other large-scale spray programmes has also shown that public opposition to the use of chemical insecticides on public lands can be significant. However, the public’s opinion of spray programmes using modern tactics has not been tested. We argue that chemical insecticides, when used, will be applied over much smaller areas than in the past (e.g., on high-value stands) and under tightly controlled conditions. Even then, chemical insecticides will only be applied to improve or optimise pest management efforts, in combination with other tactics as part of an overall integrated pest management strategy. For example, tebufenozide was recently used against spruce budworm in New Brunswick as part of an early intervention strategy targeting incipient populations (hotspots) using small spray blocks (<2000 ha) (Healthy Forest Partnership 2015).
Chemical insecticides might also be used in emergency situations. For example, the province of Newfoundland obtained an emergency registration for trichlorfon in 1998, and a temporary registration in 1999, to combat a balsam fir sawfly outbreak that was threatening valuable, pre-commercially thinned balsam fir stands (Thurston Reference Thurston2000). Sawflies are not susceptible to either B.t. or tebufenozide although a number of biological controls are available for use in an integrated pest management programmes (reviewed in MacQuarrie et al. Reference MacQuarrie, Lyons, Seehausen and Smith2015; van Frankenhuyzen et al. Reference van Frankenhuyzen, Lucarotti and Lavallée2015). Finally, systemic insecticides will continue to be used to protect high value trees, particularly in the urban forest, parks or conservation reserves as part of “slow the spread” programmes, or in economic mitigation programmes against some bark beetles and invasive insects like emerald ash borer and Asian longhorned beetle.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank R. Alfaro, D. Doucet, K. van Frankenhuyzen, D. Langor, D. Kreutzweiser, and D. Thompson for comments on earlier drafts of this manuscript.







