Introduction
Population ageing has affected the demographic landscape of European societies to the point where the traditional conception of the lifecourse, associating old age with a phase of decline and rest, is no longer realistic nor sustainable (Boudiny and Mortelmans, Reference Boudiny and Mortelmans2011). This shift has been accompanied and sustained by the emergence of the concept of ‘active ageing’. The World Health Organization (2002: 12) defines active ageing as the ‘process of optimizing opportunities for health, participation and security in order to enhance quality of life as people age’, specifying that the term ‘active’ ‘refers to continuing participation in social, economic, cultural, spiritual and civic affairs, not just the ability to be physically active or to participate in the labour force’. The concept of active ageing has rapidly and broadly spread in the scientific and political debate; additionally, the concept has guided the development of policy and interventions across Europe (Ney, Reference Ney2005; Walker, Reference Walker2006). Nevertheless, its definition is still debated, both in the scientific and political arena. In particular, there is a lack of agreement on the kinds of activities that should be considered when discussing active participation in later life. On the one hand, part of the literature adopts an exclusively economic framework and restricts the notion of activity in later life to paid work (Boudiny, Reference Boudiny2013; Foster and Walker, Reference Foster and Walker2013). However, focusing only on labour market participation overlooks a multiplicity of activities that produce social value, which is not monetised but still significant (Boudiny and Mortelmans, Reference Boudiny and Mortelmans2011; Lee et al., Reference Lee, Morrow-Howell, Jonson-Reid and McCrary2012). On the other hand, an overly broad definition of activity may prove ineffective when adopted in empirical research (Kim, Reference Kim2020). A viable compromise involves considering all kinds of activities that produce a contribution to community life, regardless of whether such activities are paid or unpaid (Bass et al., Reference Bass, Caro and Chen1993). This definition includes volunteering, care-giving, paid work and any other engagement in active roles that benefits not only the actor but also society.
Despite its popularity, the prospect of active ageing has raised some controversial issues. First, an important question concerns whether individuals can engage in various forms of activity at the same time (Lindley et al., Reference Lindley, Baldauf, Galloway, Li, Principi, Jensen and Lamura2014; Morrow-Howell et al., Reference Morrow-Howell, Putnam, Soo, Greenfield, Inoue and Chen2014). As Boudiny (Reference Boudiny2013: 1094) maintains, ‘active ageing cannot be reduced to the sum of its indicators as various forms of activity are not necessarily complementary (e.g., possible tension between work and care responsibilities)’; thus, it is important to examine the combination of and interrelations between different activity domains to grasp fully the meaning of activity in later life (van der Horst et al., Reference van der Horst, Vickerstaff, Lain, Clark and Geiger2017).
Another relevant question concerns the conditions that may favour or hinder older people's activity. The literature (e.g. McNamara and Gonzales, Reference McNamara and Gonzales2011; Kim, Reference Kim2020) shows that, above all, later-life activity patterns are influenced by human, cultural and social capital (SC); these are individual capitals, namely individual assets that provide access to other forms of resources (Bourdieu, Reference Bourdieu and Richardson1986). For example, higher educational levels predict higher levels of activity, especially paid work and volunteering (Maestas, Reference Maestas2010; Forbes and Zampelli, Reference Forbes and Zampelli2014). Exploring the mechanisms through which various forms of capital affect active ageing contributes to understanding why some older people engage in some forms of activity while others do not; thus, it is particularly relevant to broaden the opportunities available and remove existing barriers (Raymond et al., Reference Raymond, Grenier and Hanley2014). This, in turn, can prevent the widening of the gap between older adults who can age actively and those who cannot. This gap, as stressed by critical gerontologists and sociologists (Moody, Reference Moody, Cole, Achenbaum, Jakobi and Kastenbaum1993; Estes and Mahakian, Reference Estes, Mahakian, Morrow-Howell, Hinterlong and Sherraden2001), might favour the development of attitudes and practices stereotyping, in a negative way, the inactive/unproductive (dependent) older adult.
Our work follows this invitation and aims to explore whether and to what extent SC affects activity in old age. Through logistic regressions, the study analyses older people's participation in various domains of activity, namely volunteering and charity work, participation in political or community-related organisations, informal care-giving and paid work. The data analysed stem from the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE).
The research advances the literature in this area by studying SC dynamically. To our knowledge, this is the first European study to investigate the association between changes in individual SC and participation in various domains of activity over time. Specifically, the study explores how SC and changes in SC are associated with engagement in, the initiation of and continued participation in paid work, volunteering, caring and – adhering to scholars’ calls to consider a wide range of activities (Serrat et al., Reference Serrat, Villar, Giuliani and Zacarés2017; Kim, Reference Kim2020) – also political participation.
The research highlights that SC is associated with engagement in and the initiation of activities in later life. Furthermore, changes in SC, in particular in social network (SN) size, are associated with the initiation and maintenance of these activities.
Social capital and active ageing
Different forms of individual capital (including SC) affect whether and to what extent older people engage in various forms of activity (Forbes and Zampelli, Reference Forbes and Zampelli2014; Gonzales and Nowell, Reference Gonzales and Nowell2017; Kim, Reference Kim2020). The concept of capital refers to individual resources with tangible value that can be employed to obtain access to other forms of resources (Bourdieu, Reference Bourdieu and Richardson1986).
The current paper explores active ageing in relation to one form of individual capital: SC. SC can be defined as the ‘collection of resources owned by the members of an individual's personal social network, which may become available to the individual as a result of the history of these relationships’ (van der Gaag, Reference van der Gaag2005: 20).
SC is a resource that actors can use to realise their interests, and similar to physical and human capital, it can facilitate productive activities (Coleman, Reference Coleman1990). This consideration also holds true for older people; indeed, both bonding SC (characterised by closed networks and particularised trust) and bridging SC (characterised by open networks across social cleavages and generalised trust) affect older adults’ activity in later life (Musick and Wilson, Reference Musick and Wilson2007; McNamara and Gonzales, Reference McNamara and Gonzales2011). For example, regardless of their age, individuals with greater bridging SC have more chances to be recruited as volunteers (Putnam, Reference Putnam2000; Wilson, Reference Wilson2000; Musick and Wilson, Reference Musick and Wilson2007).
Conversely, the effect of bonding SC, such as family relationships, on participation in volunteering may go in two opposite directions. On the one hand, older volunteers tend to recruit other family members into volunteering (Morrow-Howell et al., Reference Morrow-Howell, McCrary, Hong and Blinne2008; Tang and Morrow-Howell, Reference Tang and Morrow-Howell2008), and consistently, married older adults are more likely to volunteer than non-married adults (Bowen et al., Reference Bowen, Andersen and Urban2000; Butrica et al., Reference Butrica, Johnson and Zedlewski2009; McNamara and Gonzales, Reference McNamara and Gonzales2011). On the other hand, family responsibilities may limit the availability of resources for volunteering (Morrow-Howell et al., Reference Morrow-Howell, McCrary, Hong and Blinne2008).
Regarding care-giving, older adults with greater SC are more often engaged in caring for grandchildren, other family members and/or friends (Kim, Reference Kim2020). It is not only the characteristics of one's SN (e.g. having a relative or friend who is chronically ill) that affects the probability of being involved in care-giving but also the degree of support received from the network's members, as this stimulates reciprocity (Wilson, Reference Wilson2000; Kim, Reference Kim2020).
Concerning participation in paid work, the characteristics of older adults’ SN affect their chances of remaining in employment. In particular, the stronger the SN ties and the higher the ties’ employment prestige, the greater the potential for one's SC to favour employment in later life. Moreover, while younger workers evaluate their human capital as their main asset in their job searches, older workers consider their SC to be more important (Gayen et al., Reference Gayen, McQuaid and Raeside2010).
Despite, overall, the literature from this field offering interesting insights into the relation between SC and various forms of activity in later life, some important gaps remain. First, with few exceptions (e.g. Gayen et al., Reference Gayen, McQuaid and Raeside2010; Forbes and Zampelli, Reference Forbes and Zampelli2014; Kim, Reference Kim2020), the literature is rather lacking studies that explore the relation between SC and older people's engagement in multiple activities at the same time.
Second, most studies overlook changes in engagement over time. Both of these gaps may exist due to the fact that most of the existing studies are cross-sectional (Forbes and Zampelli, Reference Forbes and Zampelli2014; Dávila, Reference Dávila2018) and do not allow us to understand multiple pathways of engagement. Since older people engage in various active roles at the same time (Morrow-Howell et al., Reference Morrow-Howell, Putnam, Soo, Greenfield, Inoue and Chen2014) and their domains and degrees of engagement may vary over time, longitudinally observing multiple activities allows for the adoption of a more comprehensive view of active ageing and its predictors (van der Horst et al., Reference van der Horst, Vickerstaff, Lain, Clark and Geiger2017; Strauss, Reference Strauss2021). A recent work by Kim (Reference Kim2020) constitutes an exception in relation to these gaps, as it analyses multiple activities using longitudinal data. The author explores whether human, cultural and social capital predict older adults’ baseline participation and changes in engagement in various activities over time. The study uses two waves of panel data from the National Social Life, Health, and Aging Project, a representative, population-based sampling of older adults in the United States of America. The results offer interesting insights into the factors that promote or prevent older Americans’ continued engagement in paid work, volunteering and caring. In particular, the author shows that older adults with greater SC are generally more engaged in the different activities (even though the relation between SC and activity is not apparent over the five-year period considered). Moreover, Kim (Reference Kim2020) highlights that married people are more likely to participate in care-giving and that the size of their networks is positively associated with the initiation of care-giving. Concerning participation in volunteering, the author shows that older adults with greater bridging SC are more likely to be recruited for volunteering and to continue to volunteer over time.
Third, even if some studies (Ajrouch et al., Reference Ajrouch, Antonucci and Webster2016; Strauss, Reference Strauss2021) have noted that changes in the SN structure – an important component of SC (Sabatini, Reference Sabatini2009) – may influence active ageing, none have tested this intuition empirically, studying changes in SC over time rather than analysing it at a single point in time.
Following the work of Kim (Reference Kim2020), this study aims to contribute to fill the gaps mentioned by analysing the relation between older adults’ SC and engagement in various domains of activity at the same time and adopting a dynamic view of SC. To our knowledge, this is the first European study of this kind. In particular, this work explores how changes in individual SC are associated with the initiation of and continued participation in paid work, volunteering and care-giving and, adhering to Kim's (Reference Kim2020) call to consider a wider range of activities, it includes political participation as well, which to date has been largely overlooked (Serrat et al., Reference Serrat, Villar, Giuliani and Zacarés2017; Kim, Reference Kim2020).
Specifically, the study addresses the following research questions (RQ):
(1) Is SC associated with baseline participation in activities (giving care, doing voluntary or charity work, participating in political or community-related organisations and doing paid work) in later life?
(2) Is SC associated with the initiation of activities in later life?
(3) Are changes in SC associated with the initiation of activities in later life?
(4) Are changes in SC associated with maintenance of the level of activity in the various domains under study?
Data
We use data from SHARE Waves 4–6 (Börsch-Supan, Reference Börsch-Supan2019a, Reference Börsch-Supan2019b, Reference Börsch-Supan2019c). SHARE is a biennial longitudinal study collecting data on older people's health, socio-economic status and SN (Börsch-Supan et al., Reference Börsch-Supan, Brandt, Hunkler, Kneip, Korbmacher, Malter, Schaan, Stuck and Zuber2013). The study has collected data since 2004 via computer-assisted personal interviewing on 140,000 individuals aged 50+, covering 28 European countries and Israel. For most countries, SHARE uses a multi-stage stratified sampling design (Bergmann et al., Reference Bergmann, Kneip, De Luca and Scherpenzeel2019).
Table 1. Data description

Notes: Data are weighted with Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Wave 6 cross-sectional calibration weights. SD: standard deviation.
Source: Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe.
Our analysis is conducted on Waves 4–6, given that questions on SNs are asked in Waves 4 and 6, and questions about activities and social support are asked in every wave. Data from Waves 4–6 were collected biennially between 2011 and 2015. We consider Wave 6 as the baseline (i.e. t (0), starting point for comparison) while Wave 5 represents t (−1) and Wave 4 represents t (−2). Following Strauss (Reference Strauss2021) and van der Horst et al. (Reference van der Horst, Vickerstaff, Lain, Clark and Geiger2017), we include in our analysis respondents aged 55 or older at baseline. We restrict our sample to individuals living in countries that took part in all three considered waves: Austria, Germany, France, Switzerland, Belgium, Sweden, Denmark, Spain, Italy, Czech Republic, Slovenia and Estonia. The resulting analysis sample is composed of 28,361 individuals (Table 1). However, models predicting the initiation of activities are based on a restricted sample (i.e. only respondents inactive at t (−2) and t (−1)). Models predicting maintenance are based only on respondents who are active at t (−2).
Methods
To answer our research questions, we applied a set of logistic regression models.
Dependent variables
Dependent variables are a number of indicators of activity. For each indicator we consider (a) whether the respondent participates in the activity, (b) initiates the activity and (c) maintains the activity.
To measure participation in paid work, we create a binary variable with value 1 if the respondent works at least one hour in a typical week and 0 otherwise. To measure engagement in care-giving, we create a binary variable with value 1 in the case of care-giving in the last 12 months and 0 otherwise. Care-giving includes both help within the household and help outside the household to family, friends and/or neighbours. Types of care considered are personal care (e.g. dressing, eating and getting into or out of bed), practical household help (e.g. home repairs, gardening and shopping), help with paperwork (e.g. filling out forms and settling financial or legal matters) and looking after grandchildren. We define ‘non-care-givers’ as all respondents declaring that they do not provide support on any variable (i.e. care within the household, outside the household or to grandchildren) and having missing values in all other variables. To measure participation in volunteering and political participation, we create two binary variables with value 1 in the case of participation in these activities in the last year and 0 otherwise.
Initiation is measured as participation in an activity at t (0) for those inactive at t (−1) and t (−2) (in that specific activity). The resulting four variables (namely initiation of paid work, care-giving, volunteering and political participation) take value 1 if the respondent initiated the activity at t (0) (and was inactive at t (−1) and t (−2)) and 0 if he or she never engaged in the activity. All other cases are set to missing.
Maintenance is measured through frequency of activities. For measuring maintenance, we create a variable taking value 1 if the respondent maintained constant hours or increased the number of hours worked (in a typical week) between t (0) and t (−2) (i.e. remained in the same quartile of numbers of hours worked or moved to a higher quartile) and 0 otherwise (i.e. moved to a lower quartile of numbers of hours worked/ceased the activity).
To measure maintenance in care-giving, volunteering and political participation we create binary variables – taking value 1 if the respondent maintains or increases his or her frequency of activity (which takes values: about daily, about once a week, about once a month, less often, never) and 0 if he or she decreases the frequency or stops performing the activity. Hence, we are able to distinguish between older people maintaining the same degree of involvement in a specific activity or increasing it and those decreasing their degree of involvement or stopping the activity completely. It should be noted that while for care-giving outside the household and for grandchildren, data on the frequency are available, for care-giving inside the household, only data on whether the respondent provides care are available (i.e. no information about frequency is collected). Given the pervasiveness of care-giving inside the household, we assumed that this activity requires the care-giver's involvement every day.
Explanatory variables
The explanatory variables are SC and changes in SC. Drawing on Kim (Reference Kim2020), SC is operationalised by network size, social support received and presence of a partner with/without limitations in activities of daily living (ADL). We operationalise network size as the number of contacts in the respondents’ SNs (0–7). These data are collected at Waves 4 and 6 using a SN name generator, where respondents are asked to list up to six people with whom they have discussed important matters in the last year and one additional person who is ‘important for any reason’.
Social support received includes support received from outside the household (personal care, practical household help and help with paperwork) and from inside the household. Frequency of support received inside the household takes values: about daily, about once a week, about once a month, less often or never. No information is available on the frequency of care received within the household; thus, similar to care-giving, we assume that support received within the household is very pervasive and requires involvement every day. Additionally, we consider as non-receiving support respondents declaring not to receive support in one of the two social support variables (i.e. support from inside/outside the household) and having a missing value in the other.
The presence of a partner with/without limitations in ADL is operationalised through the following categories: no partner, partner inside the household without limitations, partner inside the household with one (or more) limitations, partner outside the household, partner inside the household and no ADL data available. This variable is created by merging respondents’ data with data from partners’ interviews when available, i.e. respondents’ partner is eligible for interview (co-habiting), participated in the survey and answered the item.
Changes in SN size are measured as the difference between SN sizes at t (−2) and t (0); the resulting variable ranges between −7 and + 7. Changes in social support received are measured with a variable taking values: 1 (indicating an increase in frequency of care received), 0 (no change) and −1 (a decrease). Changes in the presence of a co-habiting partner with/without ADL are measured with the following categories: no changes; loss of a co-habiting partner with ADL (i.e. having a partner with ADL at t (−2) and any other (valid) status at t (0)); ‘acquisition’ of a co-habiting partner with ADL, i.e. having a partner with ADL at t (0) and any other (valid) status at t (−2); and no information about the co-habiting partner's ADL at t (−2) and/or at t (0).
Control variables
Demographic, socio-economic and health variables are included as controls. Specifically, the demographic variables considered are age and gender. Age is included as a continuous variable. Gender is included as a binary variable taking values 1 if the respondent is female and 0 if the respondent is male.
As indicator of social status, we use education, measured by the International Standard Classification of Education (ISCED 1997). We recode it into three categories: primary education, secondary education, and post-secondary education.
Economic situation is captured through a subjective income measure based on a question asking with which level of difficulty the household is able to make ends meet: great difficulty, some difficulty, fairly easily, and easily.
Health is measured by self-perceived health (SPH) and EURO-D. SPH is a self-reported measure of personal health varying between 1 (excellent) and 5 (poor). EURO-D is a measure of depression derived from 12 survey items. The index varies from 0 (no symptoms of depression) to 12 (all symptoms/very depressed). Following the approach proposed by Dewey and Prince (Reference Dewey, Prince, Börsch-Supan and Jürges2005) and adopted by, for example, Croezen et al. (Reference Croezen, Avendano, Burdorf and Van Lenthe2015) and Bashkin et al. (Reference Bashkin, Horne and Bridevaux2018), we recode the index as a binary variable using a cut-off score of 4 or greater to represent the presence of depression.
Finally, we control for the respondents’ countries of residence.
Modelling strategy
To investigate the association between SC and engagement in activities (RQ1), we apply logistic regression models regressing engagement in activities on SC at t (0). Separate models are estimated for each activity.
To analyse whether SC predicts the initiation of activities (RQ2), we perform logistic regression models, regressing the initiation of (each) activity on SC at t (0). Given the low share of respondents initiating activities (3.1% for political participation and 2.2% for paid work), we adopt Penalized Maximum Likelihood estimation (PMLE), a method proposed by Firth (Reference Firth1993) for modelling rare events.
To analyse whether changes in SC (ΔSC) predict the initiation of activities (RQ3), we perform logistic regression models (with PMLE), regressing initiation in (each) activity on ΔSC. To investigate the effect of ΔSC on the maintenance of frequency of engagement (RQ4), we perform logistic regression models, one for each activity.
In each model, we control for demographic, socio-economic and health variables, and for participation in the other activities at baseline. In models adopted to answer to RQ3 and RQ4, we also control for scores of SC at t (−2). To perform the analyses, we used the software Stata, version 15. Descriptive statistics are weighted with SHARE Wave 6 cross-sectional calibration weights.
Results
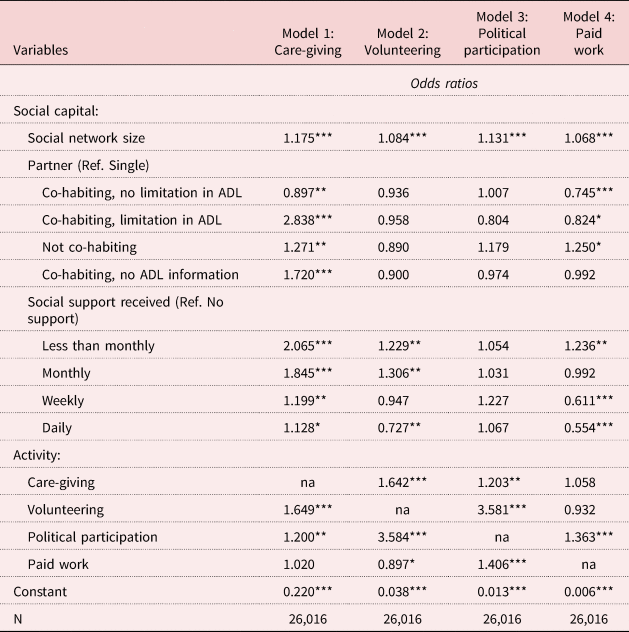
Table 2 shows the association between SC and participation in activities (RQ1). SN size is positively associated with care-giving (Model 1), volunteering (Model 2), political participation (Model 3) and paid work (Model 4).
Table 2. Logistic regression models predicting engagement in activity (RQ1)
Notes: All models include control variables: age (centred on mean), age-squared, gender, health, country, level of education and economic situation. Ref.: reference category. ADL: activities of daily living. na: not applicable.
Source: Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe.
Significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Regarding partner presence, compared to respondents who are single, those co-habiting with a partner with limitations in ADL are almost three times more likely to provide care, while those co-habiting with a partner without limitations are less likely to provide care. Thus, having a co-habiting partner does not seem to encourage care-giving through SC but instead through the presence of a dependent adult in the household. However, SC might be the driver of care-giving for respondents with a partner but not co-habiting; these respondents have a higher likelihood of giving care than respondents who are single (Model 1). With respect to paid work, older people with a co-habiting partner are less likely to work (regardless of the partner's health), whereas those with a partner outside the household are more likely to work than respondents who are single (Model 4). No effect is detected for volunteering (Model 2) or political participation (Model 3).
With respect to care-giving, in comparison to respondents not receiving support, older people who do receive support are more likely to give care; this finding seems to signal that a reciprocity effect is at play. However, the stronger the effect is, the less frequently care is received. This result is not surprising as respondents receiving care very frequently (e.g. daily) may be less able to provide care for others (Model 1). Additionally, older people receiving support rarely (e.g. less than once a month) are more likely to do voluntary and paid work (Models 2 and 4) than those not receiving any support; conversely, respondents receiving care with high frequency (i.e. daily) are less likely to volunteer and work than respondents not receiving support. These findings are consistent with the evidence obtained on care-giving: receiving frequent care might signal a level of fragility that prevents volunteering and working, while receiving care monthly or less than monthly could stimulate generativity (not through care-giving addressed to loved ones but through a service offered to the community). No association is found, at the standard statistical level, between support received and political participation (Model 3).
Last, regarding involvement in multiple activities, a complementarity effect (rather than a substitution effect) emerges for care-giving, volunteering and political participation: older people involved in one of these activities are more likely to also be involved in other activities. Conversely, paid work is positively associated only with political participation (odds ratio (OR) = 1.406), and it is negatively associated with voluntary/charity work (OR = 0.897). This evidence seems to signal a substitution effect between volunteering and working (which might be more pervasive and demanding than the other activities).
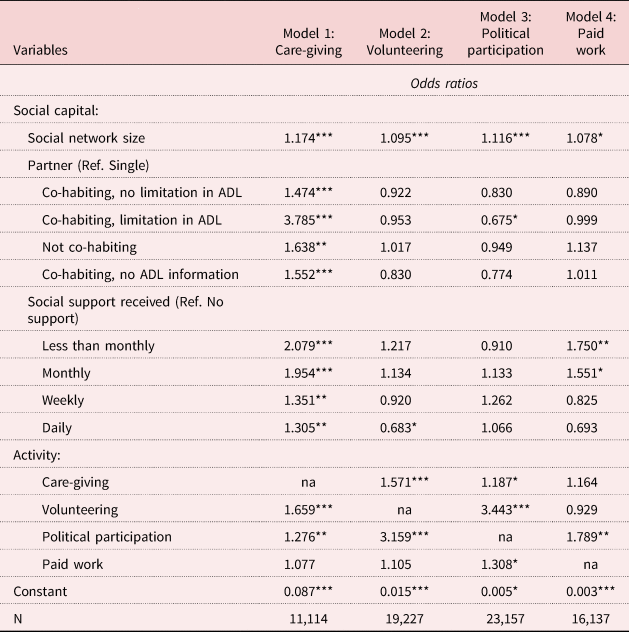
Table 3 shows the association between SC and the initiation of activities (RQ2). SN size is positively associated with the initiation of care-giving (Model 1), voluntary work (Model 2), political activities (Model 3) and paid work (Model 4). Compared to single respondents, those with a partner are more likely to start care-giving. In particular, those co-habiting with a partner with limitations are about four times more likely to start care-giving than respondents without a partner (Model 1). Conversely, older people co-habiting with a partner with limitations in ADL are less likely to initiate political activities than respondents who are single (Model 3). No association at the standard statistical level is found regarding partner presence/health condition and the initiation of voluntary and paid work (Models 2 and 4).
Table 3. Logistic regression models predicting initiation of activity (RQ2)
Notes: All models include control variables: age (centred on mean), age-squared, gender, health, country, level of education and economic situation. Ref.: reference category. ADL: activities of daily living. na: not applicable.
Source: Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe.
Significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
In comparison to respondents not receiving support, those who do receive support are more likely to initiate caring; the effect is stronger the lower the level of care received. We also detect a positive effect for starting paid work, but only for respondents receiving support rarely (versus no support received). Conversely, compared to respondents not receiving support, those receiving support daily/inside the household are less likely to start voluntary work, while no effect is found for those receiving support less frequently.
Again, a complementarity between care-giving, volunteering and political participation is found: individuals involved in one of these activities are more likely to start another activity. Complementarity is also present between political activities and paid work.
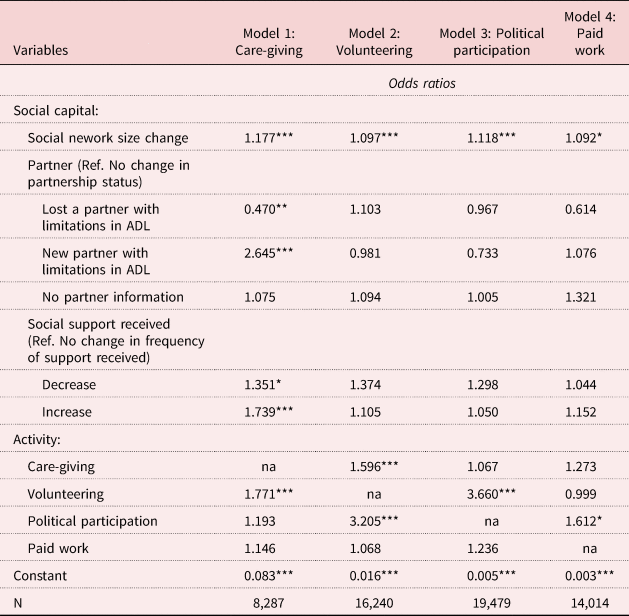
Table 4 shows effects of ΔSC on the initiation of a new activity (RQ3). An increase in SN size is positively associated with the start of a care-giving activity (Model 1), voluntary work (Model 2), political activities (Model 3) and paid work (Model 4).
Table 4. Logistic regression models predicting initiation of activity (RQ3)
Notes: All models include control variables: age (centred on mean), age-squared, gender, health, country, level of education, economic situation and social capital at Wave 4. Ref.: reference category. ADL: activities of daily living. na: not applicable.
Source: Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe.
Significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Compared to older people showing no changes in partnership status, those losing a partner with limitations are less likely to start a care-giving activity, while those with a ‘new’ partner with limitations in ADL (e.g. having a co-habiting partner whose health worsens) are about two and half times more likely to provide care. Finally, changes (increase/decrease) in support received increase the odds of initiating care for others.
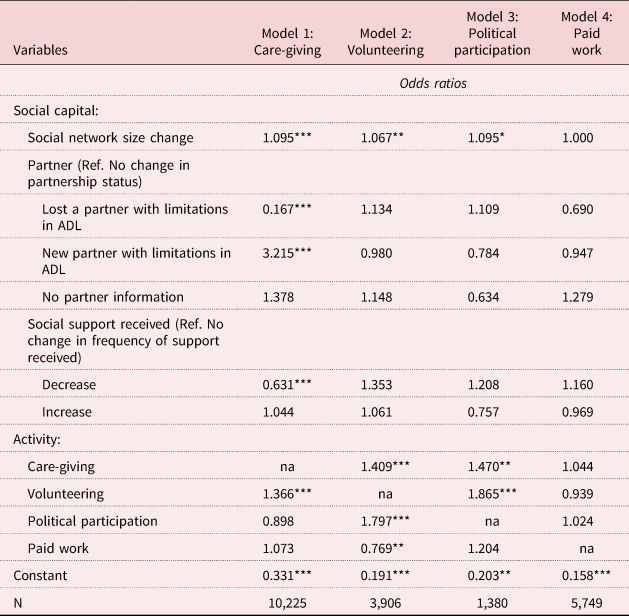
Table 5 shows the effect of ΔSC on maintenance of activity (RQ4). An increase in SN size is positively associated with maintaining/increasing the frequency of care-giving (Model 1), volunteering (Model 2) and political participation (Model 3). Older people losing a partner with limitations are less likely to maintain the same level of engagement in care-giving than respondents experiencing no changes in partner health. Respondents in the opposite situation (i.e. having a co-habiting partner with a limitation at t (0) and not having a partner with limitation at t (−2)) are about three times more likely to maintain/increase levels of engagement in care-giving. Furthermore, a decrease in support received reduces the odds of starting to care for others compared to not experiencing any changes in the amount of support received.
Table 5. Logistic regression models predicting maintenance of activity (RQ4)
Notes: All models include control variables: age (centred on mean), age-squared, gender, health, country, level of education, economic situation and social capital at Wave 4. Ref.: reference category. ADL: activities of daily living. na: not applicable.
Source: Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe.
Significance levels: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
Regarding involvement in multiple activities, we find mixed results. Regarding the association between participation in each activity and the level of maintenance, we observe complementarity between care-giving and volunteering; additionally, we observe complementarity between volunteering and political participation. Moreover, maintenance of political participation is also positively associated with care-giving, while we find no effect of political participation on maintenance of care-giving. A substitution effect emerges between paid work and volunteering. Last, maintenance of a certain degree of engagement in paid work seems not to be related to any of the variables under study.
Discussion and conclusion
This paper shows that many older people in Europe are engaged in a variety of activities that contribute to community life beyond paid work: 42 per cent of respondents give care to other people, 26 per cent do paid work, 17 per cent do voluntary work and 6 per cent participate in political activities.
Independent of participation level, we found evidence for a relationship between three key components of SC – the size of one's SN, having a partner and receiving support – and participation in, as well as the initiation and maintenance of, some of the activities under study.
In general, the analysis shows that having a larger SN is positively associated with participation in care-giving, volunteering, political organisations and paid work in later life as well as with starting to be active in these domains for those previously inactive. It is, however, beyond the scope of this analysis to assess whether this association is causal; reverse causality may also be at play given that participation in activities can increase older people's SN size.
While SN size is positively associated with participation in all domains, the relation between having a partner and being active in the various domains is not always significant at standard statistical levels. In particular, older people co-habiting with a partner have more chances to initiate care-giving (especially if the partner has health problems, as one can easily expect) and fewer chances to engage in paid work (if the partner is inside the household). Contrary to previous research (Butrica et al., Reference Butrica, Johnson and Zedlewski2009; McNamara and Gonzales, Reference McNamara and Gonzales2011), the association between having a partner (regardless of his or her health) and volunteering is not significant. The same is true for participation in political organisations, except for older people with a partner with health limitations who are less likely to start being engaged in this form of active citizenship. These results seem to confirm that, also in later life, participation in care-giving and paid work needs to be explored as part of the household needs and labour allocation. Last, receiving the support needed seems to favour activity in later life and the initiation of new activities, and this might relate, as other studies show (Kim, Reference Kim2020), to the fact that benefiting from help stimulates reciprocity. Of course, when older people receive support very often, the relation between support received and activity is negative, as needing help very often might indicate a disadvantaged condition (concerning health or material resources, among others) that prevents participation (as also speculated by Reinhardt et al., Reference Reinhardt, Boerner and Horowitz2006).
Analysing whether changes in SC are associated with active ageing, results clearly show that an increase in the number of social connections predicts a higher probability of engaging in all forms of activity under examination as well as maintaining or increasing the degree of engagement (in terms of frequency of participation), in most activities.
Another relevant aspect emerging from the study is the complementarity between some of the areas of activation. In fact, controlling for co-habitation with a partner with health limitations, we found evidence for a complementary relation between care-giving, volunteering and participation in political organisations; conversely, the relation between paid work and the other activities is less consistent. This might suggest that having a job does not always allow for the combination of paid and unpaid work. In general, these results seem consistent with the literature (see Caro et al., Reference Caro, Bruner-Canhoto, Burr and Mutchler2005) suggesting that, given certain prerequisites, a motivation to be active in later life – beyond engagement in paid work – seems to exist regardless of the specific domain of activity.
We feel that both important policy implications – as well as suggestions on further areas of research – emerge from this work. First, the study shows that older people living with a partner who has health limitations are less frequently involved in paid work and less likely to initiate participation in politics than single older individuals. Thus, our results seem to suggest the need to make emotional, practical and financial support available and easily accessible for older people co-habiting with a partner who has health limitations. In general, we agree with the claim – also highlighted in other recent contributions (see van der Horst et al., Reference van der Horst, Vickerstaff, Lain, Clark and Geiger2017) – that the combination of factors influencing older people's involvement in various domains of activities is very complex and needs to be investigated further, also through qualitative research.
Second, another important policy implication emerges from the finding that paid work does not seem to occur simultaneously with activation in other domains of activity. We do not assess whether this lack of co-activation is the result of individual preferences or whether it is associated with a lack of resources (e.g. time constraints, lack of opportunities). Nevertheless, since it has been demonstrated that participating actively in the community, e.g. through volunteering, may facilitate a smoother transition into retirement (Tang, Reference Tang2016), the promotion of a combination of paid and unpaid work in old age needs to be brought to the attention of relevant stakeholders, such as employers and human resource managers. In fact, although a certain number of good practices in the field of age management can be identified across Europe (Garavaglia et al., Reference Garavaglia, Marcaletti and Iñiguez-Berrozpe2020) and include managerial policies and practices aimed at promoting older workers’ successful transition into retirement, there is still much room for the engagement of managers and employers in this field (Oude Mulders et al., Reference Oude Mulders, Henkens, van Dalen, Czaja, Sharit and James2020).
Overall, the study results stress the importance of approaching the issue of active ageing – in particular, of the active participation of older people in various domains of social life – through a critical lens. In fact, our results show that people have differentiated opportunities to age actively. These opportunities are affected by individual conditions, and SC plays a relevant role in this sense. Thus, policy makers and all relevant stakeholders who engage in active ageing promotion need to dedicate specific resources to create the conditions necessary for activity in later life, for all. In particular, we stress the importance of providing older people, especially those living alone or in isolation, with opportunities to connect with other people and build meaningful relations. Otherwise, active ageing promotion policies and initiatives risk producing unintended marginalisation effects by broadening the gap between older adults who can age actively and those who cannot.
This study has two main limits. First, we are not able to assess whether the identified associations are causal in nature, and which is the direction of the causal link, if present. Second, while we do consider the effect of SC on activities and the complementarity/substitution effect of each activity, we do not study the effect of the interaction between SC and each activity on the other activities under study. Further research may also investigate aspects extending beyond the focus of this paper, such as gender differences and differences between age groups (within the old-age population), of the association between SC and active ageing.
Data
This paper uses data from SHARE Waves 4, 5, and 6 (10.6103/SHARE.w4.700, 10.6103/SHARE.w5.700, 10.6103/SHARE.w6.700), see Börsch-Supan et al. (2013) for methodological details. (1) The SHARE data collection has been funded by the European Commission, DG RTD through FP5 (QLK6-CT-2001-00360), FP6 (SHARE-I3: RII-CT-2006-062193, COMPARE: CIT5-CT-2005-028857, SHARELIFE: CIT4-CT-2006-028812), FP7 (SHARE-PREP: GA N°211909, SHARE-LEAP: GA N°227822, SHARE M4: GA N°261982, DASISH: GA N°283646) and Horizon 2020 (SHARE-DEV3: GA N°676536, SHARE-COHESION: GA N°870628, SERISS: GA N°654221, SSHOC: GA N°823782) and by DG Employment, Social Affairs & Inclusion through VS 2015/0195, VS 2016/0135, VS 2018/0285, VS 2019/0332, and VS 2020/0313. Additional funding from the German Ministry of Education and Research, the Max Planck Society for the Advancement of Science, the U.S. National Institute on Aging (U01_AG09740-13S2, P01_AG005842, P01_AG08291, P30_AG12815, R21_AG025169, Y1-AG-4553-01, IAG_BSR06-11, OGHA_04-064, HHSN271201300071C, RAG052527A) and from various national funding sources is gratefully acknowledged (see www.share-project.org).
Acknowledgements
We thank our colleague Emanuela Sala for useful insights and comments on an earlier version of this paper. We also thank Andrea Geraci for the useful suggestions on how to improve our analytical strategy. The responsibility for the content of the article lies entirely with the authors.
Author contributions
All authors contributed equally to the conception of the study, design of the analysis plan and interpretation of the data. PB performed the data analysis, under the supervision of AG. EG drafted the introduction, the section on the literature review and the conclusion, PB and AG drafted the section on methods and results. All authors revised, read and approved the whole manuscript.
Financial support
This work was supported by Fondazione Cariplo (grant ‘Bando 2017, ricerca scientifica: Ricerca sociale sull'invecchiamento: persone, luoghi e relazioni. Project number 2017-0946; project name ‘Aging in a Networked Society. Older People, Social Networks and Well-Being’).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
Ethical approval was not required as the empirical research is based uniquely on secondary data analysis.







