We consider a random graph model that was recently proposed as a model for complex networks by Krioukov et al. (2010). In this model, nodes are chosen randomly inside a disk in the hyperbolic plane and two nodes are connected if they are at most a certain hyperbolic distance from each other. It has previously been shown that this model has various properties associated with complex networks, including a power-law degree distribution and a strictly positive clustering coefficient. The model is specified using three parameters: the number of nodes N, which we think of as going to infinity, and 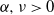 $\alpha, \nu > 0$, which we think of as constant. Roughly speaking,
$\alpha, \nu > 0$, which we think of as constant. Roughly speaking,  $\alpha$ controls the power-law exponent of the degree sequence and
$\alpha$ controls the power-law exponent of the degree sequence and  $\nu$ the average degree. Earlier work of Kiwi and Mitsche (2015) has shown that, when
$\nu$ the average degree. Earlier work of Kiwi and Mitsche (2015) has shown that, when 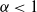 $\alpha \lt 1$ (which corresponds to the exponent of the power law degree sequence being
$\alpha \lt 1$ (which corresponds to the exponent of the power law degree sequence being 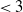 $\lt 3$), the diameter of the largest component is asymptotically almost surely (a.a.s.) at most polylogarithmic in N. Friedrich and Krohmer (2015) showed it was a.a.s.
$\lt 3$), the diameter of the largest component is asymptotically almost surely (a.a.s.) at most polylogarithmic in N. Friedrich and Krohmer (2015) showed it was a.a.s. 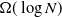 $\Omega(\log N)$ and improved the exponent of the polynomial in
$\Omega(\log N)$ and improved the exponent of the polynomial in 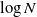 $\log N$ in the upper bound. Here we show the maximum diameter over all components is a.a.s.
$\log N$ in the upper bound. Here we show the maximum diameter over all components is a.a.s. 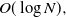 $O(\log N),$ thus giving a bound that is tight up to a multiplicative constant.
$O(\log N),$ thus giving a bound that is tight up to a multiplicative constant.