Introduction
Green kyllinga (Kyllinga brevifolia Rottb.) is a perennial weed in turfgrass throughout the warm-humid region and U.S. transition zone that spreads through rhizomatous growth under turf maintenance (Bryson et al. Reference Bryson, Carter, McCarty and Yelverton1997). Populations also emerge through seed germination that peaks between 20 and 24 C (Molin et al. Reference Molin, Khan, Barinbaum and Kopec1997). Kyllinga brevifolia is difficult to physically remove from turfgrasses, and hand pulling or digging is often ineffective. Kyllinga brevifolia regenerates new plants through rhizomatous growth, enabling populations to escape preemergence herbicides and rapidly infest turfgrasses in summer (Lowe et al. Reference Lowe, Whitwell, McCarty and Bridges2000).
Acetolactate synthase (ALS) inhibitors are the most widely utilized herbicides for postemergence control of sedges (Cyperus spp.) in established stands of warm- and cool-season turfgrasses (Lycan and Hart Reference Lycan and Hart2004). Sulfonylureas are systemic herbicides that are readily translocated in susceptible plants (Eizenberg et al. Reference Eizenberg, Goldwasser, Achdary and Hershenhorn2003; Schloss Reference Schloss and Stetter1994). These herbicides, such as sulfosulfuron and trifloxysulfuron, control multiple sedge and Kyllinga species, including purple nutsedge (Cyperus rotundus L.), false-green kyllinga (Kyllinga gracillima Miq.), and K. brevifolia (Gannon et al. Reference Gannon, Yelverton and Tredway2012). Turf managers use several ALS inhibitors for K. brevifolia control due to their efficacy and selectivity in warm-season turfgrasses. However, these herbicides have been overused, and resistance is a concern.
Resistance to ALS-inhibiting herbicides has increased exponentially in turfgrass over recent years (Brosnan et al. Reference Brosnan, Vargas, Breeden, Grier, Aponte, Tresch and Laforest2015; McCullough et al. Reference McCullough, Yu, McElroy, Chen, Zhang, Grey and Czarnota2016). ALS-inhibitor resistance has been reported in several sedge species, including, smallflower umbrella sedge (Cyperus difformis L.), yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus L.), rice flatsedge (Cyperus iria L.), and annual sedge (Cyperus compressus L.) (Busi et al. Reference Busi, Vidotto, Fischer, Osuna, De Prado and Ferrero2006; Kuk et al. Reference Kuk, Kim, Kwon, Lee, Burgos, Jung and Guh2003; McCullough et al. Reference McCullough, Yu, McElroy, Chen, Zhang, Grey and Czarnota2016; Merotto et al. Reference Merotto, Jasieniuk and Fischer2010; Riar et al. Reference Riar, Tehranchian, Norsworthy, Nandula, McElroy, Srivastava, Chen, Bond and Scott2017; Tehranchian et al. Reference Tehranchian, Norsworthy, Nandula, McElroy, Chen and Scott2014; Yu et al. Reference Yu, McCullough, McElroy, Jespersen and Shilling2020). Cyperus difformis, C. iria, and C. compressus are annuals that reproduce solely from seed. The confirmation of ALS resistance in C. esculentus is concerning due to perennial growth and ability for resistant (R) biotypes to spread asexually. Resistance to ALS inhibitors is often attributed to target-site alteration or enhanced herbicide degradation (Riar et al. Reference Riar, Tehranchian, Norsworthy, Nandula, McElroy, Srivastava, Chen, Bond and Scott2017; Tranel and Wright Reference Tranel and Wright2002). Previous reports of ALS-resistant sedges have been associated with target-site mutations (McCullough et al. Reference McCullough, Yu, McElroy, Chen, Zhang, Grey and Czarnota2016; Tehranchian et al. Reference Tehranchian, Norsworthy, Nandula, McElroy, Chen and Scott2014; Yu et al. Reference Yu, McCullough, McElroy, Jespersen and Shilling2020). Cross-resistance to other ALS inhibitors may further limit the selective herbicides available to practitioners for controlling these weeds (Kuk et al. Reference Kuk, Kim, Kwon, Lee, Burgos, Jung and Guh2003; Merotto et al. Reference Merotto, Jasieniuk, Osuna, Vidotto, Ferrero and Fischer2009).
A K. brevifolia biotype with suspected resistance to ALS inhibitors was identified on a golf course in Florida. The turf managers had noted reductions in efficacy for K. brevifolia control over time after repeated use of ALS inhibitors. There have been no reports of herbicide resistance in K. brevifolia, which could raise concerns for integrated weed management in turf and other cropping systems. The objectives of this research were to evaluate potential resistance to ALS inhibitors and sequencing of the ALS enzyme of the suspected R biotype.
Materials and Methods
Plant Material
A suspected R K. brevifolia was collected from a golf course in Florida in March 2020. The name and location of the golf course will not be disclosed to protect the privacy of the facility. The turf managers had been using sulfonylurea herbicides for over a decade to control K. brevifolia and had noticed reductions in efficacy over time. A known susceptible (S) population was also collected in April 2020. Plants were potted and placed in a greenhouse set for 30/19 C (high/low). Individual tillers were subsequently planted into potting tubes (3.8-cm diameter, 20-cm depth) filled with sand:peat moss (80:20 v/v). Pots were then irrigated daily to prevent moisture deficiencies.
Herbicide Response
The response of the two biotypes was evaluated from a rate titration of sulfosulfuron (Certainty®, Nufarm, Alsip, IL). Sulfosulfuron was applied at 10 rates, ranging 6.6 to 3,360 g ai ha−1, in a spray chamber calibrated to deliver 374 L ha−1. Nontreated checks of the two biotypes were also included. A nonionic surfactant (Activator 90, Loveland Products, Greenville, MS) was added to the spray solution at 0.25% v/v. Plants were returned to the greenhouse approximately 3 h after treatment (HAT) and did not receive irrigation until 24 HAT. Injury was rated visually at 4 wk after treatment (WAT). Fresh shoot biomass was harvested at 4 WAT and weighed immediately (Table 1).
Table 1. Shoot biomass reductions and injury of two Kyllinga brevifolia biotypes at 4 wk after treatment with sulfosulfuron in two greenhouse experiments. a

a Data were regressed with f = y 0 + β0*[1 − exp(−β1*x)], where f is shoot biomass reductions, β0 is the asymptote, β1 is the slope estimate, and x is the sulfosulfuron rate. I50, rate required to cause 50% injury.
In a separate experiment, the biotypes were treated with trifloxysulfuron, pyrimisulfan, sulfentrazone, bentazon, imazaquin, thiencarbazone + foramsulfuron + halosulfuron, and florasulam + halauxifen. A nontreated check was included. Herbicide rates are presented in Table 2. All herbicides were applied with the aforementioned surfactant, except sulfentrazone, for which it is not required. Injury was visually evaluated on a percent scale at 4 WAT. Fresh shoot biomass was harvested at 4 WAT and weighed.
Table 2. Shoot biomass reductions of two Kyllinga brevifolia biotypes at 4 wk after treatment from herbicides in three greenhouse experiments, Griffin, GA. a
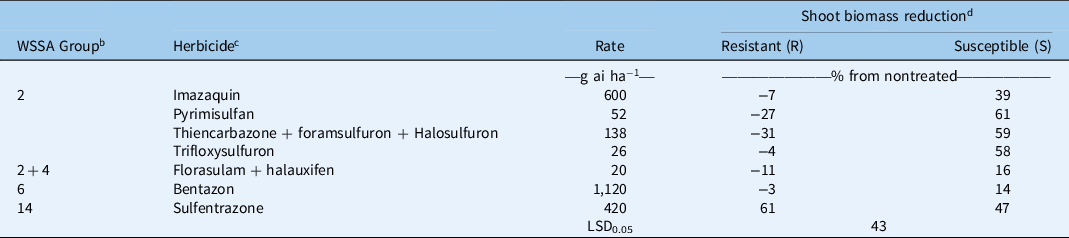
a Results were pooled over experimental runs.
b WSSA group numbers represent (2) ALS inhibitors, (4) synthetic auxins, (6) photosystem II inhibitors, (14) protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors.
c Herbicides used: trifloxysulfuron-sodium (Monument® 75WG, Syngenta, Greensboro, NC 27214), sulfentrazone + quinclorac (Image®, BASF, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709), sulfentrazone (Dismiss®, FMC, Philadelphia, PA 19104), bentazon (Basagran®, Arysta Lifescience, Cary, NC 27513), pyrimisulfan (NB38727, PBI/Gordon, Shawnee, KS 66226), thiencarbazone + foramsulfuron + halosulfuron (Tribute® Total, Bayer Environmental Science, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709), florasulam + halauxifen-methyl (Relzar™ 40%, Corteva Agriscience, Wilmington, DE 19805). All herbicides except sulfentrazone were applied with a nonionic surfactant at 0.25% v/v. The surfactant used was Activator 90 (Loveland Products, Greenville, MS 38703). The application rates chosen were the highest labeled use rates for postemergence weed control in turfgrass.
d Shoot biomass of the nontreated averaged 0.559 g (±0.055) and 0.483 g (±0.043) for the R and S biotypes, respectively. Negative numbers are increases in shoot mass from the nontreated plants.
Kyllinga Mapping Methods
Detection of possible single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were evaluated using Illumina next-generation sequencing, assembly of ALS transcripts, and mapping of reads to known ALS nucleotide AB719979.1. mRNA from R and S biotypes was extracted using the RNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany, http://www.qiagen.com). The quantity and quality of mRNA was checked using Nanodrop (Nanodrop One, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, http://thermofisher.com). Both R and S K. brevifolia biotypes were sequenced using the Illumina HiSeq Platform to generate 150-bp paired-end DNA sequencing reads. Sequencing was conducted by Novogene (http://en.novogene.com). Reads were first quality checked using FastQC (https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc), and adaptors were removed using Trimmomatic, http://www.usadellab.org/cms/?page=trimmomatic). Transcriptomes of the biotype were assembled using Trinity v. 2.8 (https://github.com/trinityrnaseq/trinityrnaseq/wiki). Mapping of putative R (KYR2) and S (KYS2) K. brevifolia fastq sequences against a known K. brevifolia ALS nucleotide sequence from NBCI (AB719979.1) was conducted to identify SNPs associated with ALS resistance. The consensus nucleotide transcripts from KYR2 and KYS2 read mappings were also aligned against the AB719979.1 sequence to compare any potential SNPs. All mapping and alignments were performed using Qiagen CLC Genomics Workbench 21.0 (https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com).
Experimental Design and Data Analysis
The designs in the greenhouse experiments were randomized complete blocks with five replications. A block design was used to reduce the potential variability of greenhouse location on plant responses to herbicides. Three separate runs were conducted for greenhouse experiments.
Data were subjected to ANOVA in SAS v. 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) to test for treatment by experimental run interaction. For the dose–response experiments, data were regressed in SigmaPlot v. 11.0 (Systat, San Jose, CA) against the following equation:
where f is injury/biomass, β0 is the asymptote, β1 is the slope estimate, and x is the sulfosulfuron rate. Shoot mass reductions were calculated as a percent reduction of the treated against the corresponding nontreated plant per replication.
For the evaluation of various herbicides, shoot biomass data were converted to percent reductions of the nontreated by replication. Means were separated with Fisher’s LSD test at α = 0.05. Treatment by experimental run interactions were not detected, and results were therefore combined for presentation.
Results and Discussion
Herbicide Response Experiments
Injury was expressed as tissue chlorosis and stunted growth of the S biotype. The sulfosulfuron rate required to cause 50% injury (I50) was >3,360 g ha−1 and 189 g ha−1 for the R and S biotypes, respectively (Figure 1; Table 1). The rate required to cause 50% shoot mass reductions (SR50) in the R and S biotypes was 792 and 10 g ha−1, respectively (Figure 2). Results support the supposition that the K. brevifolia biotype was resistant to sulfosulfuron.

Figure 1. Injury of two Kyllinga brevifolia biotypes at 4 wk after treatment. Results were pooled over experimental runs. Vertical bars represent standard errors of the mean. Data were regressed with f = y 0 + β0*[1 − exp(−β1*x)], where f is injury, β0 is the asymptote, β1 is the slope estimate, and x is the sulfosulfuron rate.

Figure 2. Shoot biomass reductions of two Kyllinga brevifolia biotypes at 4 wk after treatment. Results were pooled over experimental runs. Vertical bars represent standard errors of the mean. Data were regressed with f = y 0 + β0*[1 − exp(−β1*x)], where f is shoot biomass reductions, β0 is the asymptote, β1 is the slope estimate, and x is the sulfosulfuron rate.
In the other experiments, shoot biomass of the S biotype was reduced 39% to 61% by the ALS inhibitors evaluated at 4 WAT (Table 2). However, the R biotype did not have reductions in biomass and was significantly different from the S biotype at all treatment levels. Both biotypes responded similarly to other sites of action tested, including bentazon, florasulam + halauxifen, and sulfentrazone. Bentazon and florasulam + halauxifen did not cause a meaningful reduction in biomass for either biotype at the rates tested, but sulfentrazone reduced biomass an average of 54%. Biomass reductions of the R biotype from sulfentrazone were greater than for all ALS inhibitors evaluated.
Within the Cyperaceae family, ALS resistance has been reported in annual sedges (McCullough et al. Reference McCullough, Yu, McElroy, Chen, Zhang, Grey and Czarnota2016), C. difformis (Tehranchian et al. Reference Tehranchian, Riar, Norsworthy, Nandula, McElroy, Chen and Scott2017), C. iria (Riar et al. Reference Riar, Tehranchian, Norsworthy, Nandula, McElroy, Srivastava, Chen, Bond and Scott2017), and C. esculentus (Scarabel et al. Reference Scarabel, Farinati and Sattin2020; Tehranchian et al. Reference Tehranchian, Norsworthy, Nandula, McElroy, Chen and Scott2014). However, the only species with confirmed resistance in established turfgrass stands is C. compressus (McCullough et al. Reference McCullough, Yu, McElroy, Chen, Zhang, Grey and Czarnota2016; Yu et al. Reference Yu, McCullough, McElroy, Jespersen and Shilling2020). Although bentazon and florasulam + halauxifen did not provide meaningful reductions in shoot biomass, sulfentrazone may provide an alternative site of action to ALS inhibitors in selectively controlling K. brevifolia in turfgrass.
Kyllinga Mapping Results
Illumina sequencing allows for the evaluation of all possible SNPs in the ALS gene that are known to confer target-site resistance (TSR). Based on read mapping and alignment of assembled ALS transcripts, an amino acid change from aspartic acid (Asp) to glutamic acid (Glu) at position 376 in the R biotype was observed (GenBank accession numbers MZ558475 and MZ558476 for R and S biotypes, respectively). Both reference AB719979 and S assembled consensus ALS contained only Asp (Figure 3). Asp-376-Glu has been identified previously as a TSR mechanism in ALS resistance.

Figure 3. Gene sequencing for the ALS enzyme of the two Kyllinga brevifolia biotypes.
Implications from These Findings
Repeated use of ALS inhibitors encourages the establishment of R populations through selection pressure (Tranel and Wright Reference Tranel and Wright2002). Due to this risk of resistance, a wider variety of techniques must be employed along with herbicide usage. Turf managers should incorporate preemergence herbicides into their integrated weed management programs to help limit the spread of K. brevifolia from seed (Belcher et al. Reference Belcher, Walker, Van Santen and Wehtje2002). However, use of these herbicides may be limited by cost, turfgrass injury potential, and limitations for controlling perennial infestations of K. brevifolia.
Detecting herbicide resistance in a perennial species has important implications for management programs. Kyllinga brevifolia is able to overwinter in many environments, and postemergence herbicides are often the only means for selective control. Sulfonylureas have been the most selective herbicides for controlling K. brevifolia patches in turfgrass, and resistance to this site of action may limit the options for long-term management. Other control programs may include spot treatment with glyphosate or physically hand pulling K. brevifolia plants with suspected resistance. These options may not be practical or applicable for large areas of turf, such as sod farms and golf courses. Cultural practices, along with herbicide rotation, will be another critical component of managing resistant Kyllinga populations. Factors such as mowing, irrigation, and fertilization could warrant modifications to help reduce infestations and enhance competitive growth of desirable turf with these infestations (Abu-Dieyeh and Watson Reference Abu-Dieyeh and Watson2006; Busey Reference Busey2003).
The main hindrance to controlling the spread of ALS inhibitor–resistant K. brevifolia is the limited number of alternative sites of action available for selective control. This is especially concerning in cool-season turfgrasses, such as bentgrass (Agrostis spp.), that require low use rates of many herbicides to minimize injury potential compared with other turfgrass species. Sulfentrazone appears to have the greatest potential to control ALS-resistant K. brevifolia in turfgrass. Although bentazon offers an alternative site of action to ALS inhibitors, applications did not appear to provide sufficient efficacy for controlling either K. brevifolia biotype at the rate tested. These results are similar to previous experiments on the efficacy of bentazon for control of K. brevifolia in bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.] (McElroy et al. Reference McElroy, Yelverton and Warren2005). As resistant populations of K. brevifolia increase through repeated use of ALS inhibitors, further research is needed on application timings, rates, and regimens of herbicides with alternative sites of action, such as sulfentrazone, for selectively controlling infestations in turfgrass and other cropping systems.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Vijaya Mantripragada and Catherine McCullough for technical assistance with this research. This research received no specific grant from any funding agency or the commercial or not-for-profit sectors. No conflicts of interest have been declared.








