Anaemia is a major and global public health problem that affects around a third of the world’s population and is defined as a level of Hb:
-
<13 g/dl in men older than 15 years;
-
<12 g/dl in non-pregnant women older than 15 years and
-
<11 g/dl in pregnant women(Reference Goddard, James and McIntyre1).
In 2016, anaemia affected a total of 430 million adolescents, almost one in four adolescents globally, and had increased by 20 % since 1990. While the increase had largely been driven by changing demography, decrease over the years has been slow, with < 0·5 % reduction observed since 1990(Reference Azzopardi, Hearps and Francis2).
Most cases of anaemia worldwide have a primary nutritional origin; therefore, anaemia can be a useful indicator of undernutrition, particularly relevant for adolescents in the context of rapid growth and menstruation(Reference Kassebaum3). At the same time, previous studies reported strong association between BMI and anaemia status(Reference Ghose, Yaya and Tang4).
Micronutrient deficiencies are a leading risk factor for the global burden of disease and iron deficiency anaemia account for the majority of disability-adjusted life years associated with micronutrient deficiencies (>2500 disability-adjusted life years per 100 000 adolescents)(Reference Black, Victora and Walker5), especially among young girls(Reference Akseer, Al-Gashm and Mehta6).
More than one in three pregnant women worldwide has iron deficiency anaemia(Reference Lewkowitz and Tuuli7), which is known to negatively impact the course and outcome of future pregnancies(Reference Lewkowitz and Tuuli7), especially in the first and second trimester, enhancing the risk of low birth weight, premature birth and increased risk of infectious diseases and perinatal mortality in both the mother and the child. Anaemic mothers are 30–45 % less likely to incur favourable pregnancy outcomes, and their infants are estimated to have less than a half of normal iron reserves(Reference Peña-Rosas, De-Regil and Garcia-Casal8).
Almost 200 million adolescents (45 % globally) with anaemia live in India and China and young girls are at higher risk(Reference Azzopardi, Hearps and Francis2).
Despite having had an anaemia control programme for 50 years, India has the highest burden of the disease, and the lack of anaemia reduction in the country is surprising, considering India’s rapid economic growth during the last 20 years, as anaemia rates are expected to decline approximately a quarter as fast as income increases(Reference Nguyen, Scott, Avula and Tran9).
As pointed out by a recent analysis, research is needed around factors influencing anaemia over time at individual, household and community levels(Reference Nguyen, Scott, Avula and Tran9). Also, given that only 25 %(Reference Petry, Olofin and Hurrell10) to 50 %(Reference Kassebaum3) of anaemia is thought to be due to iron deficiency, the traditional approach of iron supplementation might fall short and policy-makers are challenged to understand which investment will have the greatest impact on anaemia reduction in India in the future.
In view of the above, using the latest two rounds of India Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) (2015 and 2015), this paper seeks to: (1) explore changes in trend of anaemia and BMI among currently pregnant nullipara adolescent women against socio-economic determinants, (2) explore the association between anaemia in currently pregnant nullipara adolescent women v. currently pregnant nullipara older women of reproductive age.
Methods
Population, setting and data
DHS are nationally representative household surveys targeting all or ever-married women of reproductive age (15–49 years)(Reference Rustein and Rojas11). Questionnaire is administered face-to-face by trained personnel and is translated into major local languages. The core content for every round of DHS is standard to guarantee the information comparability across countries. At the same time, errors like non-sampling, coverage and data processing are minimised through extensively training data collectors/health investigators on the standard internationally recommended protocols and data confidentiality(12).
Women aged 15–49 years are identified for anaemia testing, which is conducted in the household by measuring Hb level in the capillary blood samples collected from a finger prick. Individuals eligible for anaemia testing are advised about the objectives, potential risks, voluntary participation in testing and confidentiality of the anaemia testing procedures, as part of the DHS informed consent process(Reference Kothari, Coile and Huestis13). Parents or guardians of never-married adolescents aged 15–17 are asked for approval before consent of the adolescent is sought. After obtaining informed consent, a finger is cleaned with a swab, impregnated with 70 % isopropyl alcohol, allowed to air dry and pricked with a disposable self-retracting lancet. The first two blood drops are wiped away; the third drop is collected with a microcuvette for measurement of the Hb level using the HemoCue® Hb 201+ analyzer (www.hemocue.com) and results are provided to participants immediately(Reference Kothari, Coile and Huestis13).
DHS also collect the BMI for all participant women, calculated as weight (kg) divided by the square of height (m2).
For the current study, we excluded data for ever pregnant as well as currently pregnant women. Missing data are flagged in the DHS and were excluded from the analysis.
Main outcome, exposure and other variables
A standard biomarker questionnaire is used in the DHS to record Hb that is used to categorise the degree of anaemia. A cut-off of Hb < 12·0 g/dl for non-pregnant women as recommended by WHO was considered for classifying anaemia in the study.
Also, the conventional threshold of a BMI < 18·5 (underweight) was traced as additional outcome.
We explored several covariates. Place of residence was split into urban and rural settings; a wealth index based on asset ownership and household characteristics data (categorised using the quintiles ‘poorest’, ‘poorer’, ‘middle’, ‘richer’ and ‘richest’) was considered as a proxy for socio-economic status(Reference Corsi, Neuman and Finlay14). As for literature(Reference Ackerson, Kawachi and Barbeau15), educational attainment was stratified in ‘0–6 years’ and ‘>6 years’.
Statistical analysis
We use counts and percentages to describe the distribution of anaemia and BMI among 15–19 years old by residence, wealth and education, both for the India 2005 and the India 2015 DHS.
Chi-squared or Fisher exact and trend P-value tests were utilised to evaluate differences across the levels of the covariates. To evaluate the risk of anaemia by adolescent nullipara women v. older nullipara women, we computed unadjusted and adjusted OR by logistic regression. For multivariable analysis, we adjusted for residence, wealth and education. Within-DHS correlation was controlled for by running a non-linear mixed logistic random effect model(Reference Donner and Klar16).
We used Stata v13.1 SE (StataCorp. LP.) for statistical analysis.
Results
Anaemia prevalence among 696 adolescent girls in the India 2005 DHS ranged from around 61·7 % (n 87) in the poorest wealth level to 50·0 % in the richest (n 43). Likewise, the low BMI prevalence significantly decreased with increasing wealth, from 22·0 % (n 31) to 14·0 % (n 12). While non-significant changes in anaemia prevalence were found when exploring residence (urban v. rural), stratification by years of schooling showed significant reduction of anaemia prevalence and low BMI with higher number of years of schooling (Table 1).
Table 1 Prevalence of anaemia and BMI < 18·5 by wealth, residence and schooling among 696 nullipara adolescent girls of the India 2005 DHS and from 3401 nullipara adolescent girls of the India 2015 DHS
Findings from the India 2015 sample (3041 adolescent girls) showed a very similar trend. Prevalence of anaemia among the poorest and the richest was respectively 56·2 % (n 474) and 38·9 % (n 75). Also, a BMI < 18·5 significantly decreased from 17·6 % (n 148) to 12·0 % (n 23). Anaemia and BMI < 18·5 were significantly higher in adolescent girls living in rural areas and with fewer years of schooling (Table 1).
The 10-year transition from the 2005 to the 2015 DHS registered important improvements in terms of decreased anaemia prevalence, across all wealth categories. However, the time trend clearly shows the differences between the poorest and richest section of the society, with heaviest gains in anaemia reduction over time among the latter (from 50·0 to < 40·0 %) (Fig. 1). BMI also improved over the years, although much less in comparison with anaemia.

Fig. 1 Prevalence trend of anaemia and low BMI prevalence across wealth categories among nullipara adolescent girls in India from 2005 to 2015. ![]() , 2000;
, 2000; ![]() , 2015
, 2015
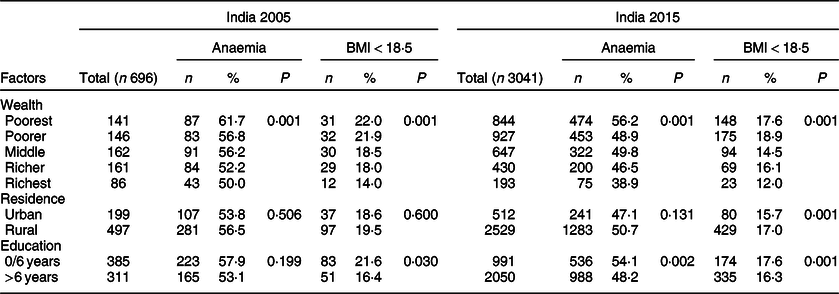
The prevalence trend stratified by education showed steady improvement, especially for anaemia, from 2005 to 2015 (Fig. 2). The reduction was slightly more pronounced among adolescent girls with more than 6 years of schooling (from around 55·0 % in 2005 to < 50·0 % in 2015).
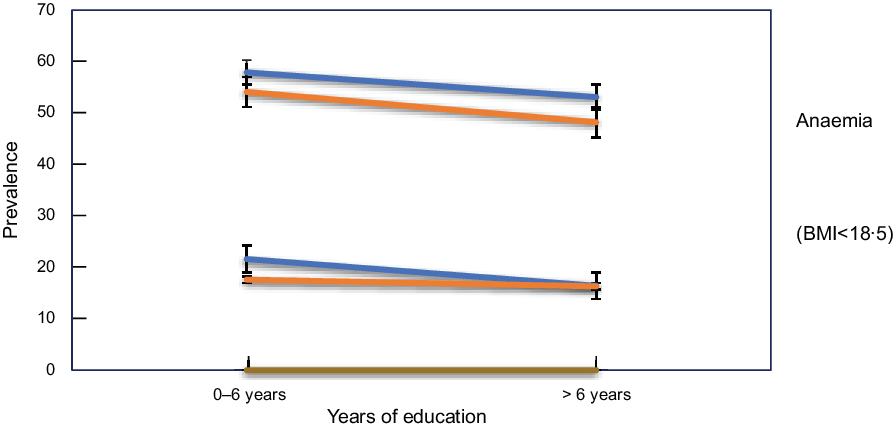
Fig. 2 Prevalence trend of anaemia and low BMI prevalence across education categories among nullipara adolescent girls in India from 2005 to 2015. ![]() , 2000;
, 2000; ![]() , 2015
, 2015
Differences in the distribution of anaemia and low BMI held stable when investigating the place of residence (Fig. 3). While both indicators (anaemia and BMI) slightly improved from 2005 to 2015, adolescent girls living in rural areas showed higher prevalence of both anaemia and BMI < 18·5.
Fig. 3 Prevalence trend of anaemia and low BMI prevalence across residence categories among nullipara adolescent girls in India from 2005 to 2015. ![]() , 2000;
, 2000; ![]() , 2015
, 2015
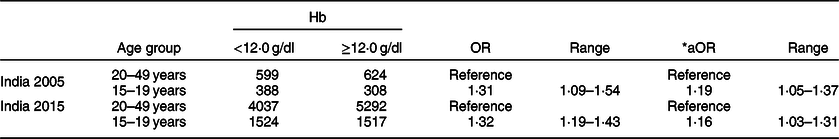
At multivariable regression, the odds of anaemia were significantly higher among the adolescent population when compared with adult women and the findings were almost the same when evaluating the India DHS 2005 and the India DHS 2015 (Table 2).
Table 2 Multivariable logistic model of anaemia (≥12·0 v. <12·0 g/dl) in adolescent girls compared with adult women for the India 2005 and the India 2015 DHS (model adjusted for age, place of residence, BMI, education)
* Logistic regression adjusted by wealth, education, residence and BMI.
Discussion
Individual level data analysis using the two-consecutive population-based nationally representative India DHS surveys (2005 and 2015) revealed an overall improvement in both the prevalence of anaemia (from 55·6 to 50·1 %) and of BMI < 18·5 (from 19·2 to 16·7 %) for adolescent nullipara girls. Improvements in the level of anaemia were registered for almost all categories taken into consideration, particularly wealth and residence; on the other hand, the inequalities evidenced during the first round of DHS were also reported in the 2015 survey.
The impact of socio-demographic index on the variability years lived with disability (YLD) rates due to iron deficiency anaemia was confirmed on a global scale by the Global Burden of Disease project(17). In 2016, iron deficiency anaemia showed a large decline in the expected YLD estimates with enhancing socio-demographic index (17).
The present study also confirms in both DHS surveys how adolescent nullipara girls are at significant higher risk of anaemia when compared with their adult counterparts. This last finding is in line with adolescent girls’ physiology: iron requirements of 14-year-old girls are 30 % higher than the ones of their mothers(Reference Hallberg18); in addition, energetic, proteic and mineral requirements increase significantly during adolescence due to rapid somatic growth and the beginning of menses. On the other hand, several factors like psychological changes and changes in eating habits also due to the influence of media and peer pressure contribute to make young girls vulnerable to diet-related anaemia(Reference Mariath, Henn and Matos19).
Iron deficiency anaemia was among the ten causes with larger prevalence on a global scale in 2016, with 1·24 (1·21–1·28) billion prevalent cases, and among the seven main causes of YLD in the same year, contributing to 34·7 million (23·0–49·6 million (4·3 %, 3·5–5·2)) YLD(17). In thirty-four out of 195 countries/territories, iron deficiency anaemia was the leading cause of age-standardised YLD rates for women in 2016. However, considering only low- and middle-income countries, iron deficiency anaemia was by far the leading cause of YLD in 2016, primarily in India, Bhutan, Sudan, Yemen and Mali(17). In India and Bhutan, YLD due to iron deficiency anaemia was much higher than expected in 2016(17).
With more than 70 % of its women and children being anemic, India has the highest prevalence in the world(Reference Gupta, Pingali and Pinstrub-Andersen20), and up to 90 % of anaemia cases are estimated to be the result of iron deficiency(Reference Thankachan, Muthayya and Walczyk21), traditionally due to a diet based on a high consumption of cereals (which inhibit absorption of iron) and inadequate consumption of meat and vitamin C-rich foods (which enhance absorption of iron)(Reference Underwood22). Further factors contributing to anaemia in India are illiteracy, poor nutrition education, cultural taboos and social norms as women ‘eating last’(Reference Gupta, Pingali and Pinstrub-Andersen20).
Despite Indian governments starting since the 1970s policies targeting nutrition education like the National Rural Health Mission and the National Nutritional Anemia Prophylaxis Programme, anaemia continues to remain a public health concern in the country. The recently released ‘Adolescents, Diets and Nutrition: Growing Well in a Changing World’ UNICEF report revealed that the governmental nutritional schemes are not reaching the adolescents, namely almost 25·0 % of girls do not receive any of the four school-based services (mid-day meal, biannual health check-ups, biannual deworming and weekly iron folic acid supplementation). Also, the report underlines how adolescent girls suffer from multiple nutritional deprivations when compared with young boys and investing on adolescent girls is crucial to break India’s intergenerational cycle of malnutrition(23).
Overall, in low- and middle-income countries, 12 % low birth weight, 19 % preterm births and 18 % perinatal mortality are estimated to be linked to maternal anaemia(Reference Rahman, Abe and Rahman24). Despite severely impacting the course and outcome of their pregnancies, women of low-income countries as India affected by iron deficiency anaemia may be unaware of their nutritional status during gestations. Universal health care coverage, with implementation of accessible and affordable primary health care, including reproductive health services, would ensure women to understand their nutritional status and adopt earlier measures to minimise the health risks associated with anaemia during their pregnancies(Reference Rahman, Abe and Rahman24).
The present study has several strengths. DHS questionnaires are standardised and pre-tested to ensure comparability over time and across populations; national coverage and response rates typically exceeding 90 %, together with standard collection procedures, guarantee reliability and representativeness of health status in a broad range of low- and middle-income countries(Reference Pullum25).
The use of the outcome anaemia represents another strength as it is an objective measure, minimising the risk for bias.
The current study also has several limitations. No information was available regarding medical conditions causing iron deficiency anaemia such as haematological disorders, malaria and other infections. Similarly, no information was available for other conditions leading to iron deficiency, such as excessive menstrual blood loss and intensive physical activity. Furthermore, we were not able to control for dietary habits either.
In our analysis, we did not distinguish between girl users of contraception and non-users, especially in regard to oral contraception, which has been found to be protective against anaemia in the long run(Reference Bellizzi and Ali26).
Conclusions
Despite an overall improvement in the prevalence of both BMI < 18·5 and anaemia among nullipara adolescents in India, the risk of anaemia in this category was still significantly higher when compared with their adult counterparts. While the change in the prevalence of BMI < 18·5 from 2005 to 2015 was influenced by all factors examined (wealth, years of schooling and residence), only wealth and years of schooling had a significant impact on the improvement of anaemia over time.
Since the inequalities evidenced during the first round of DHS remained unchanged in 2015, and since a lower socio-demographic index was consistently associated with anaemia and BMI < 18·5 in both surveys, more investments in universal health care are needed in India, with implementation of accessible primary care services enabling women to monitor their nutritional status and adopt prompt measures to minimise the health risks associated with eventual anaemia during their pregnancies.
Acknowledgements
Acknowledgements: Not applicable. Financial support: Not applicable. Conflict of interest: None. Authorship: S.B., C.F. and L.C. conceived the project and conducted the research; G.P., C.M.P.N., P.S. and M.F. collected material for research including literature review and retrieval of datasets; S.B. and L.C. analysed data; all authors interpreted data; S.B., G.P. and C.F. wrote the first draft; S.B. and L.C. reviewed and finalised the current version of the manuscript; S.B. had primary responsibility for final content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics of human subject participation: The current study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki and all procedures involving research study participants were approved by the India national ethical committee as well as by the Institutional Review Board of International Consulting Firm (ICF) of Calverton, Maryland, USA. Written consent was witnessed and formally recorded.








